02 Image Formation
Vector, Matrix, etc.#
根据 GAMES 101 slides 的复习
Transformation#
- scale
- reflection
- shear
- rotate
- translation (homogeneous)
Matrix Determinant#
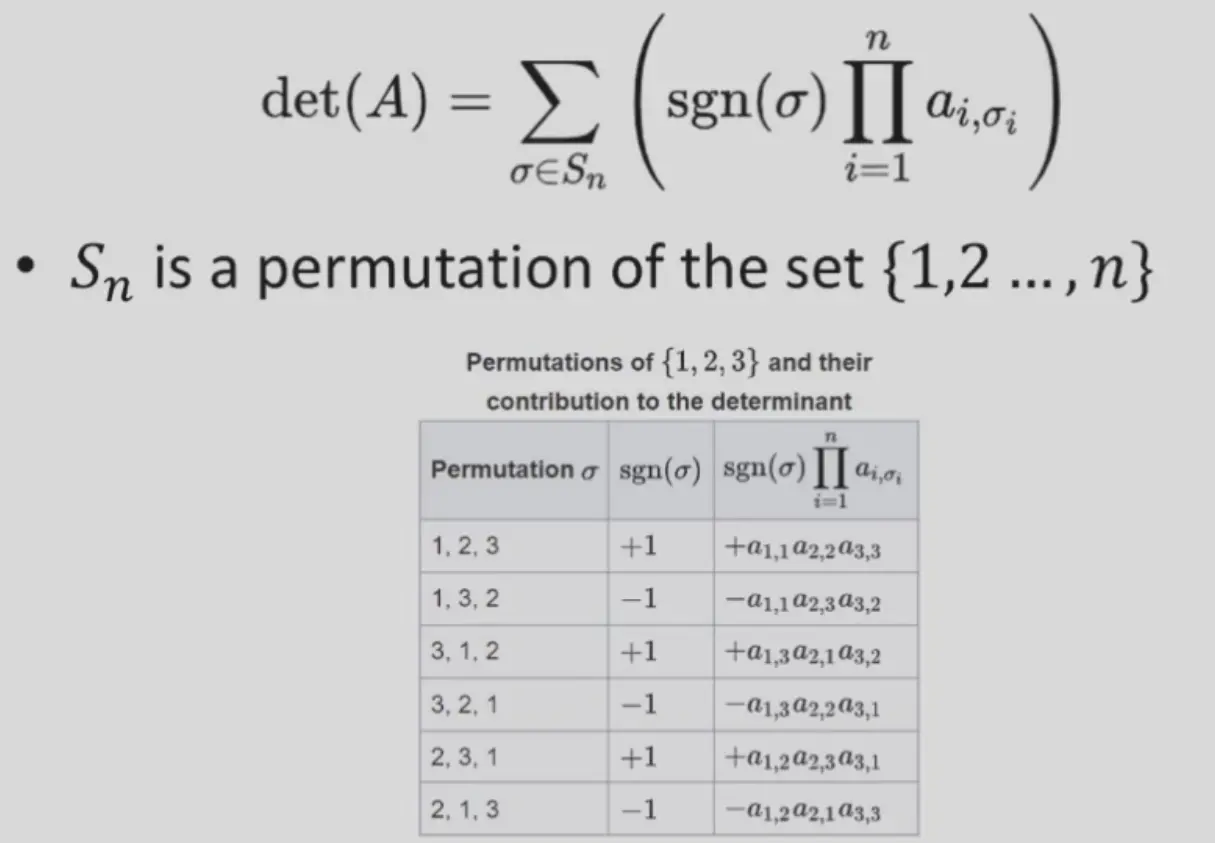
几何意义:三个列向量表示的顶点与原点,构成的平行六面体的体积
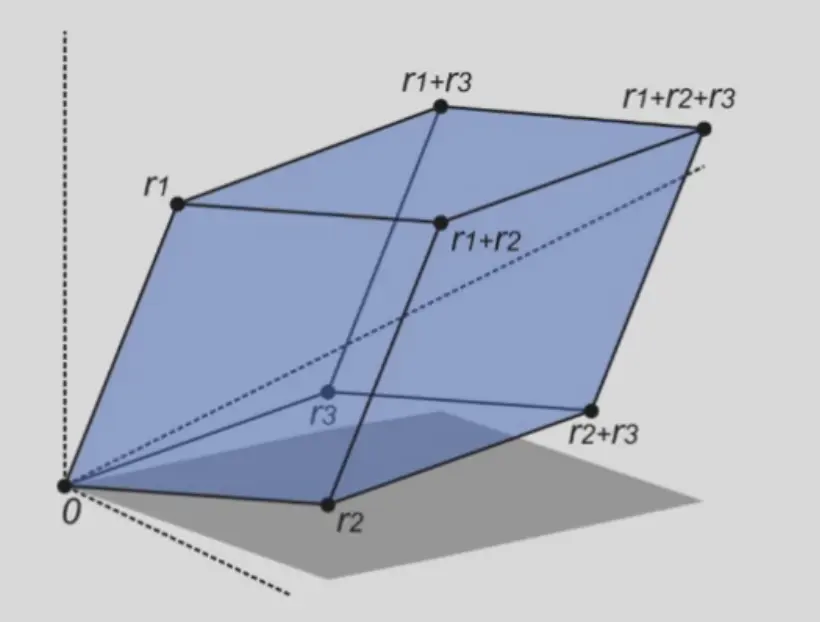
