06 Geometry
Geometry#
Implicit Geometry#
基于将点分类,例如使用数学公式描述
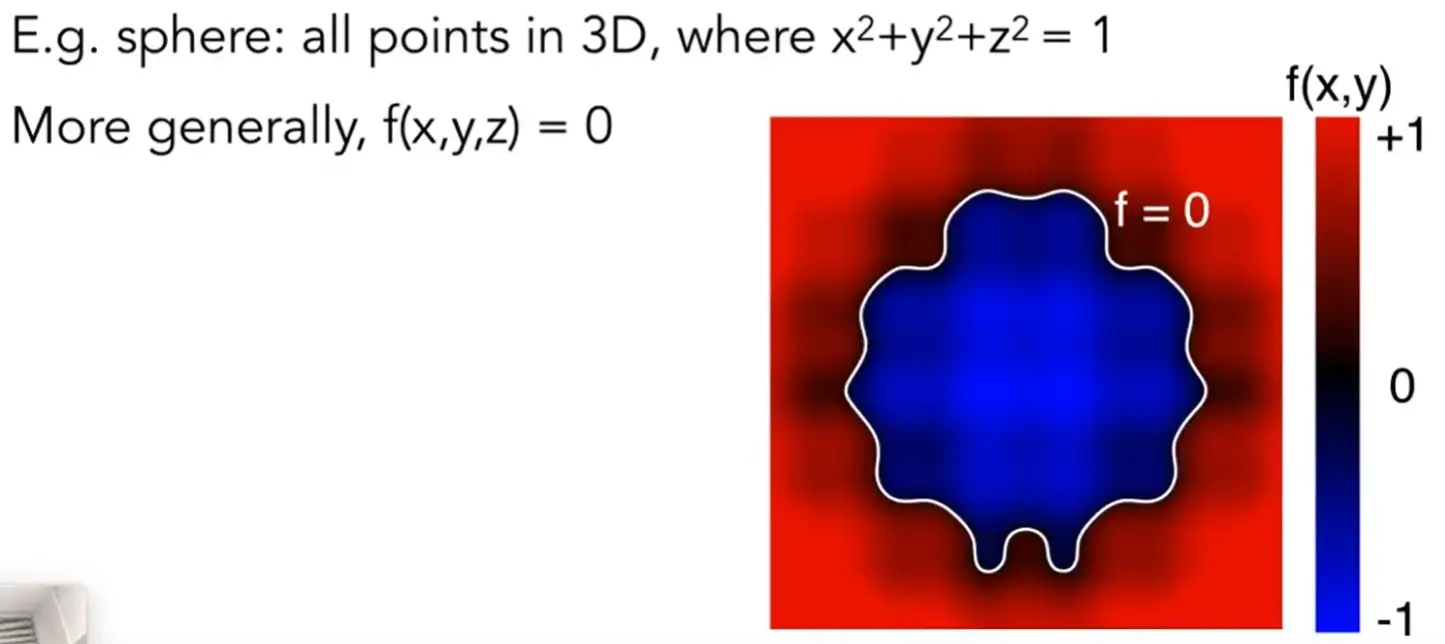
Note
- 判断一个点是否在表面上很简单
- 找到表面上所有的点很难
Algebraic Surfaces#
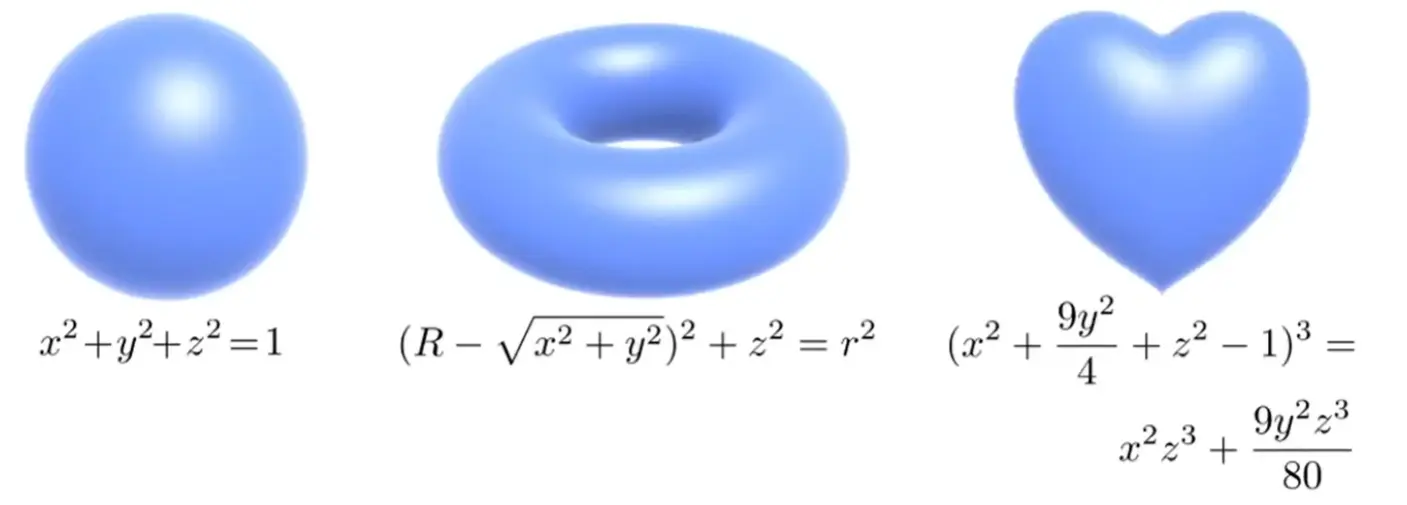
简单,但是不直观
Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG)#
