05 Shading
intro
Shading, noun, The darkening or coloring of an illustration or diagram with parallel lines or a block of color. In this course, the process of applying a material to an object.
A Simple Shading Model (Blinn-Phong Reflectance Model)#
- specular highlights 高光(镜面反射)
- diffuse reflection 颜色渐变(漫反射)
- ambient lighting 间接光照
the model#
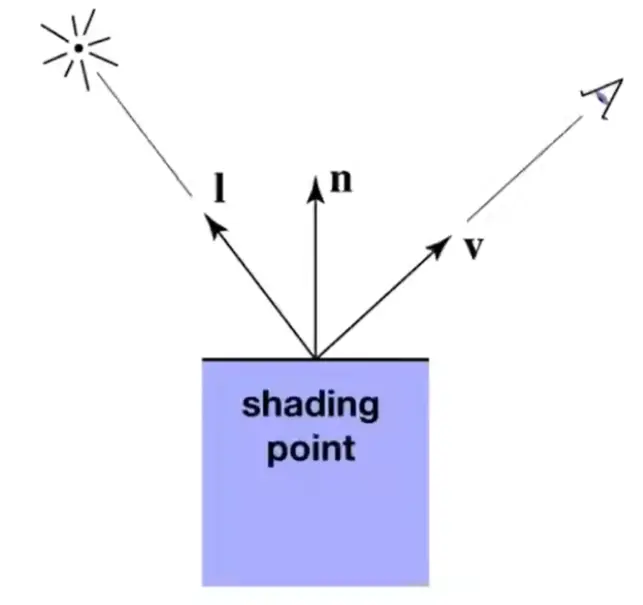
- viewer direction, \(\hat{v}\)
- surface normal, \(\hat{n}\)
- light direction, \(\hat{l}\)
- surface parameters: color, shiness, ...
shading is local