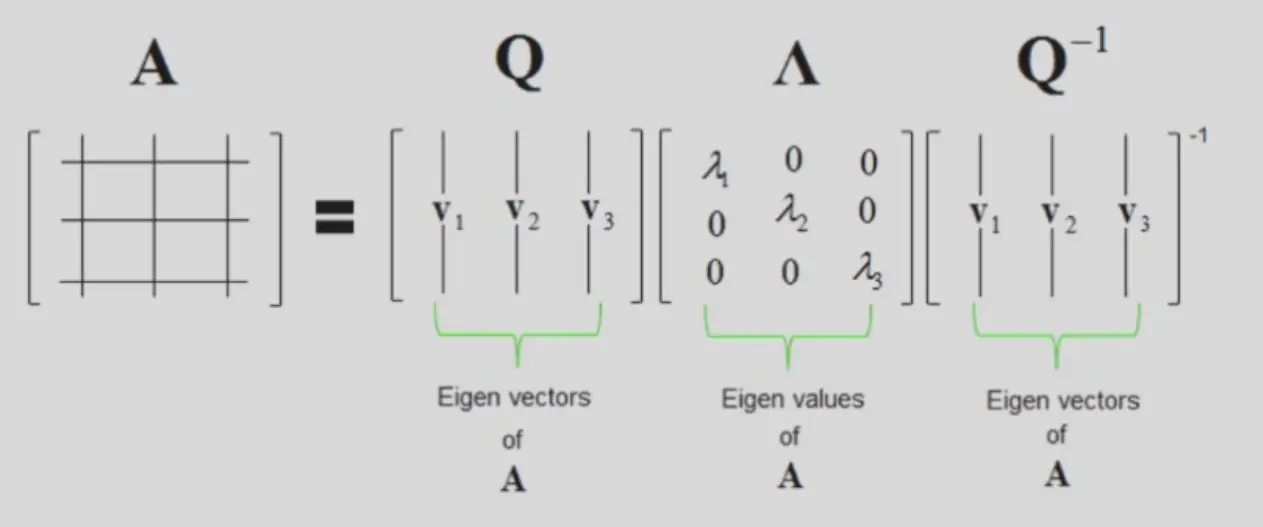
Eigenvectors and eigenvalues#
- \(\mathbf{Ax}=\lambda\mathbf{x}\)
- \(\mathbf{x}\) 是一个特征向量(\(\mathbf{x}\neq\mathbf{0}\)),\(\lambda\) 是其对应的特征值
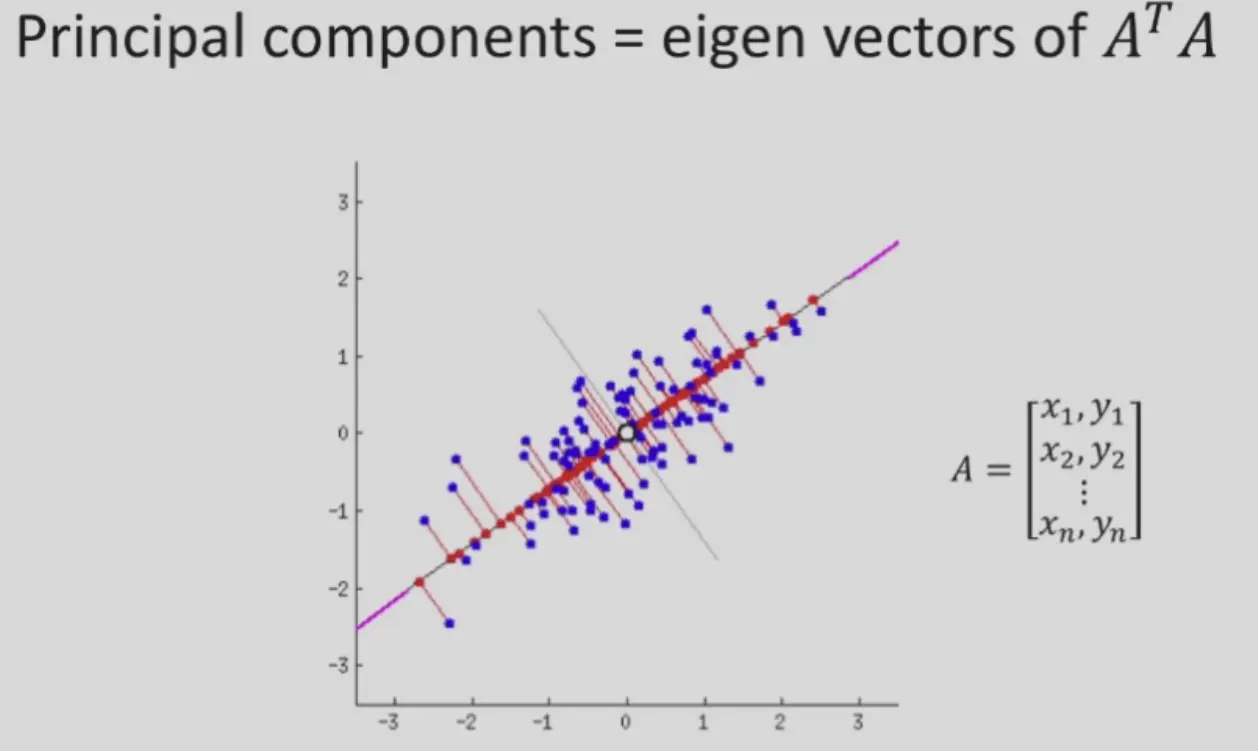
Application: PCA#
Camera and Lens#
Lens#
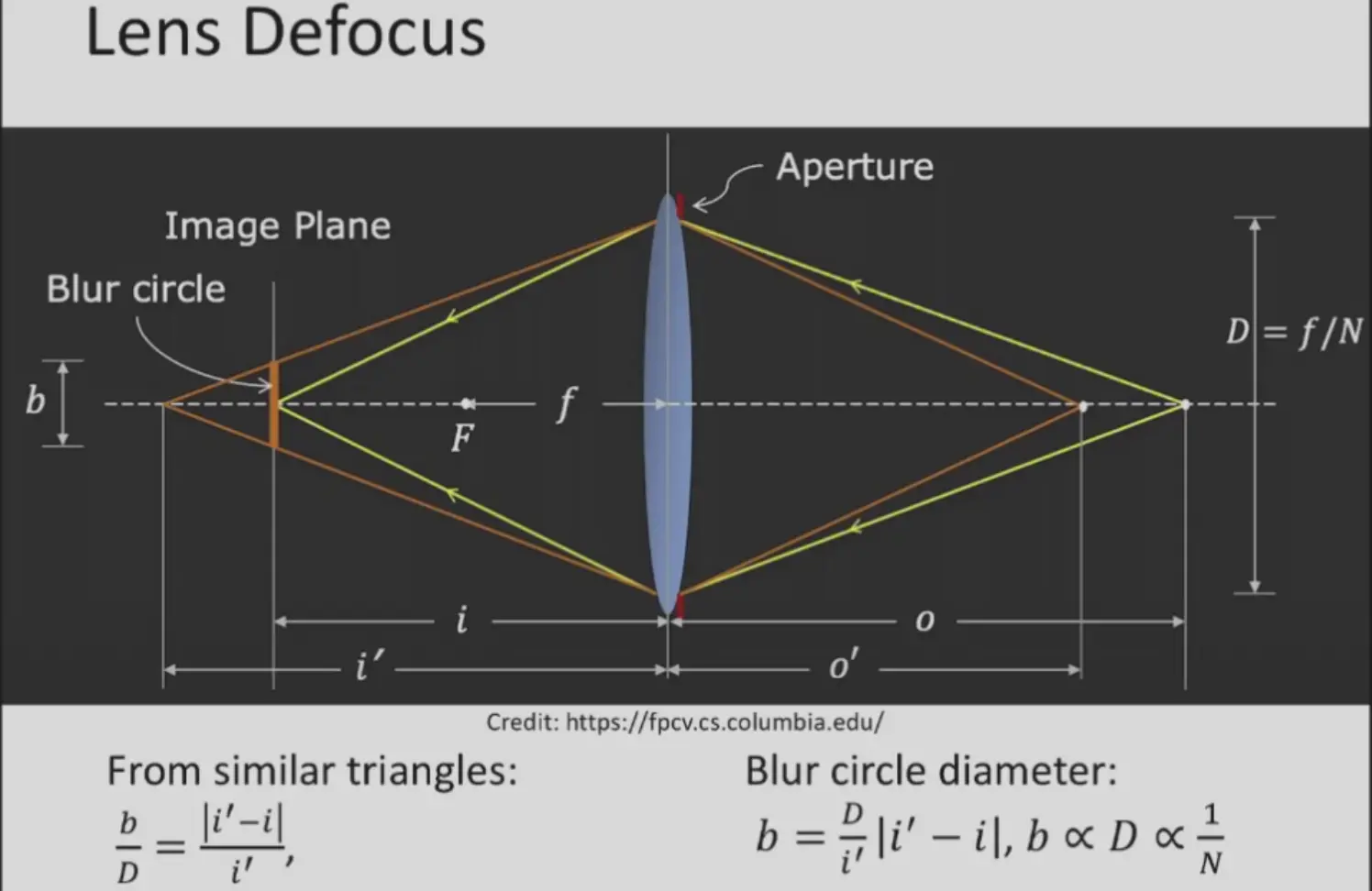