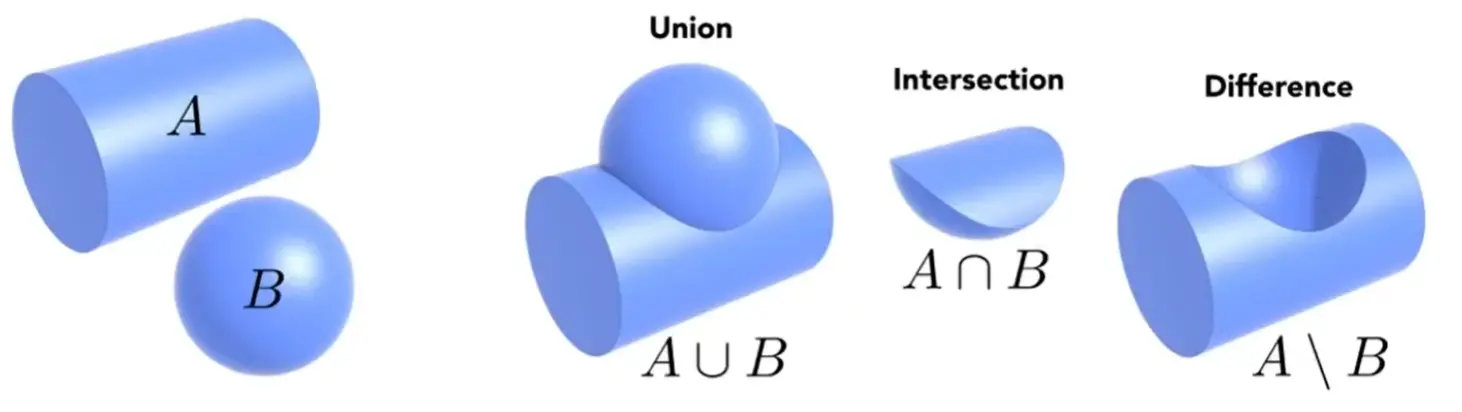
基本几何的布尔运算
Distance Functions#
给定空间中任何一个点到表面的最短距离,不同的距离函数可以融合
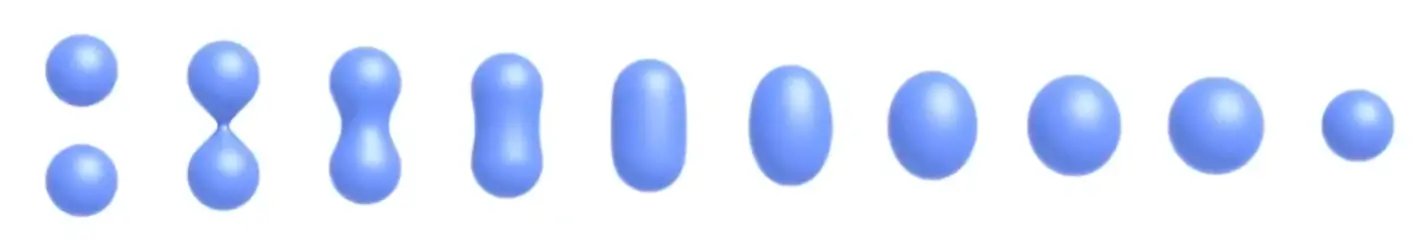
example#
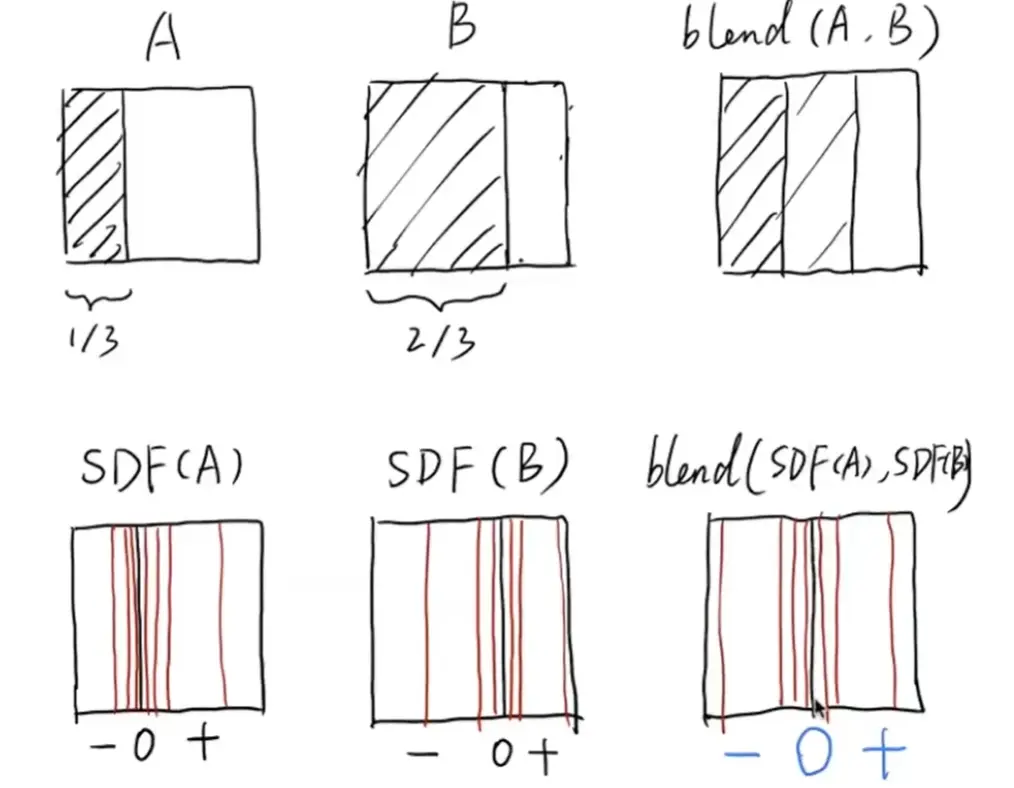
怎么表示从 A 到 B 的运动?