shading 并没有考虑光线的遮挡关系,不会画出阴影 shading \(\neq\) shadow
Diffuse Refelction#
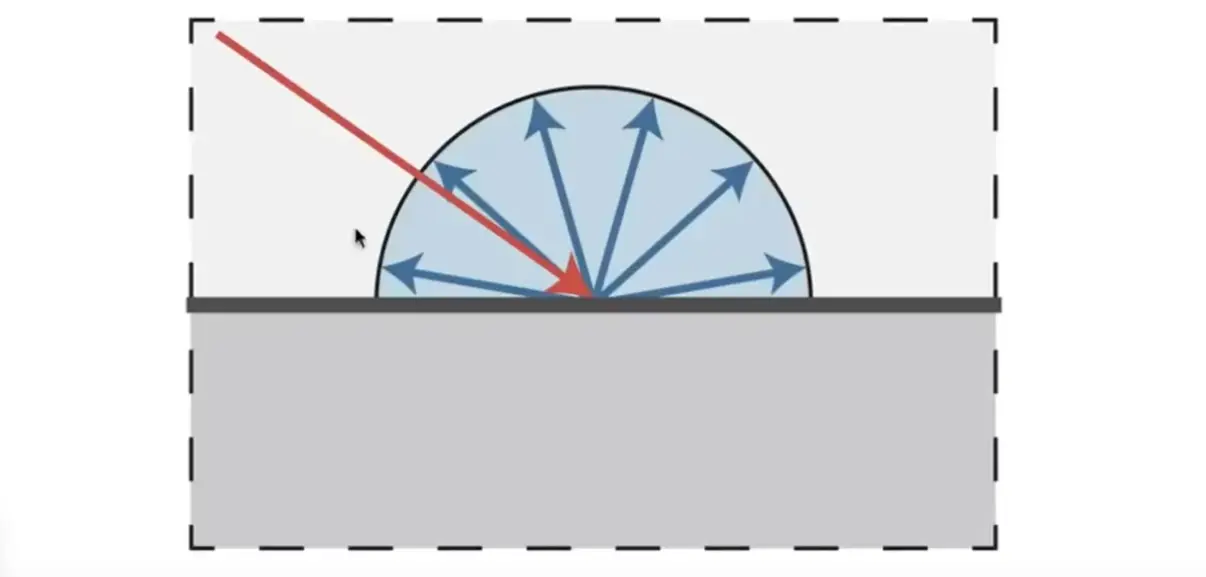
光线向着所有方向均匀反射
Note
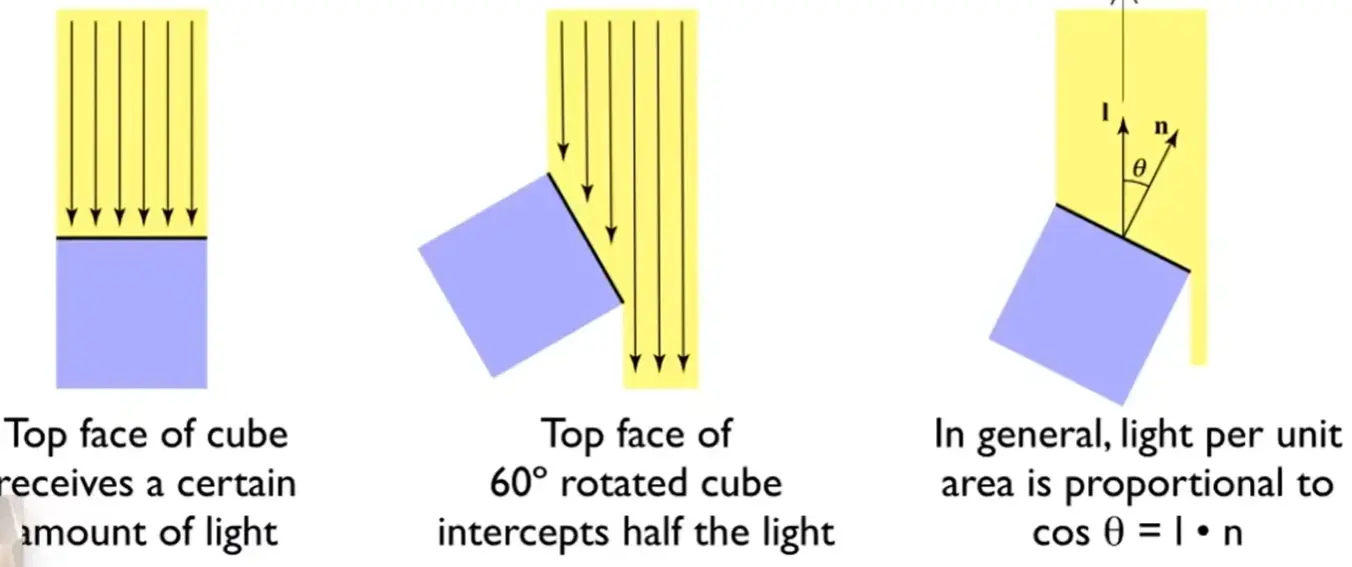
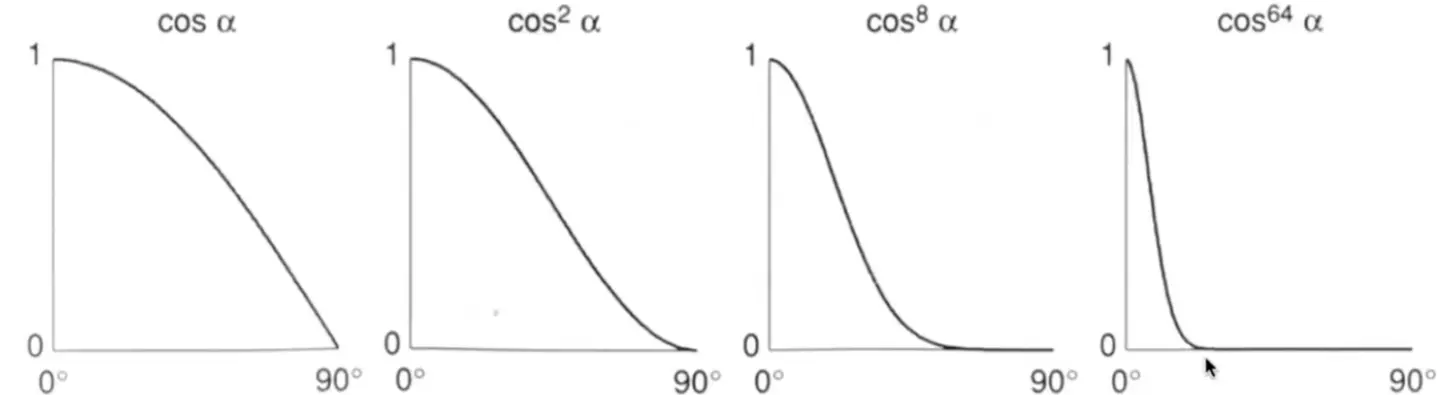
- 平行光情景下,单位面积接收光强与 \(\cos \theta=\hat{l}\cdot \hat{n}\) 成正比
- 点光源情境下,单位面积接收光强与 \(r^2\) 成反比
Lambertian (Diffuse) Shading:
- \(k_{d}\) diffuse coeffficient,与表面性质、波长有关
- \(r\) 是光源与 shading point 的距离
Specular Term#
birght near mirror reflection direction
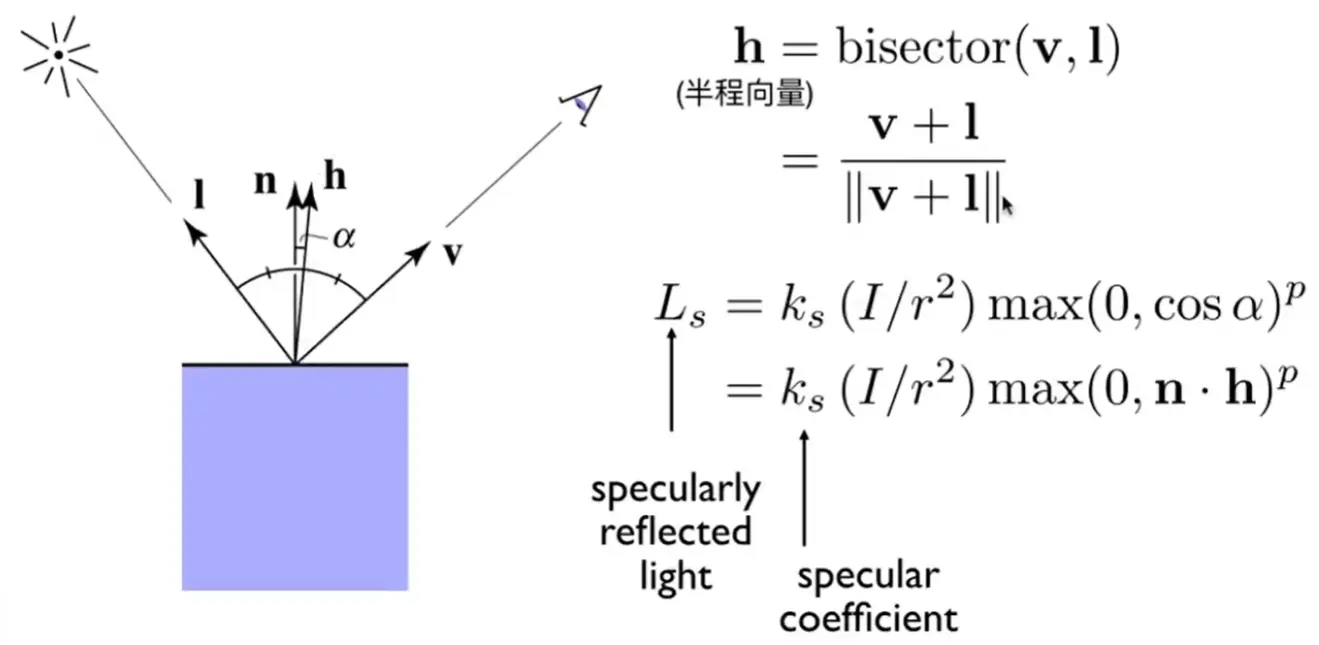
bisector vector \(h\):
其中指数 \(p\) 有利于控制镜面反射范围,一般取 100~200