- focal length 焦距 \(f\),满足 \(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{i}+\frac{1}{o}\)
- magnification 放大率 \(m=\frac{h_i}{h_o}\)
- 和焦段有关
- field of view (FOV) 视场角
- 取决于焦段和传感器大小
- aperture 光圈
- F-number 的定义:\(N=\frac{f}{D}\),其中 \(D\) 是光圈直径
- Lens Defocus 失焦
- Depth of Field (DoF) 景深,和光圈、焦段都有关
Geometric Image Formation#
Perspective Projection#
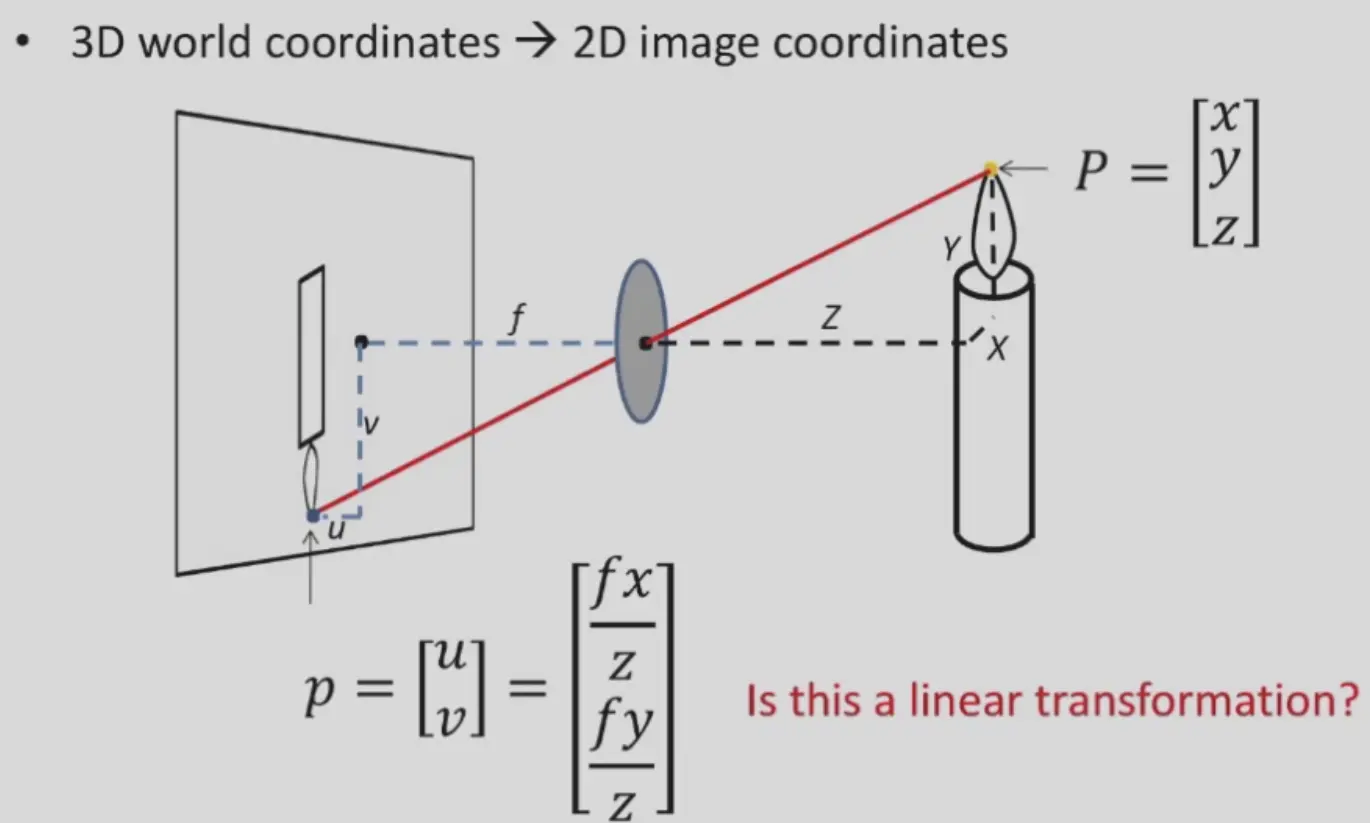
- \(p=\begin{bmatrix}u \\ v\end{bmatrix}\)
- \(P=\begin{bmatrix}x \\ y \\ z\end{bmatrix}\)
存在几何关系:
\[
p=\begin{bmatrix}\frac{fx}{z} \\ \frac{fy}{z} \end{bmatrix}
\]
in Homogeneous Coordinates#
\[