- 线性叠加,中间是灰色的
- A B 各自定义一个距离函数,然后 blend,相当于找到了边界的中间位置,类似插帧
Level Set Methods#
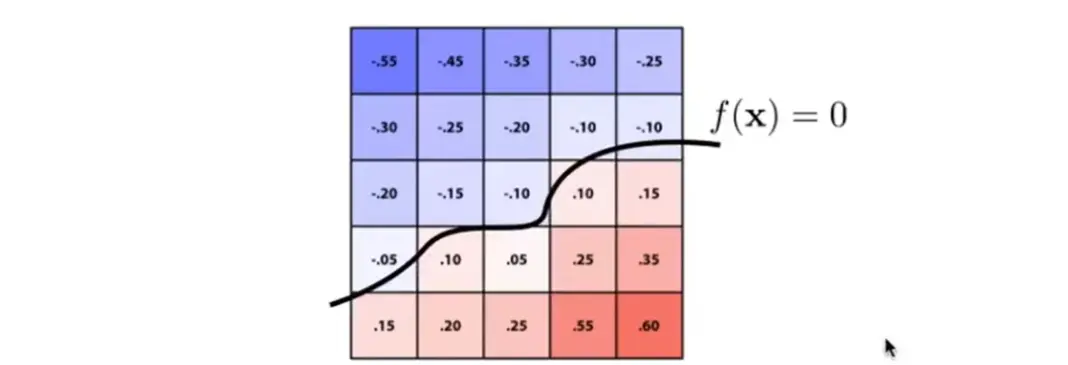
Note
- 是距离函数的另一种表示
- e.g. 有人体的三维密度信息,在密度为某个值的位置画表面,可以画出骨骼
Fractals 分形#
Conc.#
- Pros
- compact description (e.g., a function)
- certain queries easy (inside or outside, distance to surface)
- good for ray-to-surface intersection
- for simple shapes, exact description / no sampling error