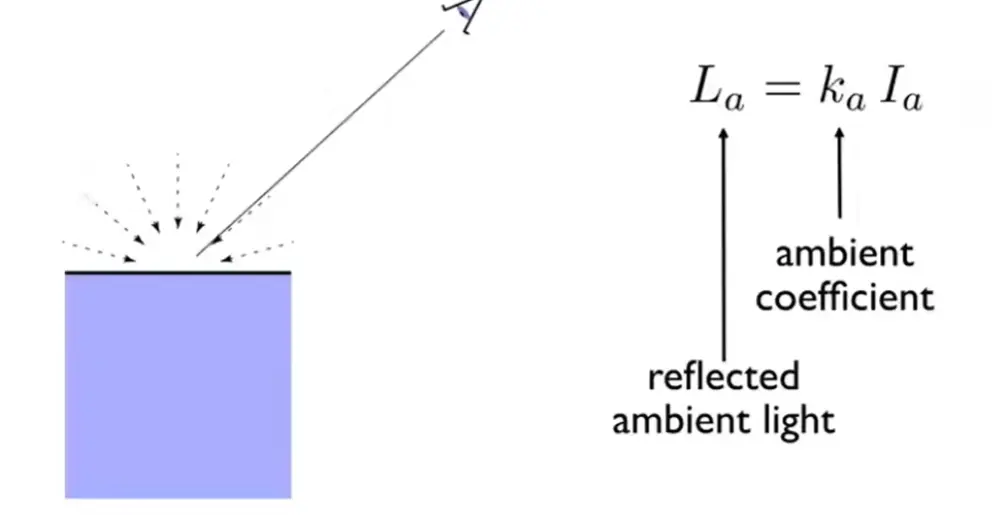
Ambient Term#
假设环境光强为定值 \(I_{a}\)
Conclusion#
Note
并不考虑 viewer 距离对亮度的影响
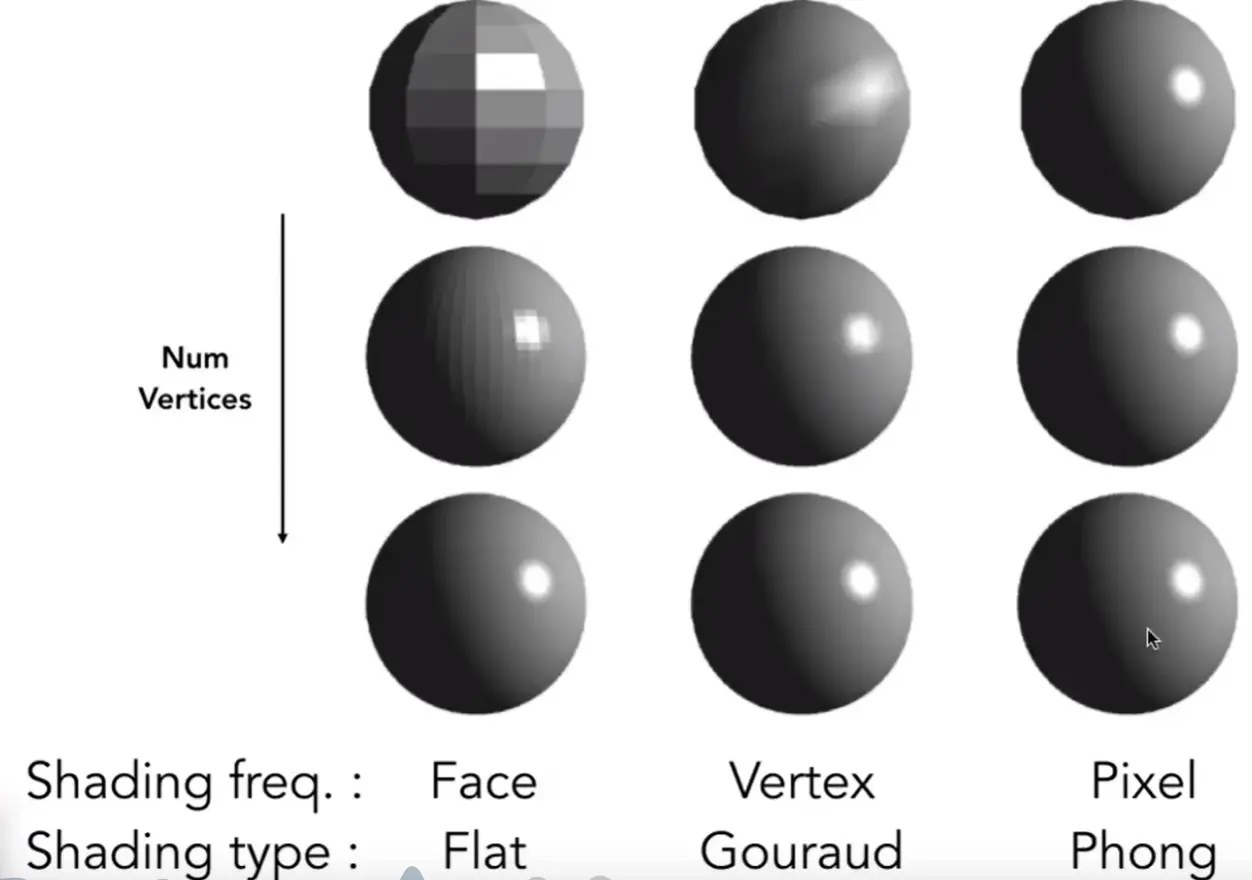
Shading Frequencies#
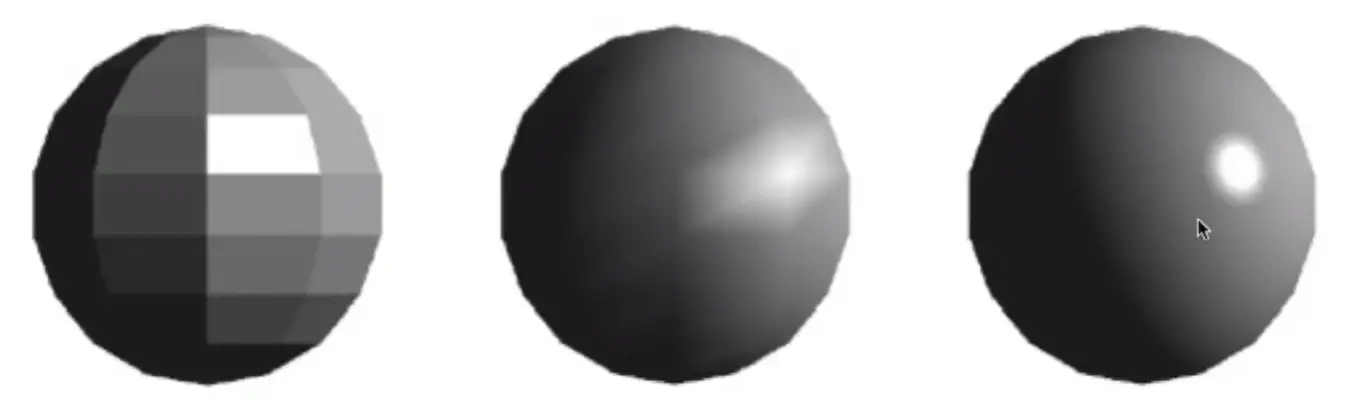

上图中分别是平面着色 (Flat shading)、顶点着色再插值 (Gouraud shading) 和像素着色 (Phong shading)
Note
模型面数足够多时,Flat 也可能和 Phong 一样好
per-vertex normal vectors#
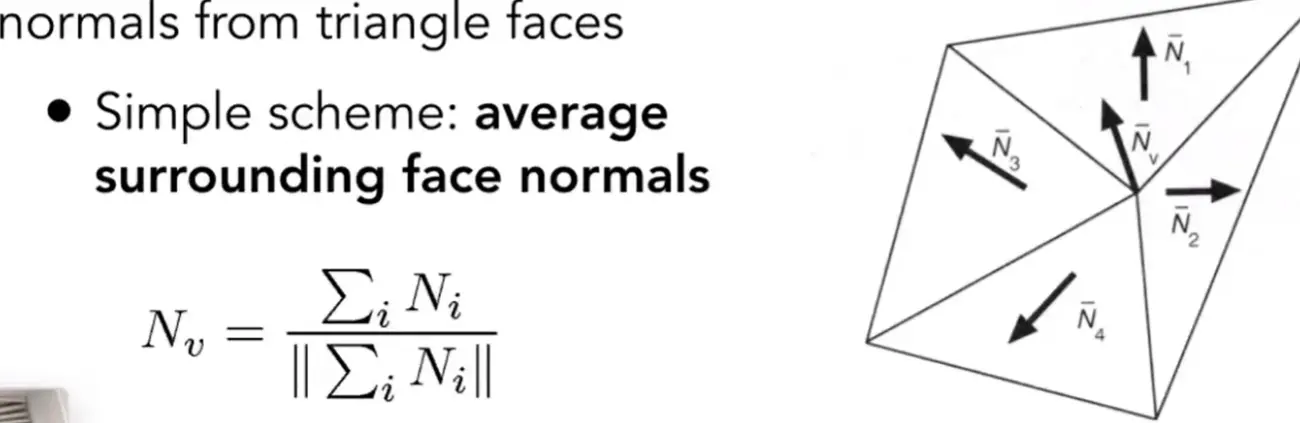
Note
可以平均,也可以加权平均
per-vertex normal vectors#
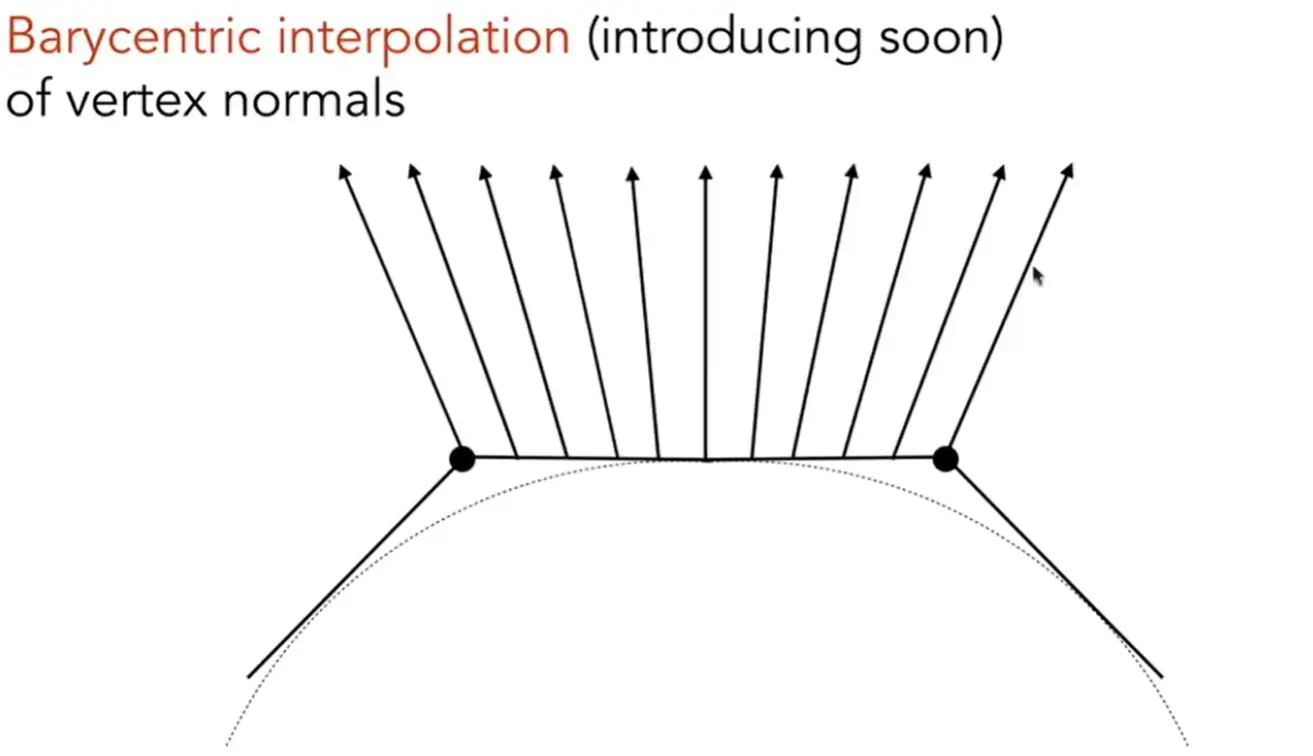
Note
使用重心坐标插值方法
Graphics (Real-time Rendering) Pipeline#