\begin{bmatrix}
f & 0 & 0 & 0 \\
0 & f & 0 & 0 \\
0 & 0 & 1 & 0
\end{bmatrix}
\begin{bmatrix}
x \\
y \\
z \\
1
\end{bmatrix}=
\begin{bmatrix}
fx \\
fy \\
z
\end{bmatrix}\cong
\begin{bmatrix}
f\frac{x}{z} \\
f\frac{y}{z} \\
1
\end{bmatrix}
\]
Note
齐次坐标乘以一个常数,仍然代表同一个点
其中透视投影矩阵为
\[
\Pi=\begin{bmatrix}
f & 0 & 0 & 0 \\
0 & f & 0 & 0 \\
0 & 0 & 1 & 0
\end{bmatrix}
\]
Properties#
- 大部分深度信息丢失
- 长度不保持
- 角度不保持,平行于焦平面的
- 直线仍是直线
- 灭点的位置只和直线和相机的相对朝向有关,和位置无关
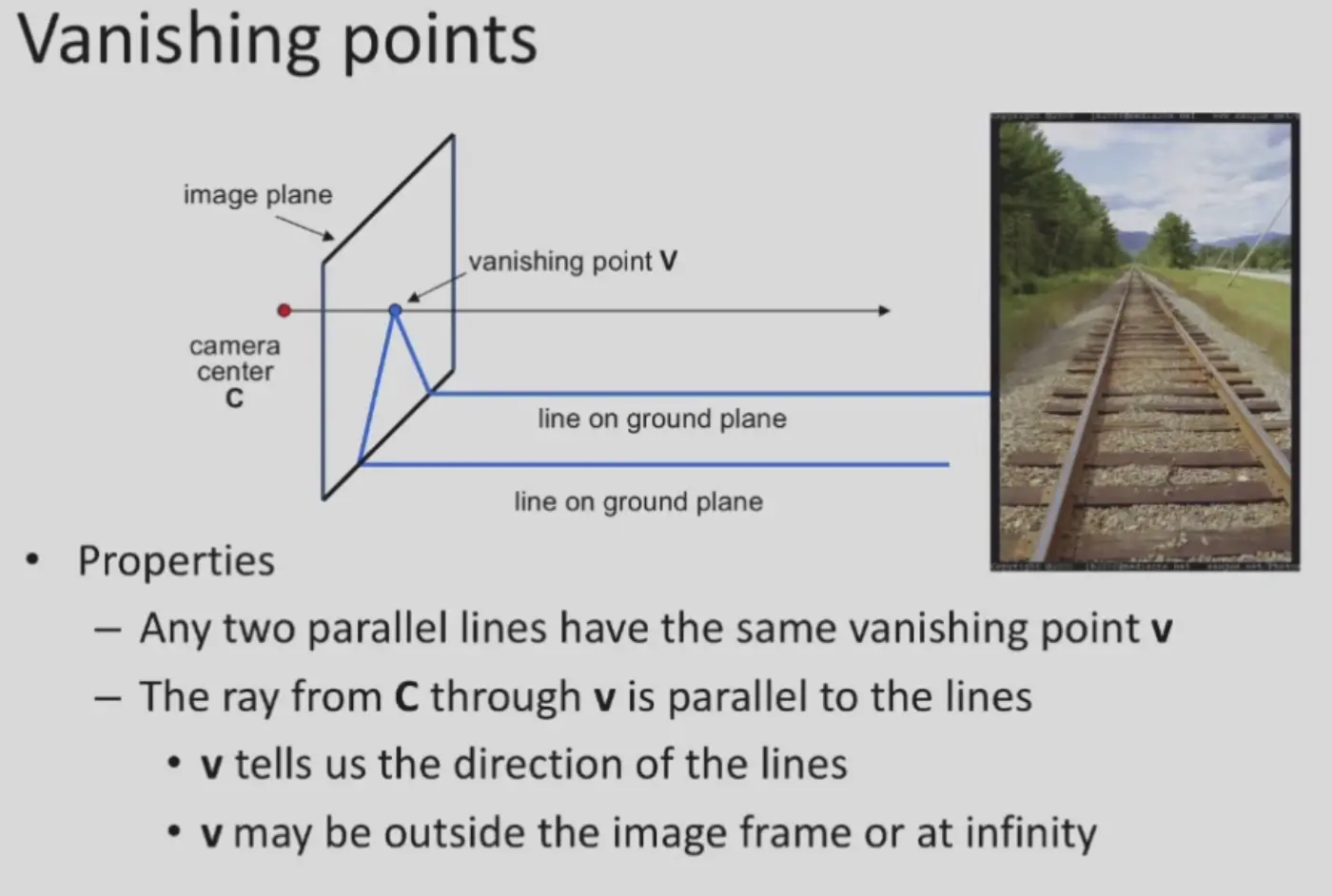
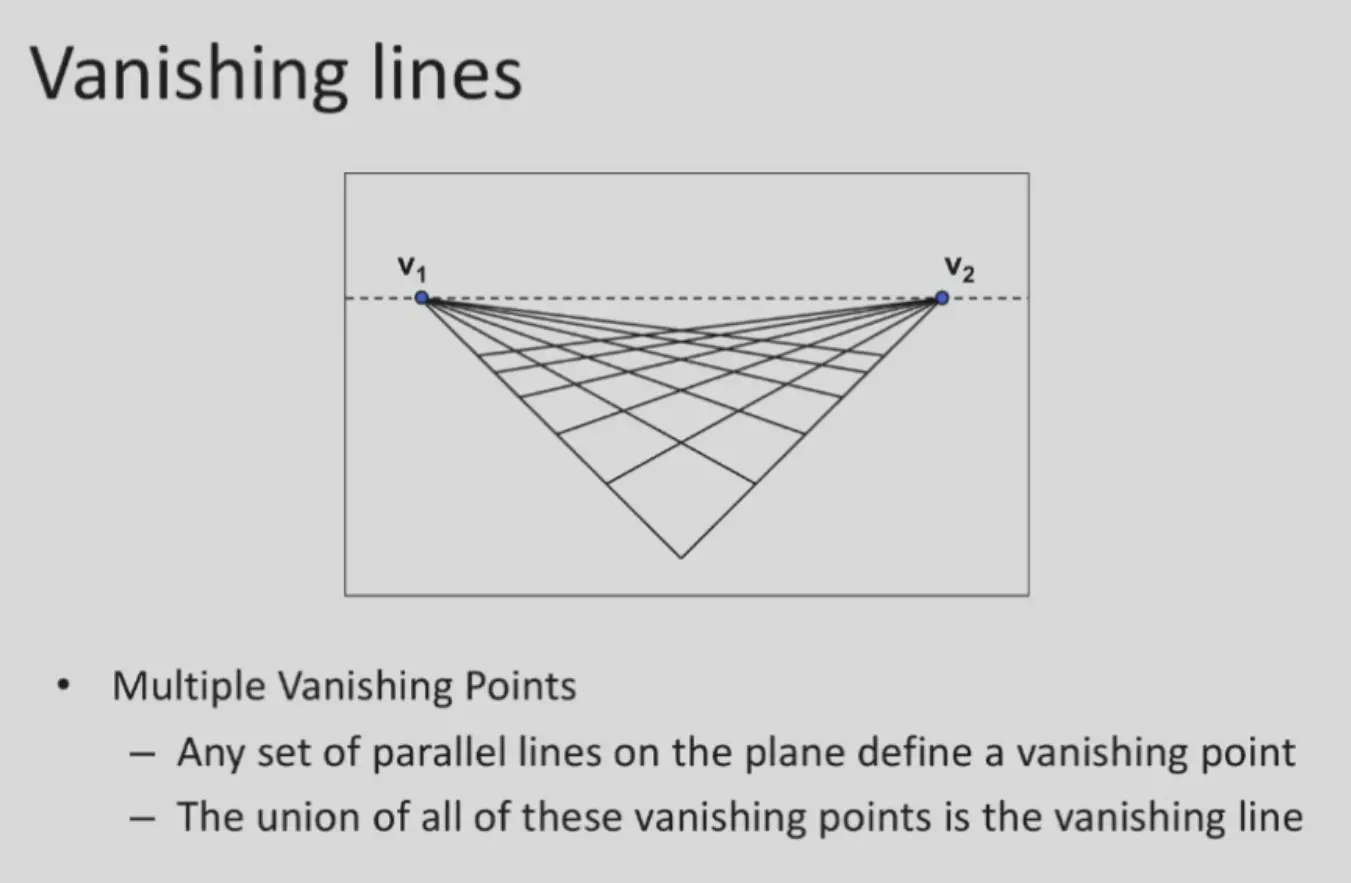
- 灭线只和相机位置和平面的朝向有关
Perspective Distortion#
透视畸变
- 越靠近两边,畸变越大