- easy to handle changes in topology (e.g., fluid)
- Cons
- difficult to model complex shapes
Explicit Geometry#
all points are given directly or via parameter mapping
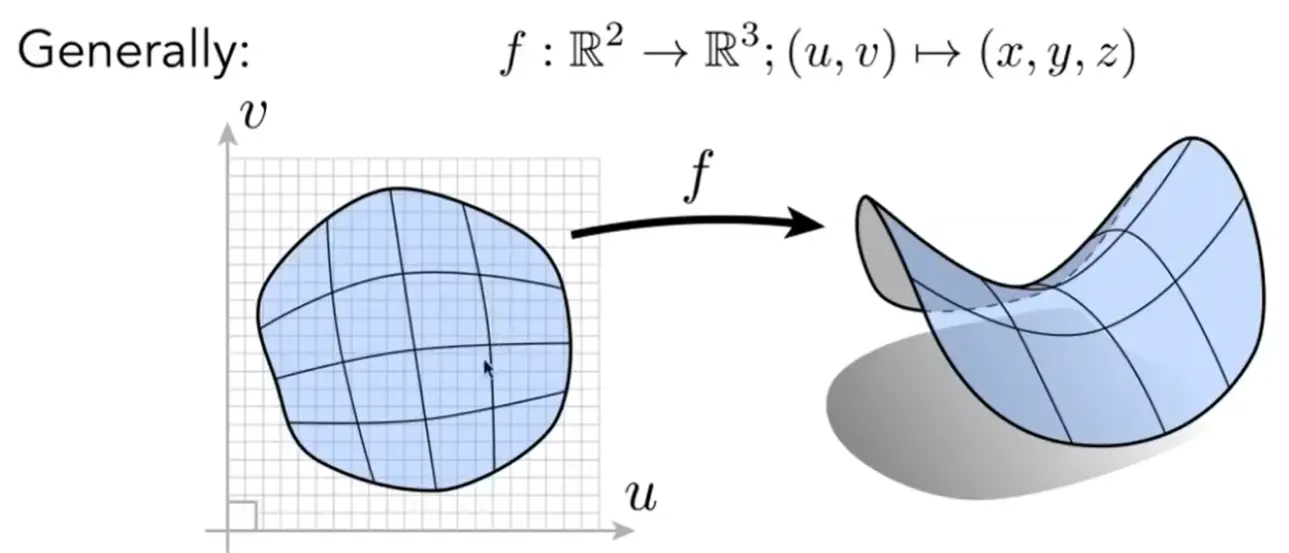
Note
- 找到一个表面上所有点很简单,直接遍历
- 判断一个点是否在表面上很难
Point Cloud#
lists of points, often converted into polygon mesh
Polygon Mesh#
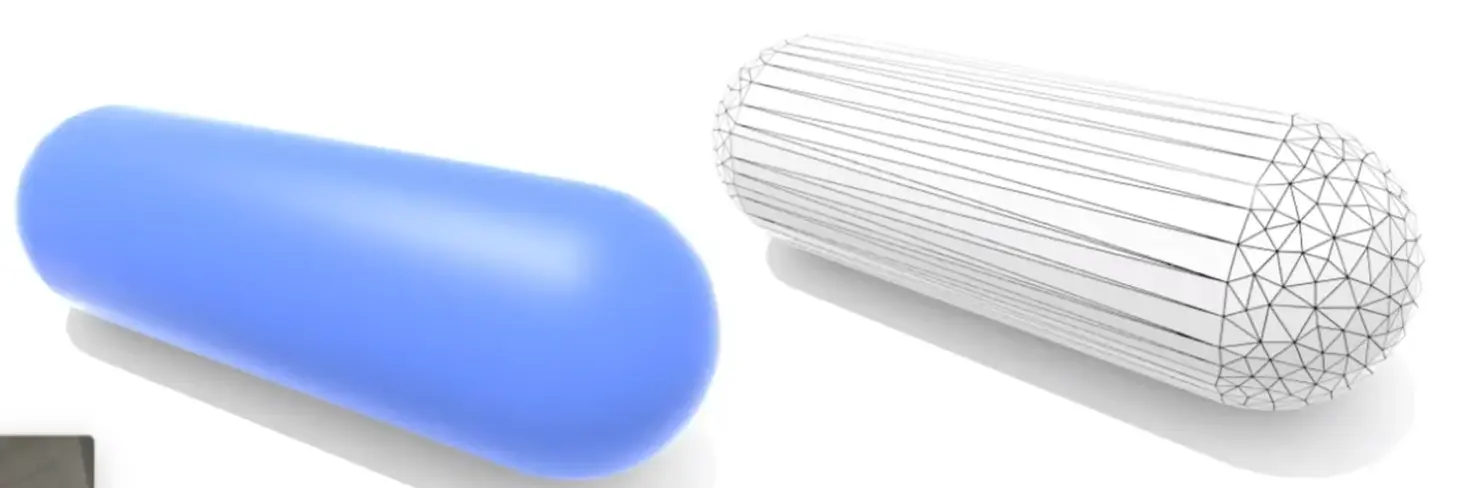
often triangle or quad
Wave front Ogjest File (.obj) Format#