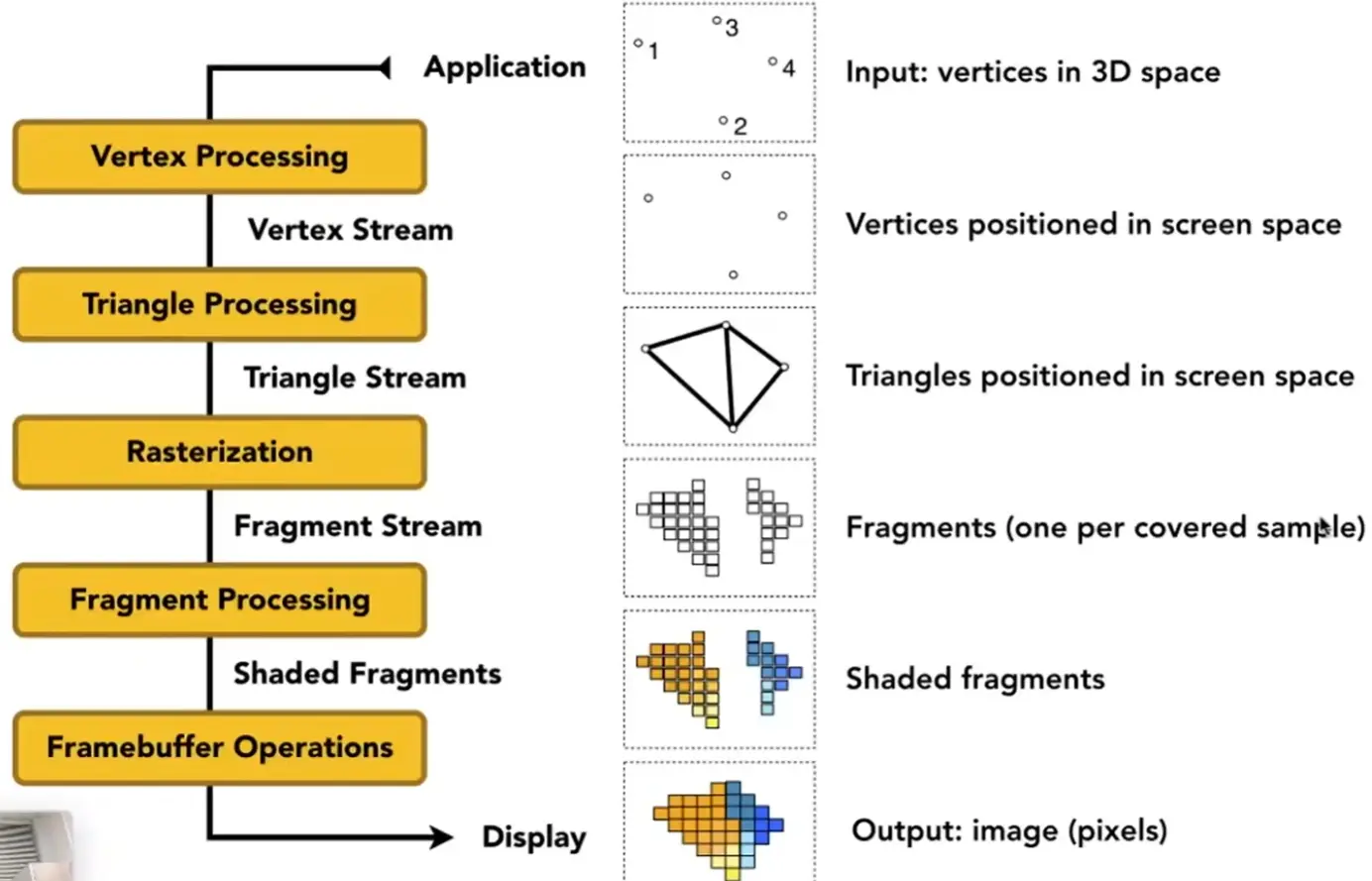
Shader Programs#
Goal: highly complex 3D scenes in realtime#
Texture Mapping#
在物体不同位置定义不同的属性
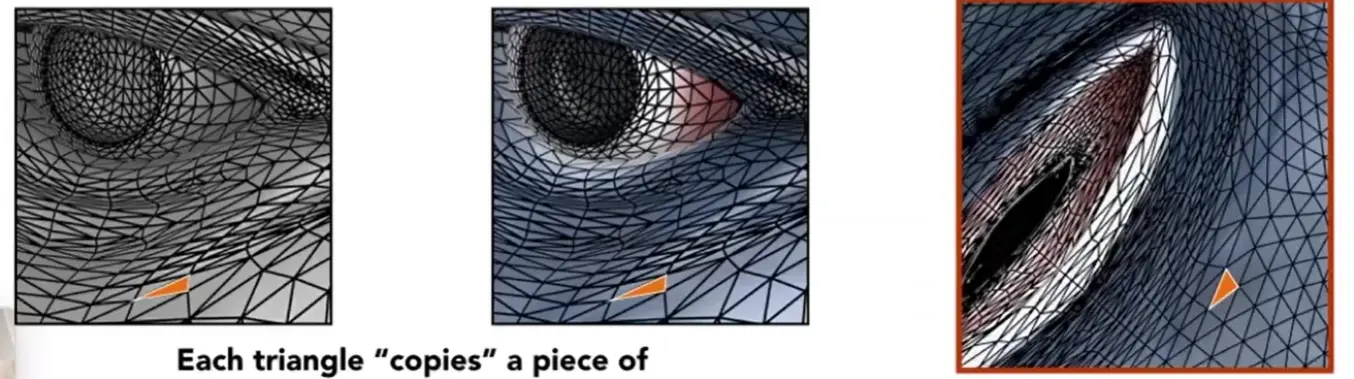
Note
- 制作纹理时,需要实现三维模型尽可能简单地展开成平面纹理,扭曲越小越好
- 渲染时,需要实现纹理三角形到模型三角形的映射
Texture Coordinates#
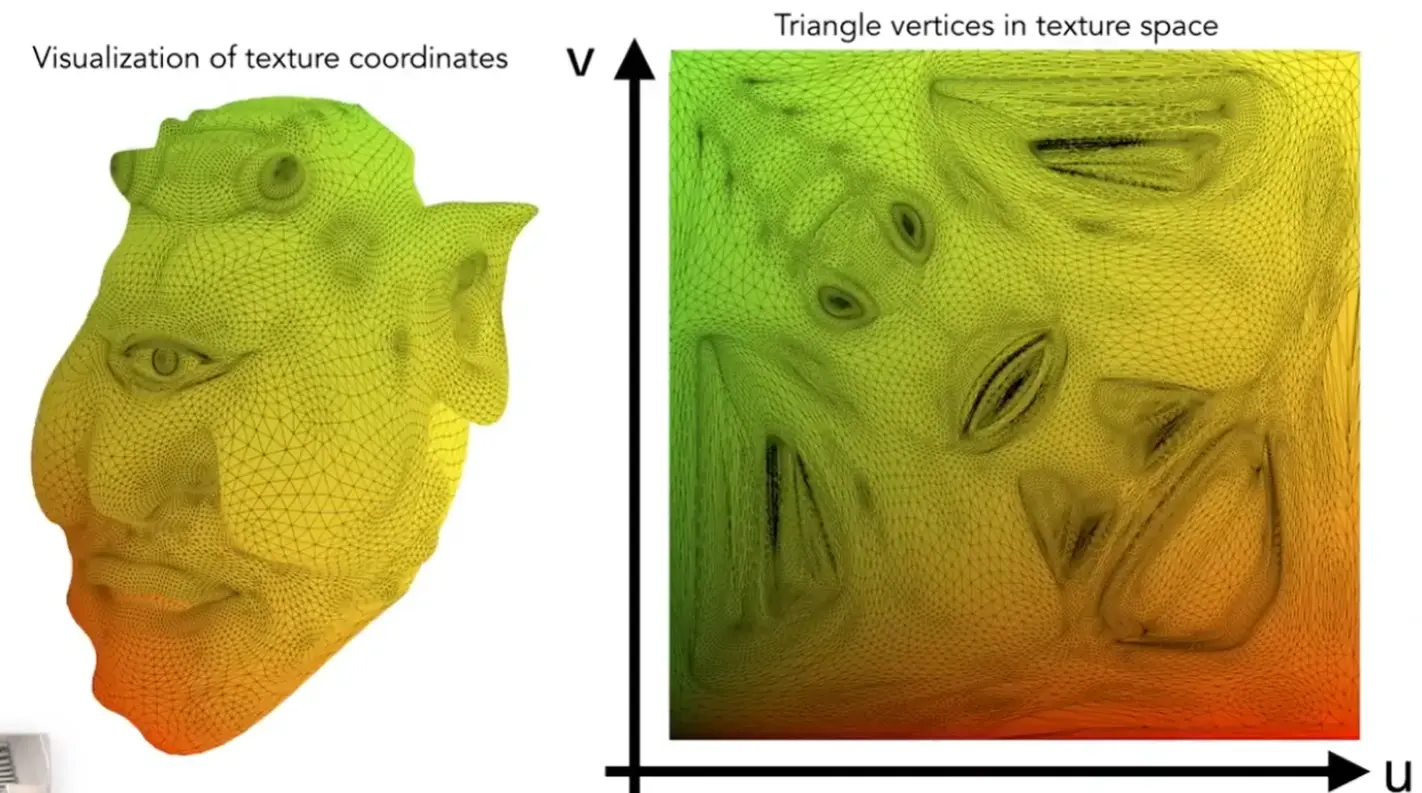
Note
- 约定 \(u,v\in[0,1]\)
- 模型上每个三角形的顶点都在纹理图上有一个 \((u,v)\) 映射
- 三角形内部的点用插值计算
Simple Texture Mapping: Diffuse Color#
what if the texture is too small?#
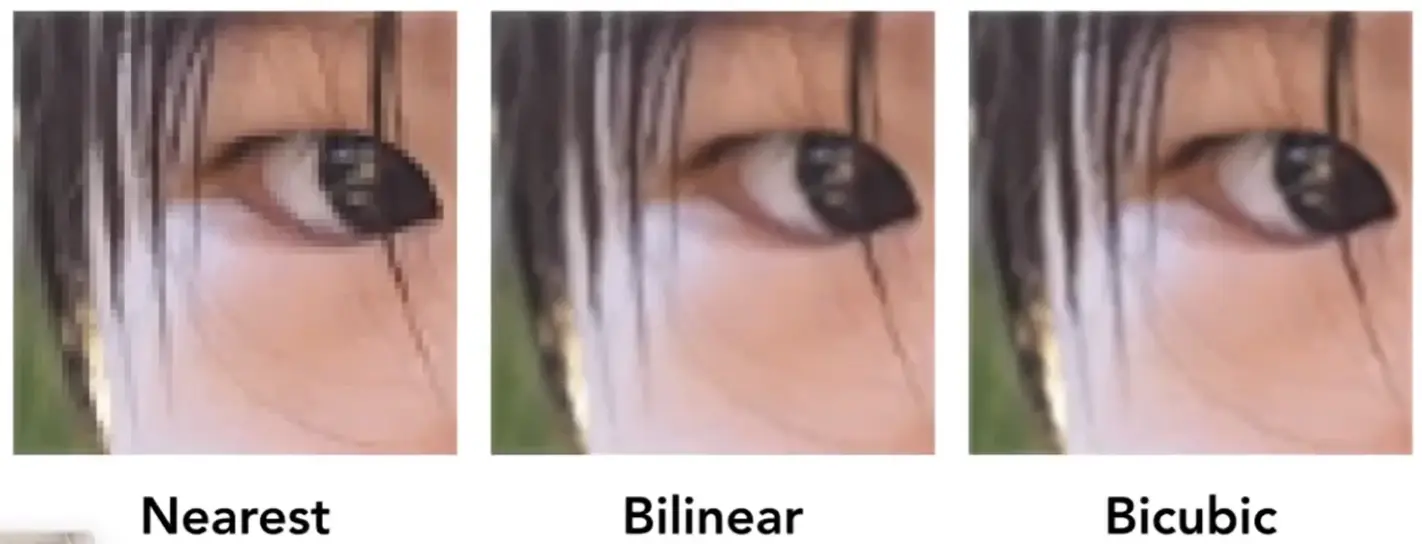

- texel 纹理元素,纹素
- 一个 pixel 会映射到文理上的一个坐标,不一定能刚好到一个 texel,如果直接四舍五入会导致分辨率不高