- 移轴,可以让光轴不经过成像中心
Radial Distortion#
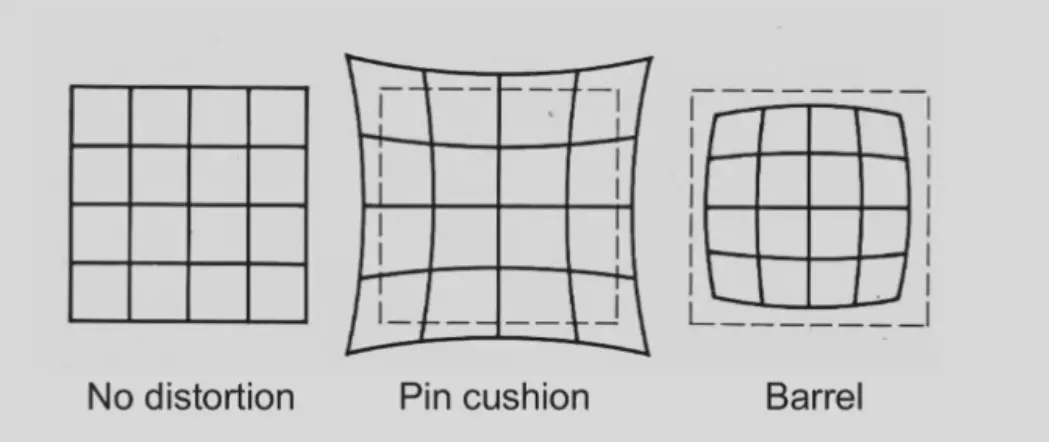
一种近似表达
\[
\begin{array}
{rcl}r^2 & = & {x_n^{\prime}}^2+{y_n^{\prime}}^2 \\
x_d^{\prime} & = & {x_n^{\prime}}(1+\kappa_1r^2+\kappa_2r^4) \\
y_d^{\prime} & = & {y_n^{\prime}}(1+\kappa_1r^2+\kappa_2r^4)
\end{array}\]
- 距离中心越远,畸变越明显