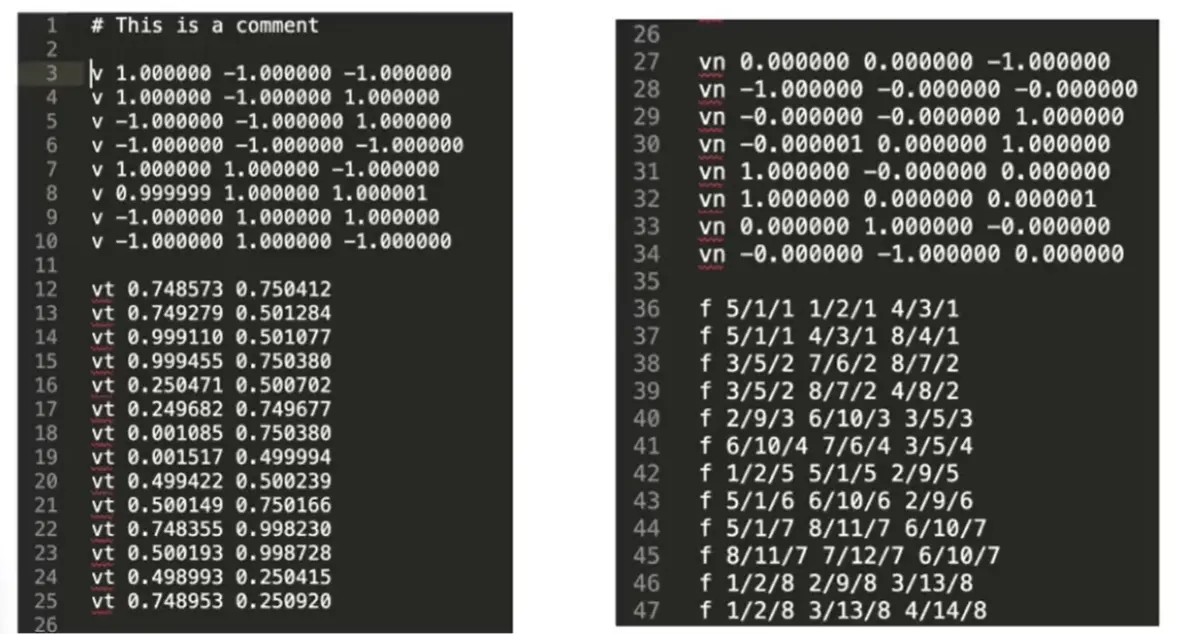
Note
定义点、纹理坐标、法向量和三角形面的连接方式
Bezier Curves#
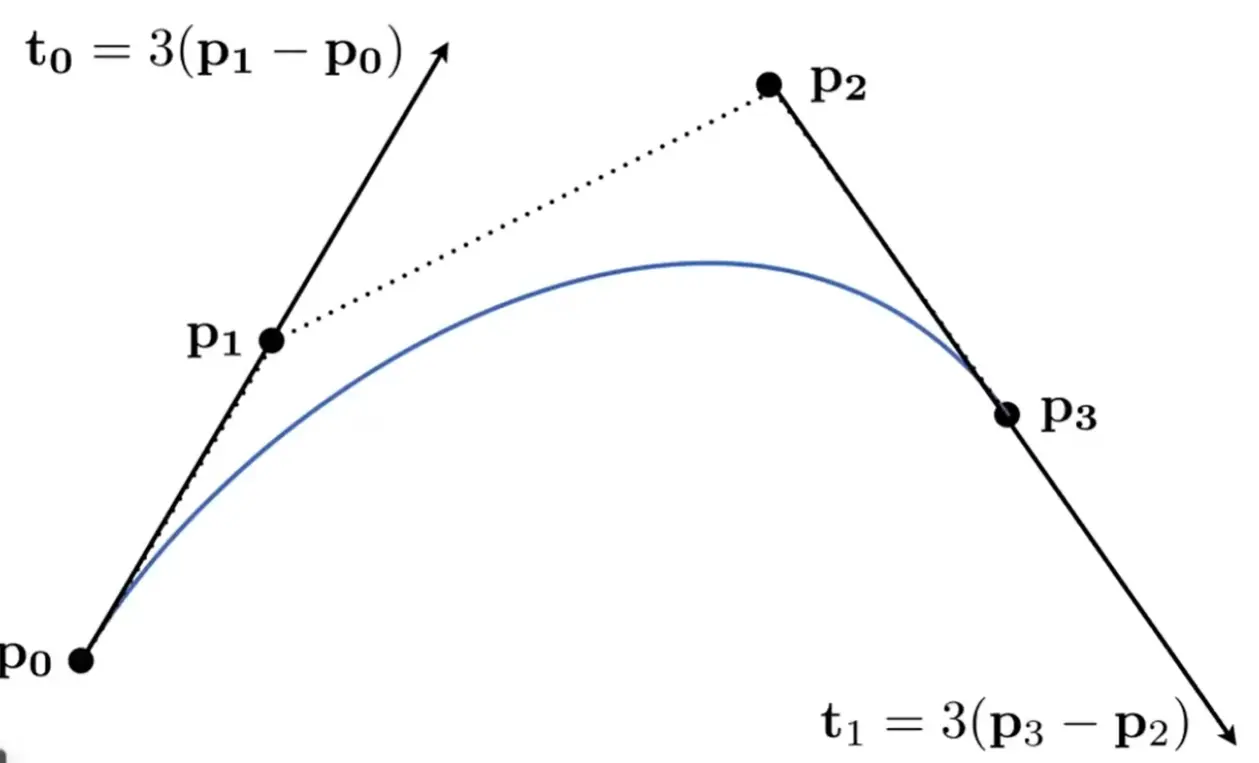
Note
给定一些控制点,画出一条连续的曲线
de Casteljau Algorithm#
3 point#
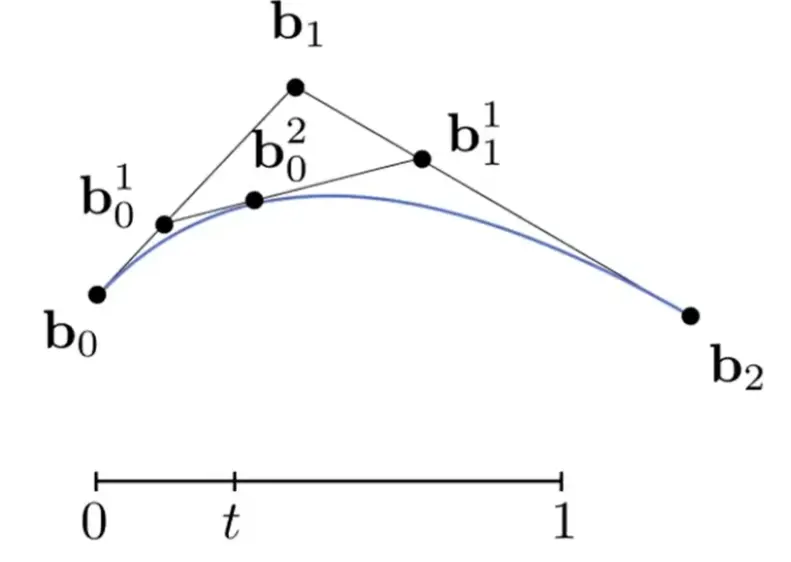
\[
\begin{aligned}
\mathbf{b}_{0}^{1}(t)&=(1-t)\mathbf{b}_0+t\mathbf{b}_1 \\
\mathbf{b}_{1}^{1}(t)&=(1-t)\mathbf{b}_1+t\mathbf{b}_2 \\ \\
\mathbf{b}_{0}^{2}(t)&=(1-t)\mathbf{b}_0^1+t\mathbf{b}_1^1 \\ \\