- 需要进行插值
Bilinear Interpolation#
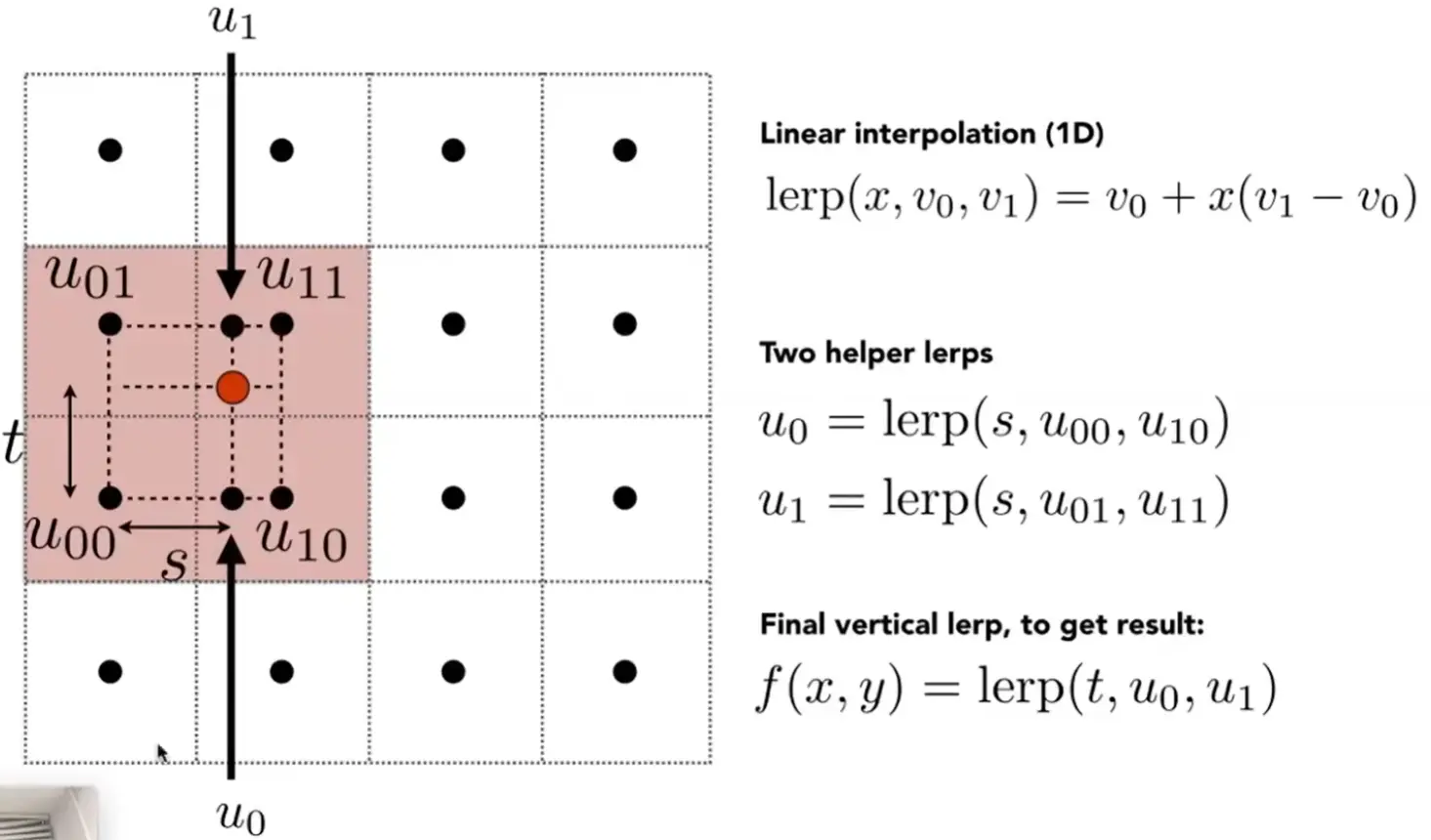
Bicubic Interpolation#
- 取了周围十六个
- 进行三次插值
what if the texture is too big?#
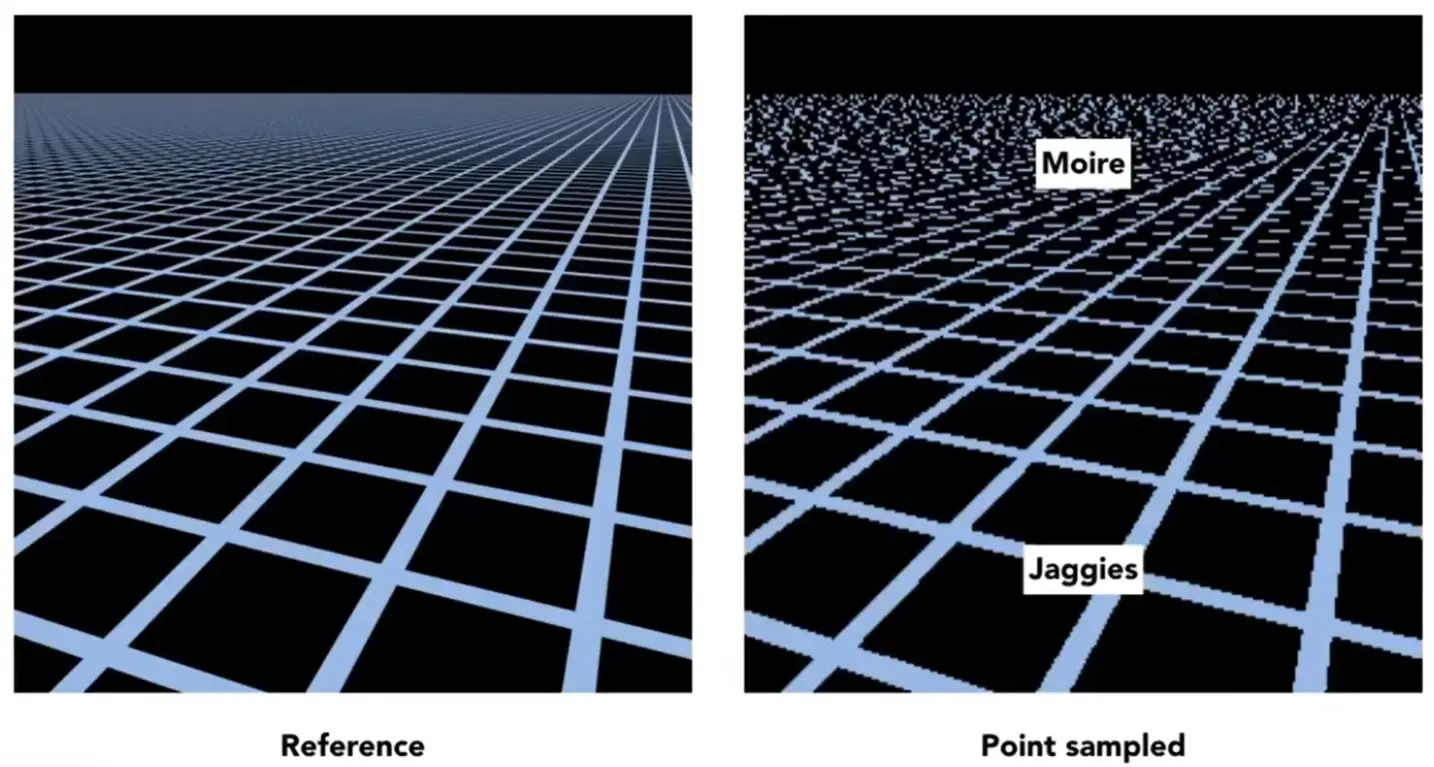
联系前面的走样问题 GAMES101 04 Rasterization#Antialiasing
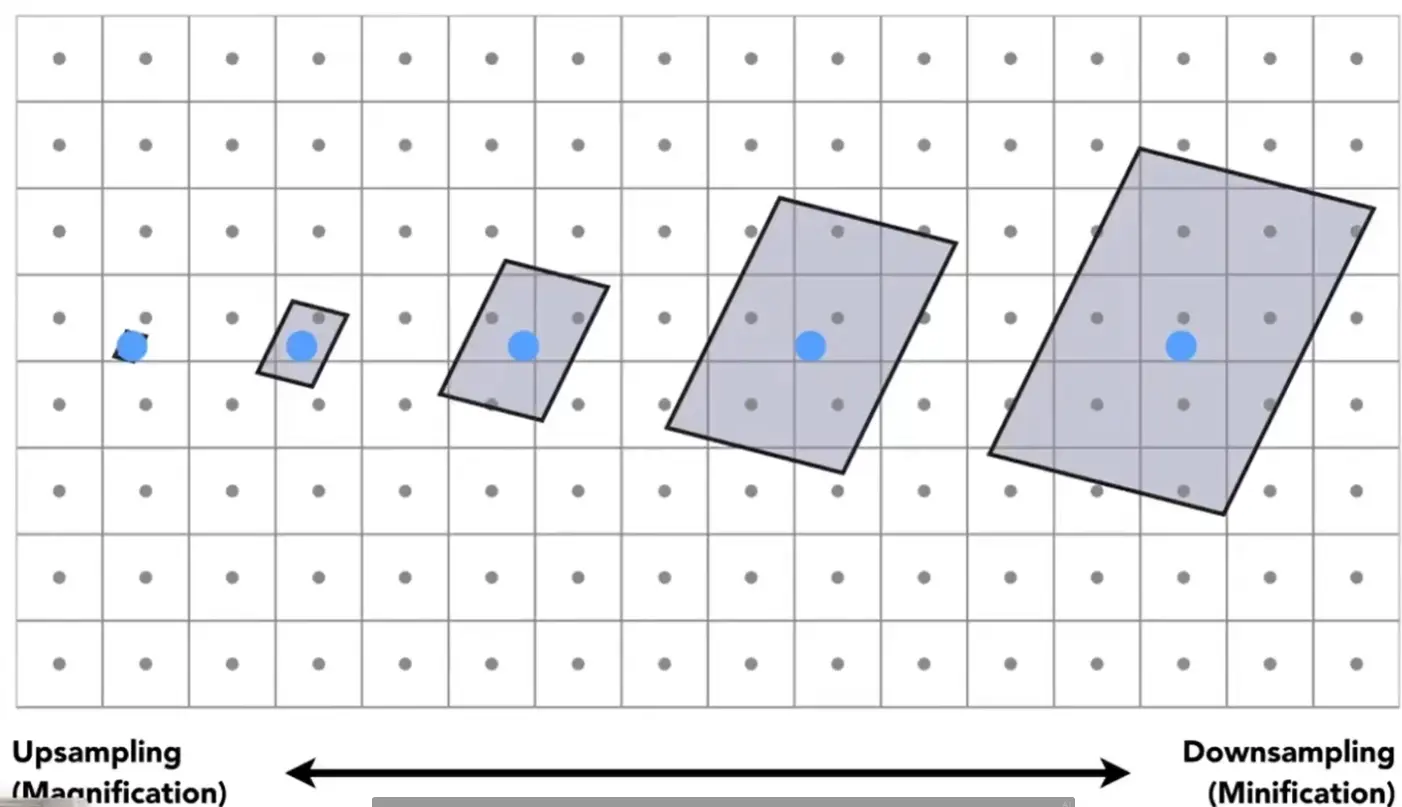
Note
在远处,一个像素覆盖的纹理区域大小非常大,但也是用像素重心采样,导致失真
supersampling?#
- 一个像素内有高频的信息,于是使用超采样的方法,一定能解决
-
但是会导致效率很低
Mipmap#
intro
range query: 给定一个区域,快速得到区域的平均值 Mipmap: allowing (fast, approx., square) range query
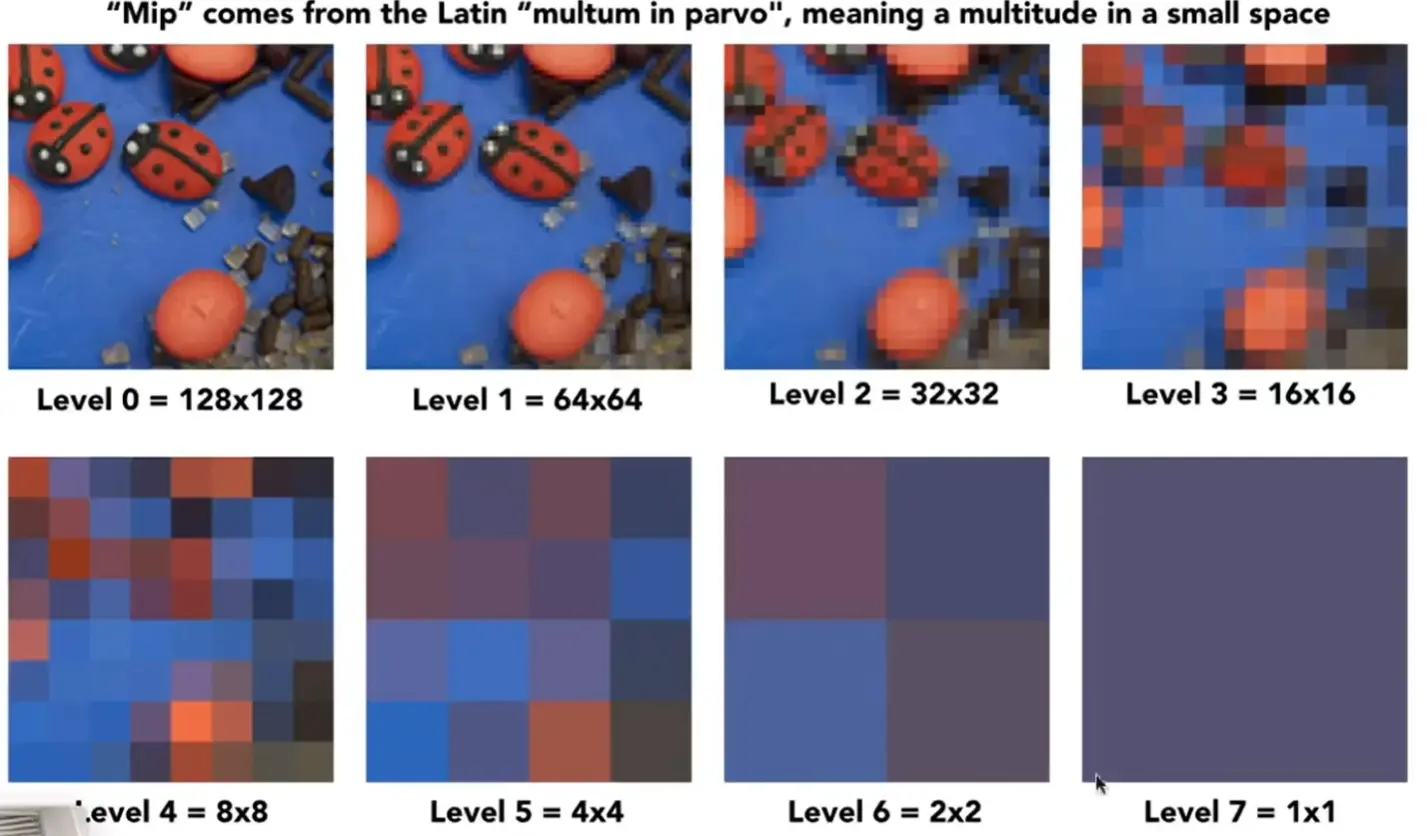