- 求出 \(\kappa_1,\kappa_2\) 就能消除畸变
- 长焦一般有枕形畸变,广角一般有桶形畸变
Orthographic Projection#
正交投影,直接将 xy 投影过来
Photometric Image Formation#
Camera#
- 一个像素位置的颜色是快门时间内光线的积分
- 光线的颜色对应波长,但计算机中用 RGB 来表示
- 颜色空间:RGB HSV
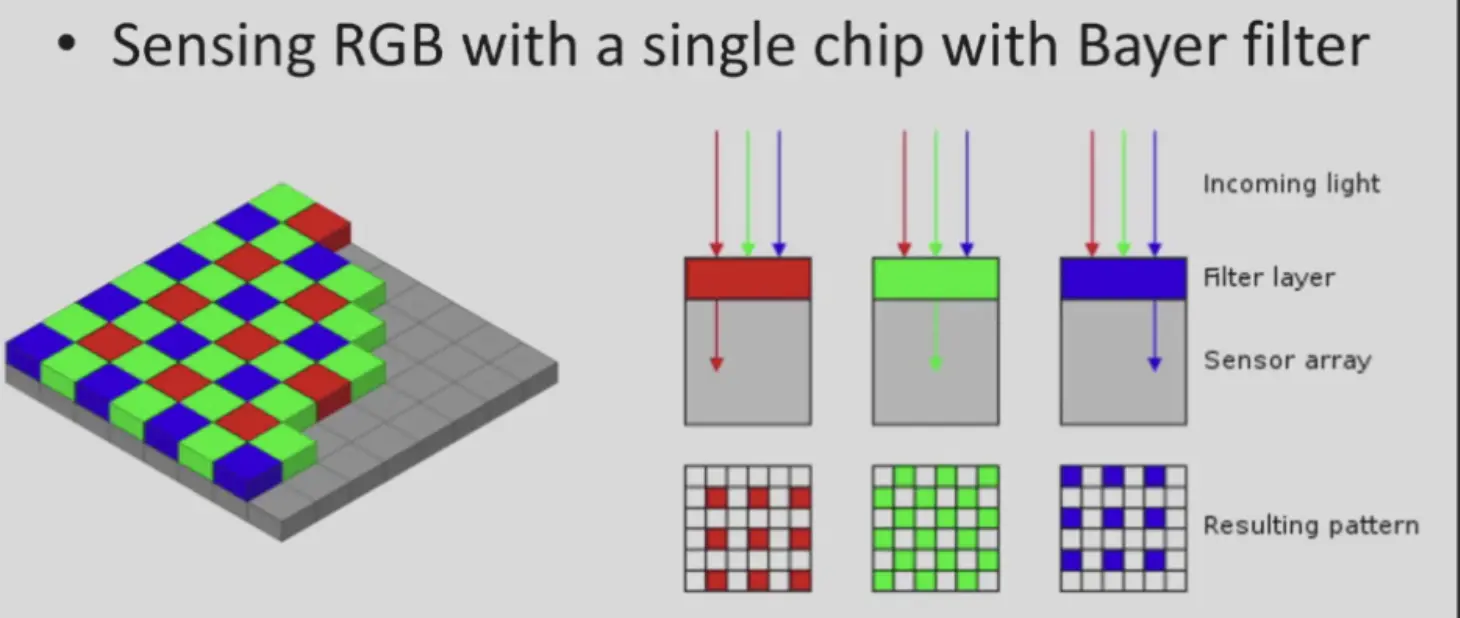
- 拜尔阵列
Shading#
法向、BRDF、Blinn-Phone(漫反射+镜面反射+环境光)