\implies\mathbf{b}_0^2(t)&=(1-t)^2\mathbf{b}_0+2t(1-t)\mathbf{b}_1+t^2\mathbf{b}_2
\end{aligned}
\]
4 point#
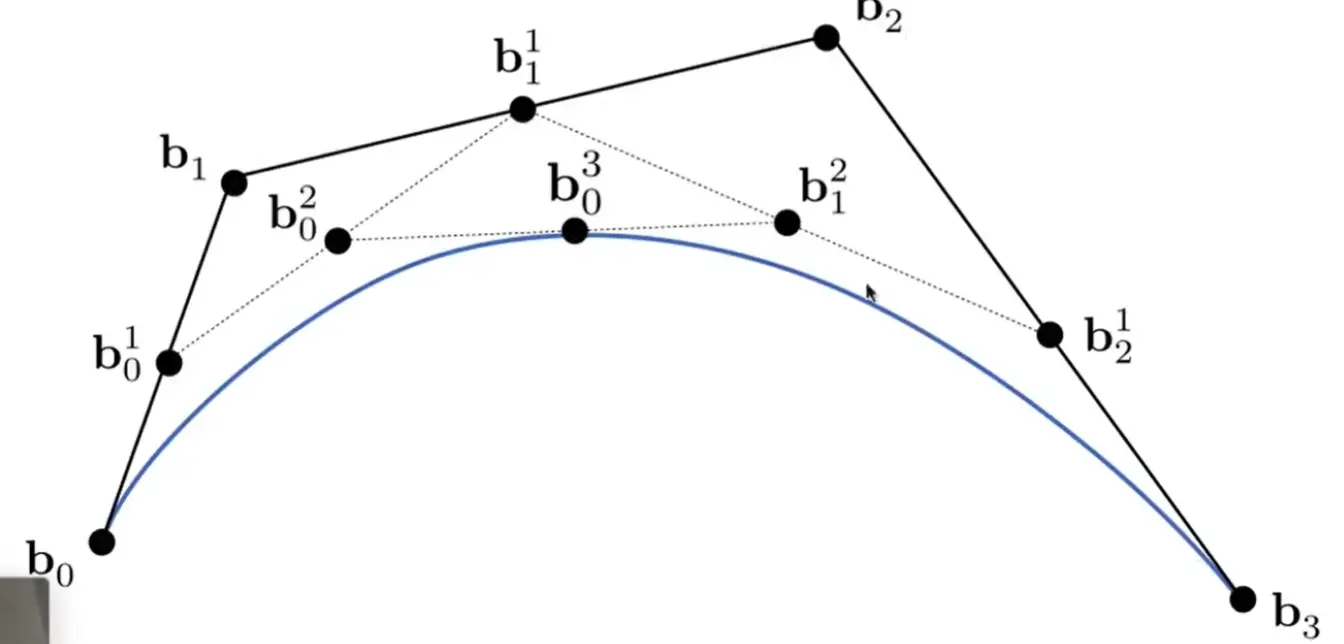
\[
\mathbf{b}^n(t)=\mathbf{b}_{0}(1-t)^{3}+\mathbf{b}_{1}3t(1-t)^{2}+\mathbf{b}_{2}3t^{2}(1-t)+\mathbf{b}_{3}t^{3}
\]
normal form#
\[
\begin{align}
\mathbf{b}^n(t)&=\mathbf{b}_0^n(t)=\sum_{j=0}^n\mathbf{b}_jB_j^n(t) \\
B_i^n(t)&=
\begin{pmatrix}
n \\
i
\end{pmatrix}t^i(1-t)^{n-i}
\end{align}