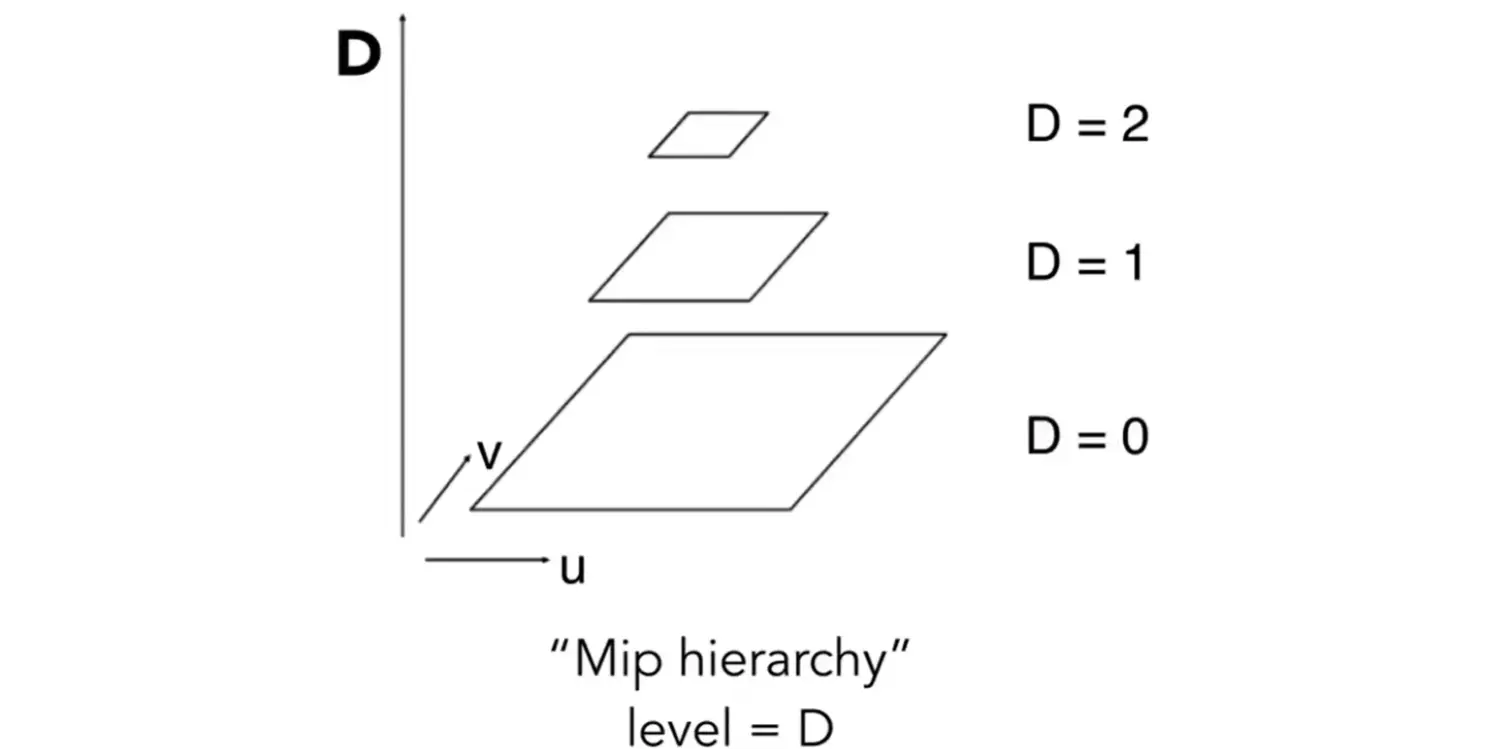
- \(O(\log n)\) levels
- \(O(\frac{4}{3}n)\) space
step 1: pixel to texels#
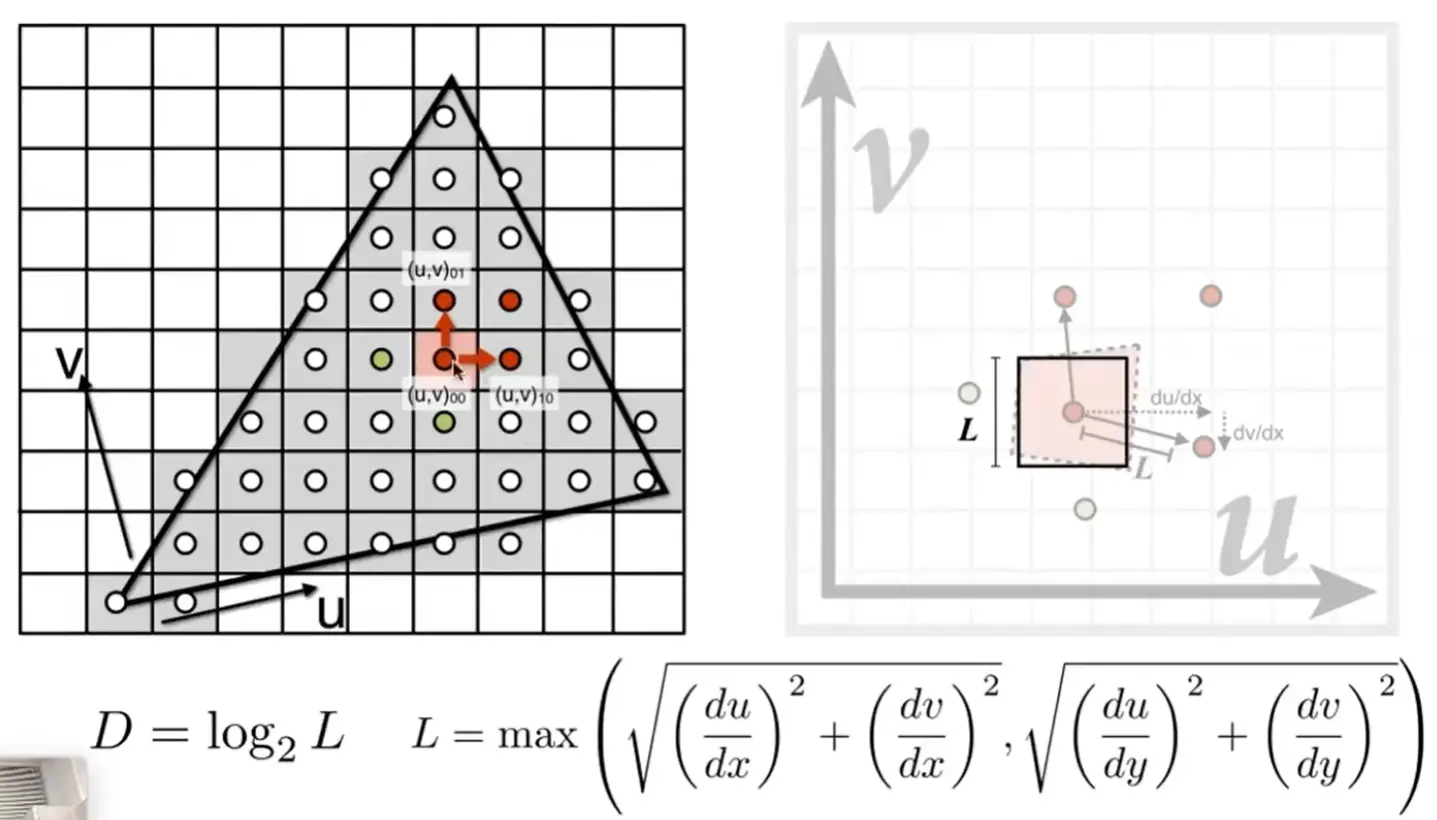
- 对于需要渲染的像素,将其和其四个邻居都映射到纹理图上,得到对应坐标
- 找到纹理上距离到最远邻居的距离 \(L\)
- 将 texel 区域近似为边长为 \(L\) 的正方形区域
step 2: use mipmap#
- 在 \(D=\log_{2}L\) 层,这个正方形区域的大小正好是一个像素,在这一层进行查找
- 进行双线性插值
step 3: trilinear interpolation#
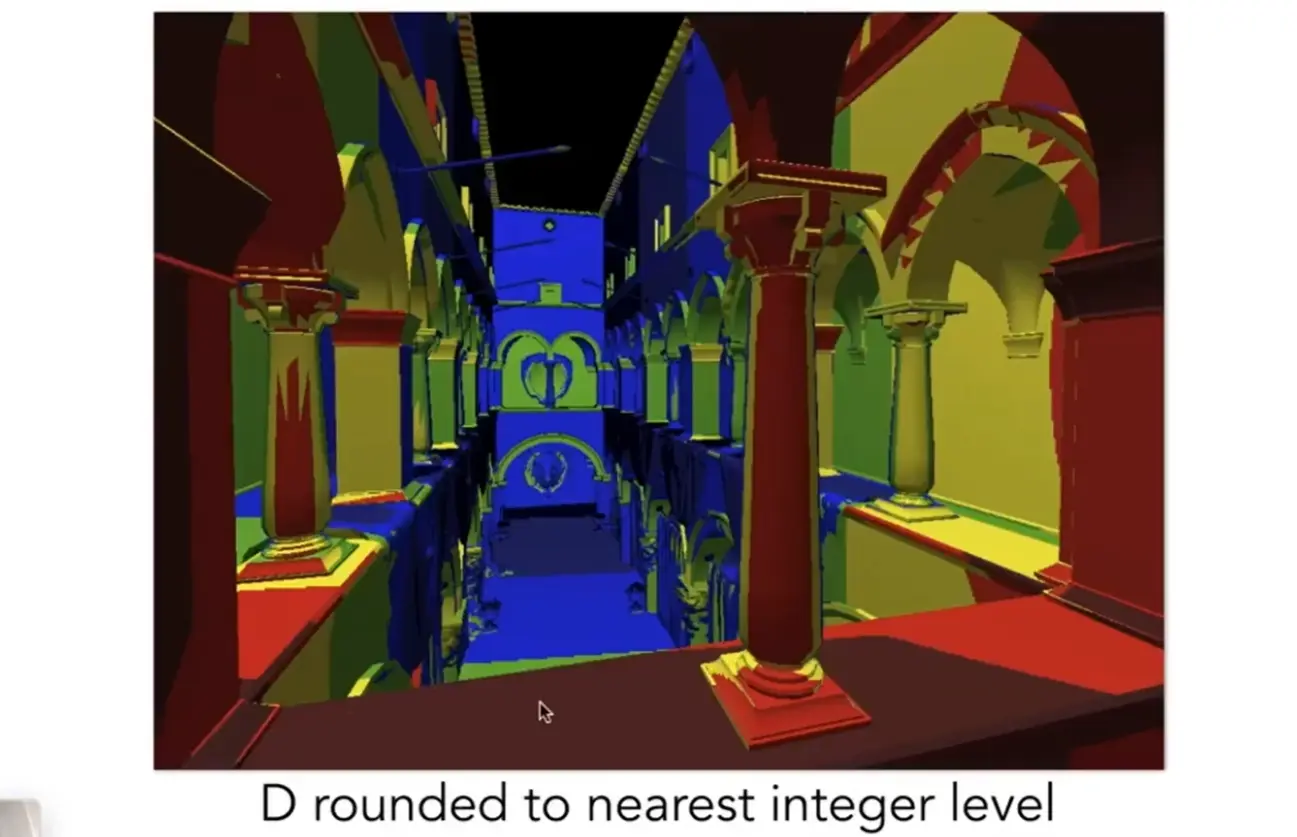

Note
- 上图中,距离近的位置 \(D\) 很大,需要在很深的层去查询
- 存在边缘,会导致不连续
- 需要让 \(D\) 是小数时的变化连续
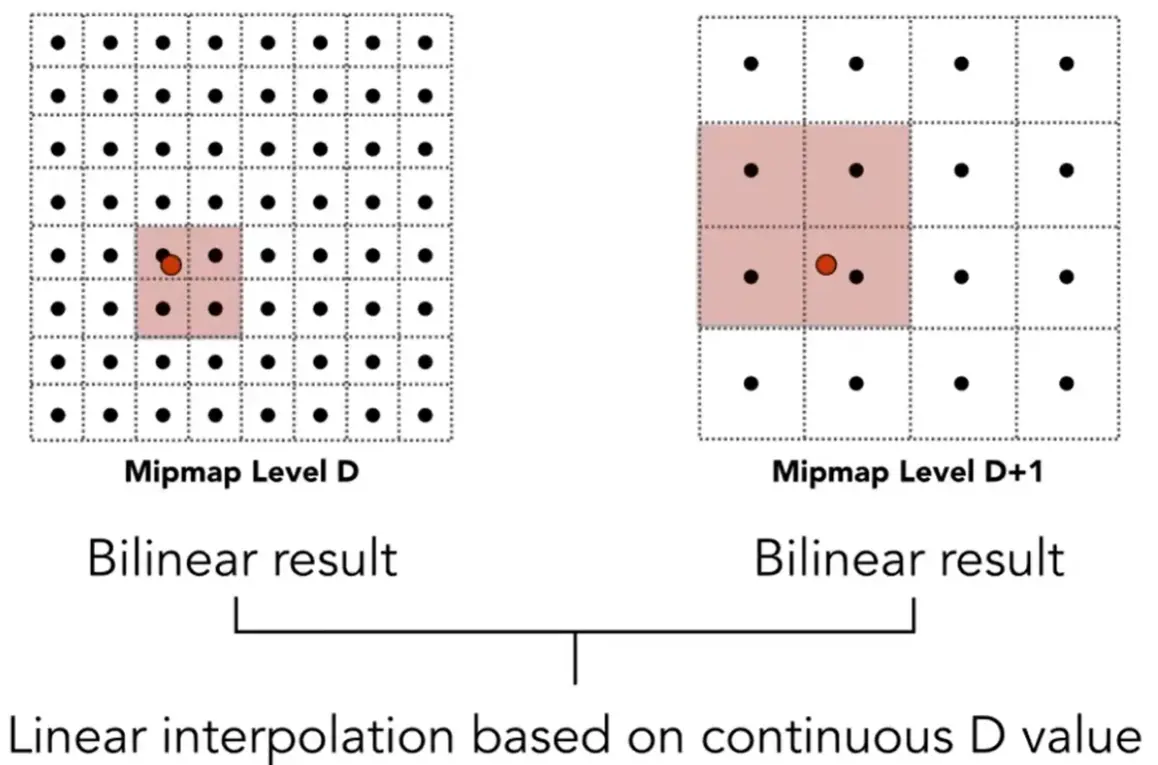
在层间进行第三次插值
Anisotropic Filtering#
各向异性过滤