\]
Bernstein Polynomials
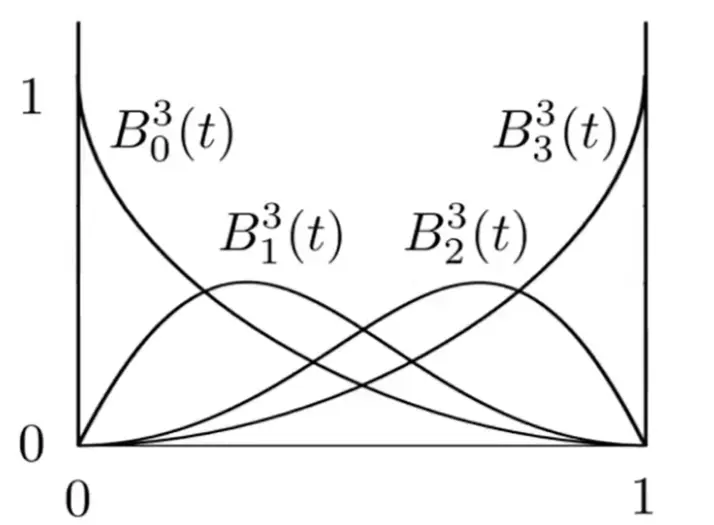
\[
B_i^n(t)=
\begin{pmatrix}
n \\
i
\end{pmatrix}t^i(1-t)^{n-i}
\]
property
- 贝塞尔曲线仿射变换前后不变
- 投影变换会改变
- 凸包性:曲线一定在控制点的凸包内
Piecewise Bezier Curves#
Problem
- 控制点很多时,bezier curve 很平滑,但是控制点几乎无法影响曲线的形状
- 使用分段 bezier curve 来解决
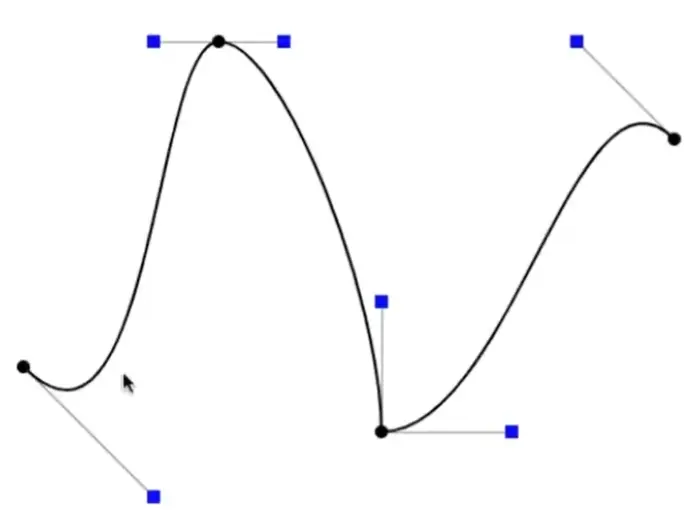
Continuity#
- \(C^0\) continuity: \(\mathbf{a}_{n}=\mathbf{b}_{0}\)