mipmap limitations
overblur,远处的细节都糊掉了,原因是近似成正方形差的太多了,例如当 texels 是一个很长的矩形时

Note
- mipmap 只是预计算了对角线上的
- 各向异性过滤预计算了不同比例矩形的小图,\(O(4n)\) space
EWA Filtering#
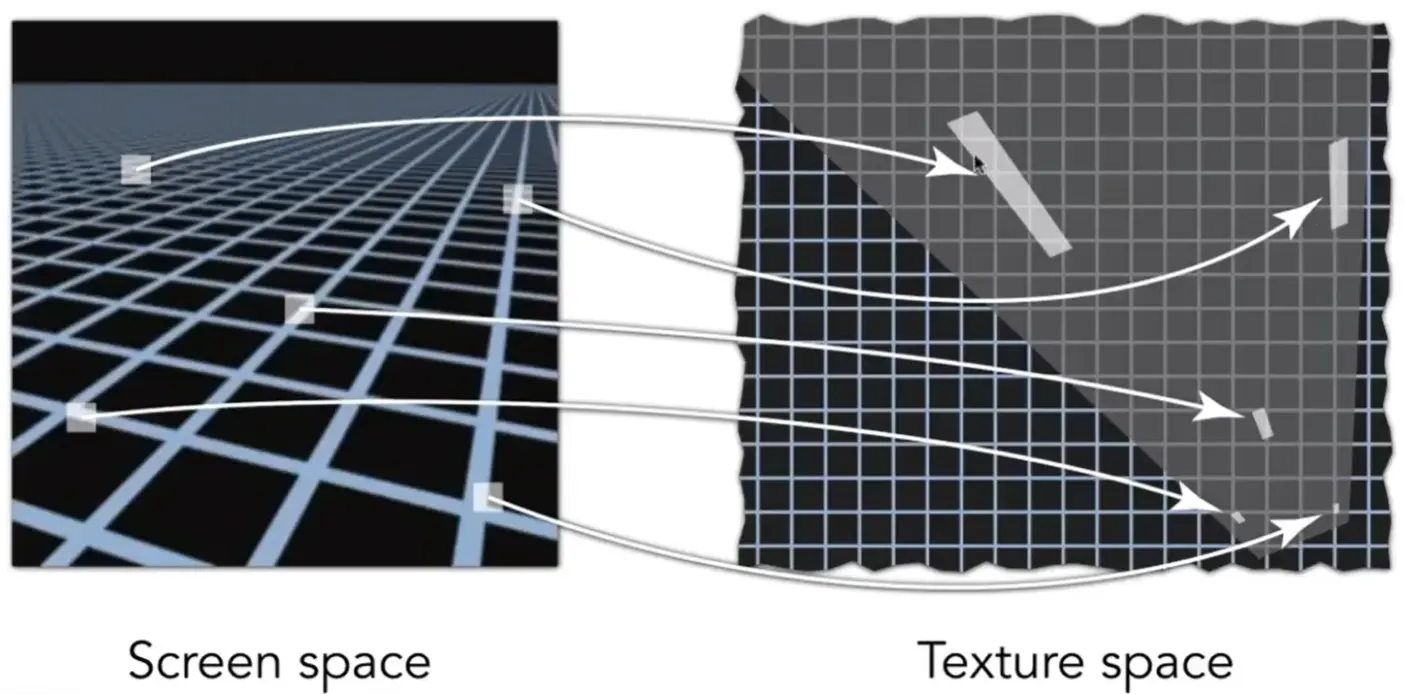
Note
同理,各向异性过滤无法处理矩形斜着的问题
- use multiple lookups
- weighted average
- mipmap hierarchy still helps
- can handle irregular footprints
Application of Textures#
纹理不一定需要是图像,也可以是其他属性
Environment map#
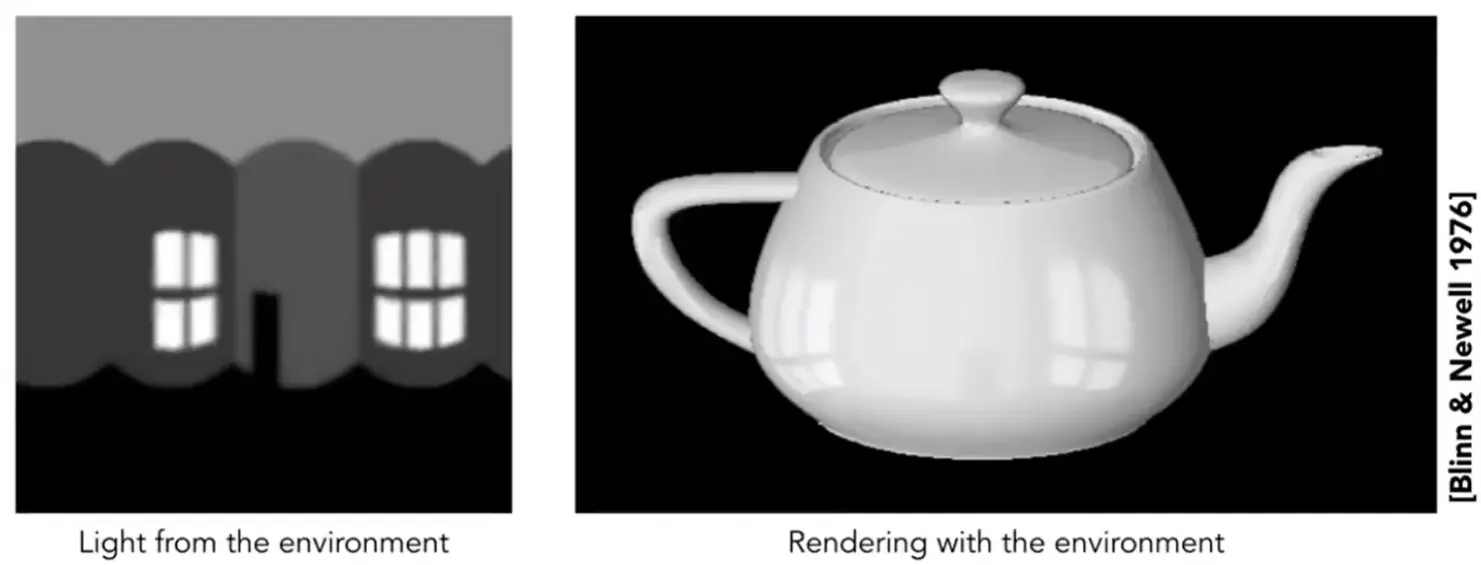

- 可以用一个球来记录整个环境光
-
展开之后会有变形类比世界地图
-
- 用外接立方体来记录环境光,变形比较小
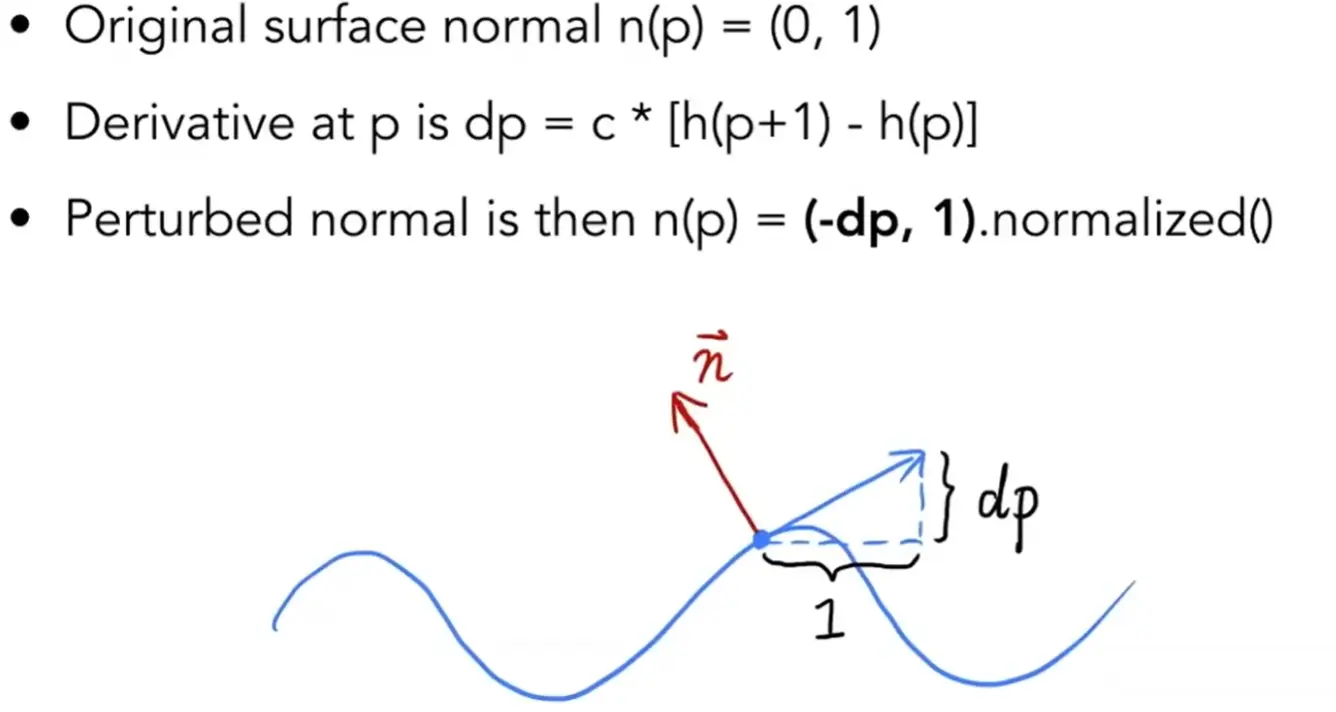
Bump mapping#

- 凹凸贴图,在模型不变的情况下改变法向量

Displacement mapping#
Bump mapping limitations
- 边缘看不到起伏
- 凹凸部分无法在物体本身上投下阴影

-
需要模型的三角形要足够细,采样率高于贴图
- direct x: 先有基本的模型,按照需要增加三角形个数
3D Procedural Noise + Solid Modeling#
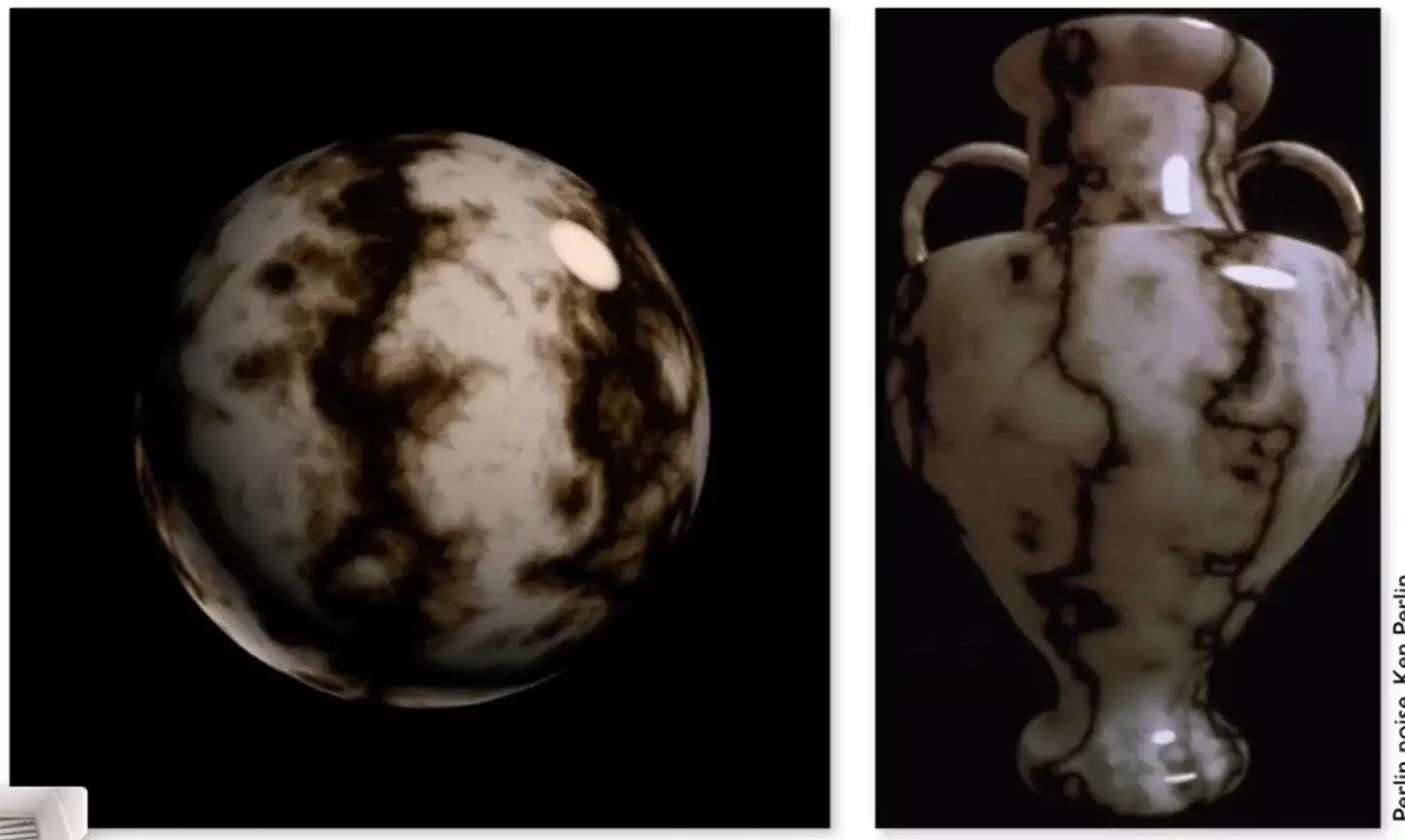
- 柏林噪声
Precomputed shading#
3D Textures#
Interpolation Across Triangles: Barycentric Coordinates 重心坐标#
Barycentric Coordinates#
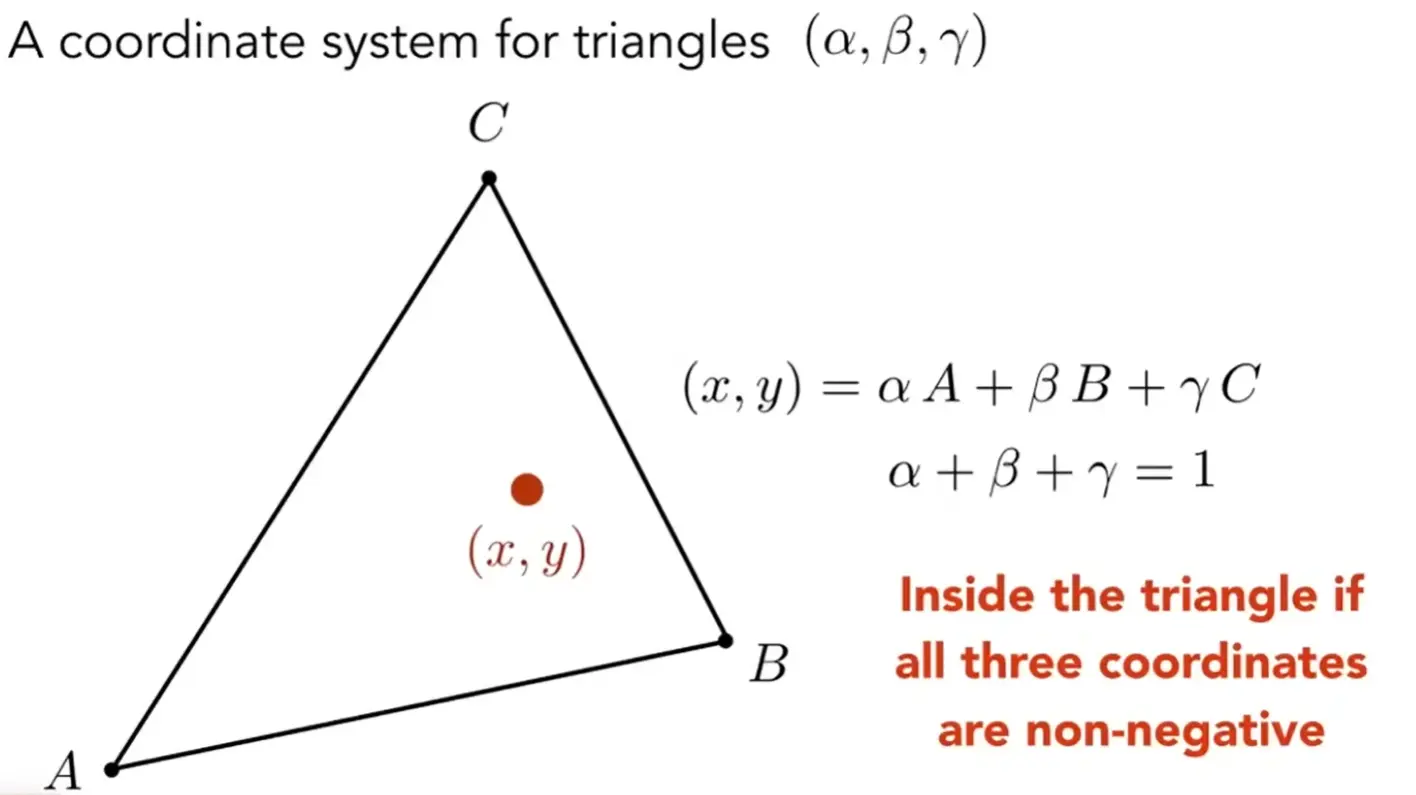
如果 \(\alpha,\beta,\gamma\geq0\),那么在三角形内。
可以通过面积的比例关系求解重心坐标:
也可以使用公式:
Using Barycentric Coordinates#
Warning
空间三角形经过投影之后,重心坐标并不是不变的,所以要先在三维空间中完成插值