- \(C^1\) continuity: \(\mathbf{a}_n=\mathbf{b}_0=\frac{1}{2}\left(\mathbf{a}_{n-1}+\mathbf{b}_1\right)\)
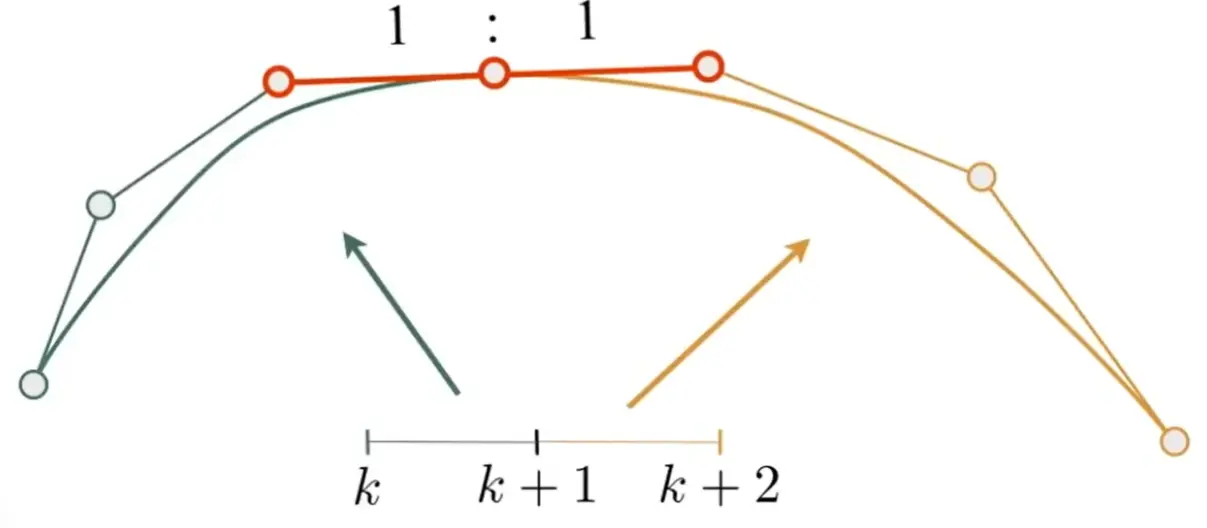
other curves#
- Splines
- B-splines
- 具有局部性,改动一处不影响曲线的其他部分
- NURBS 非均匀有理 B 样条
Surfaces#
Bezier Surfaces#
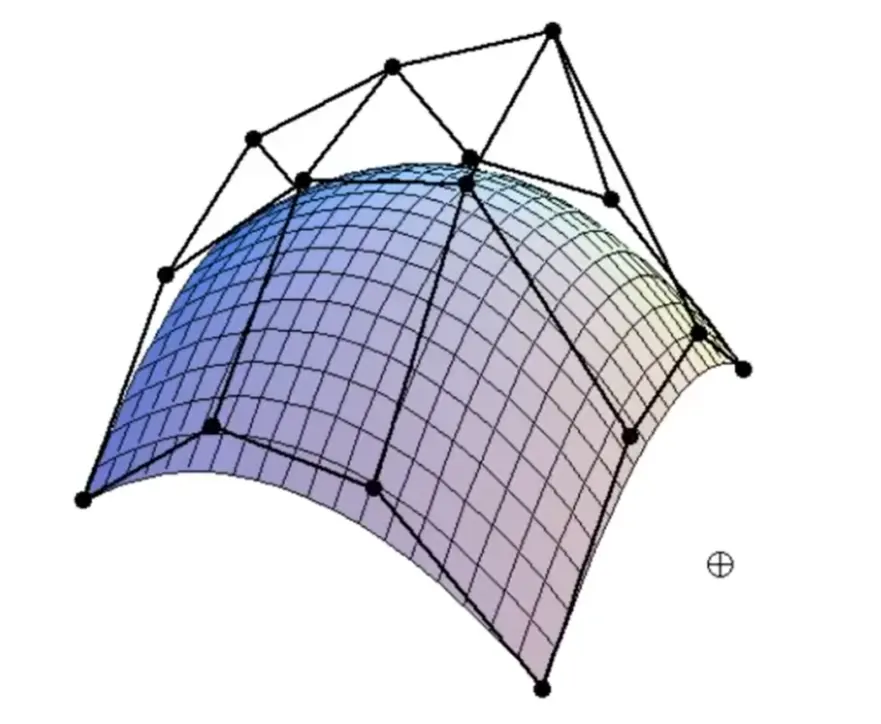
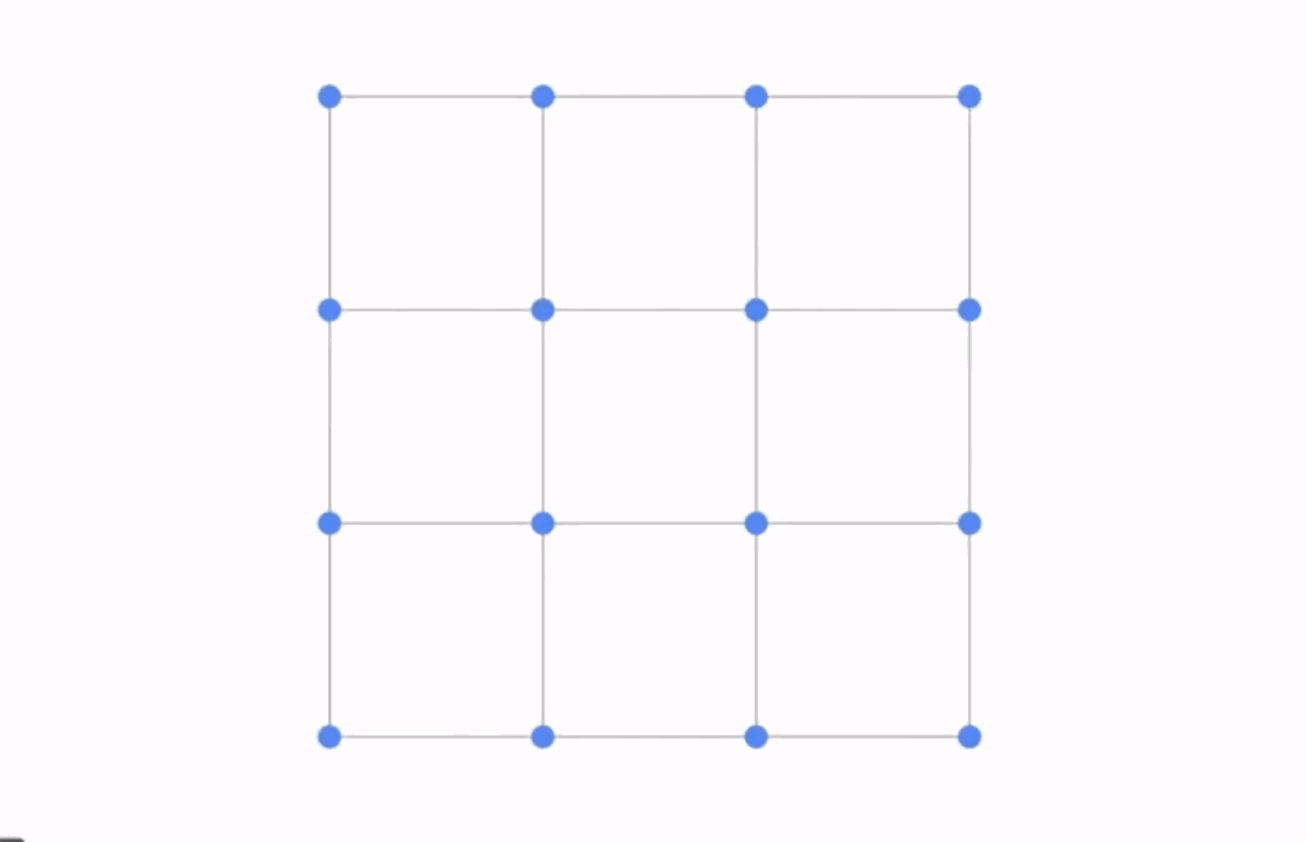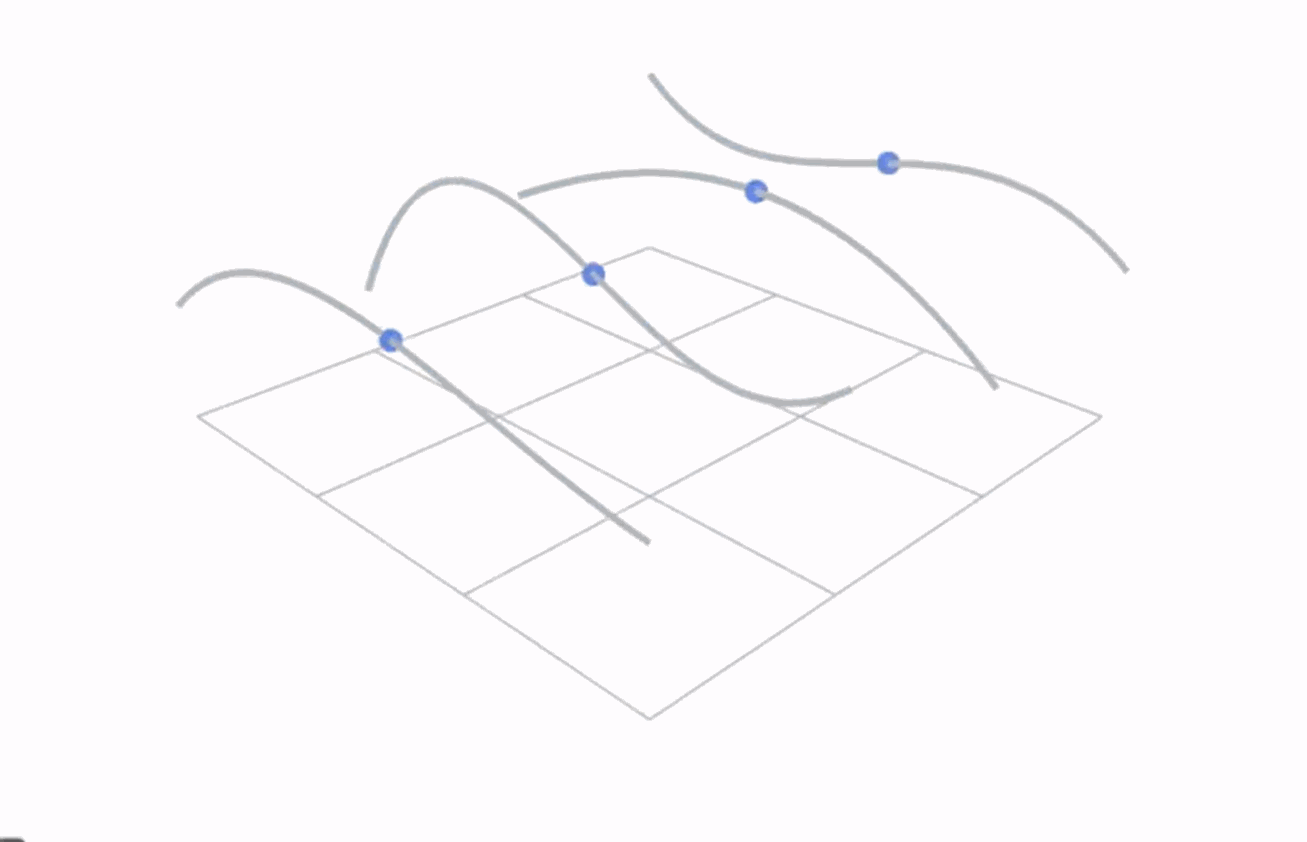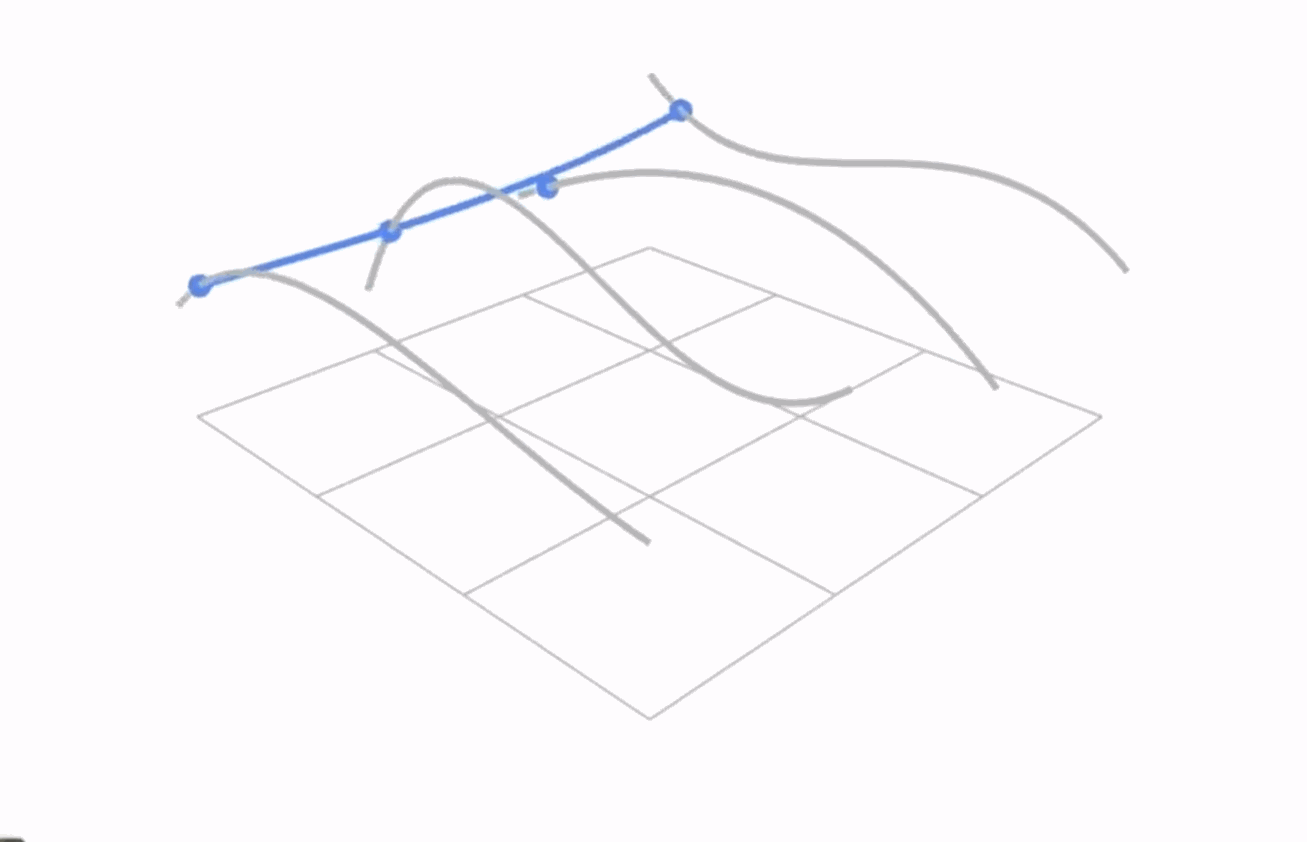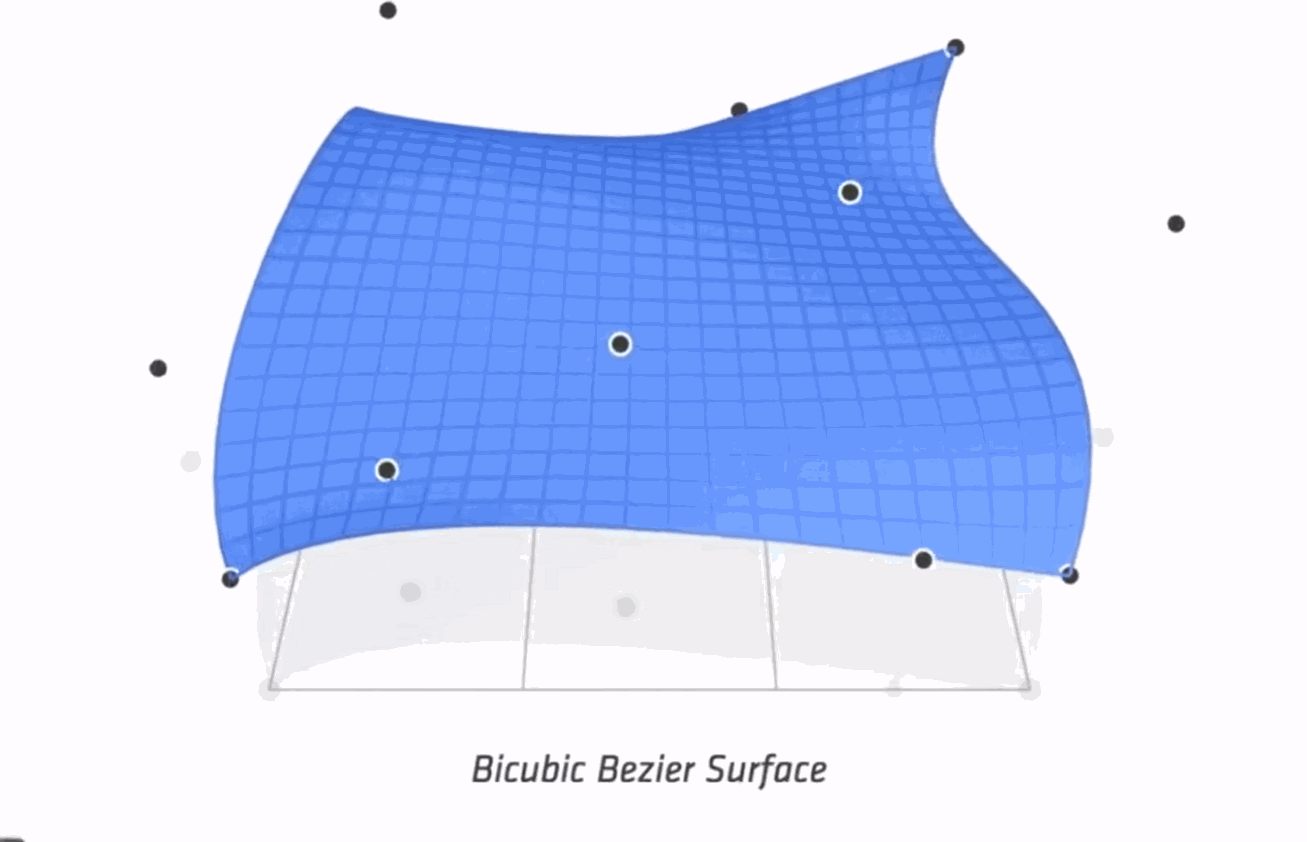
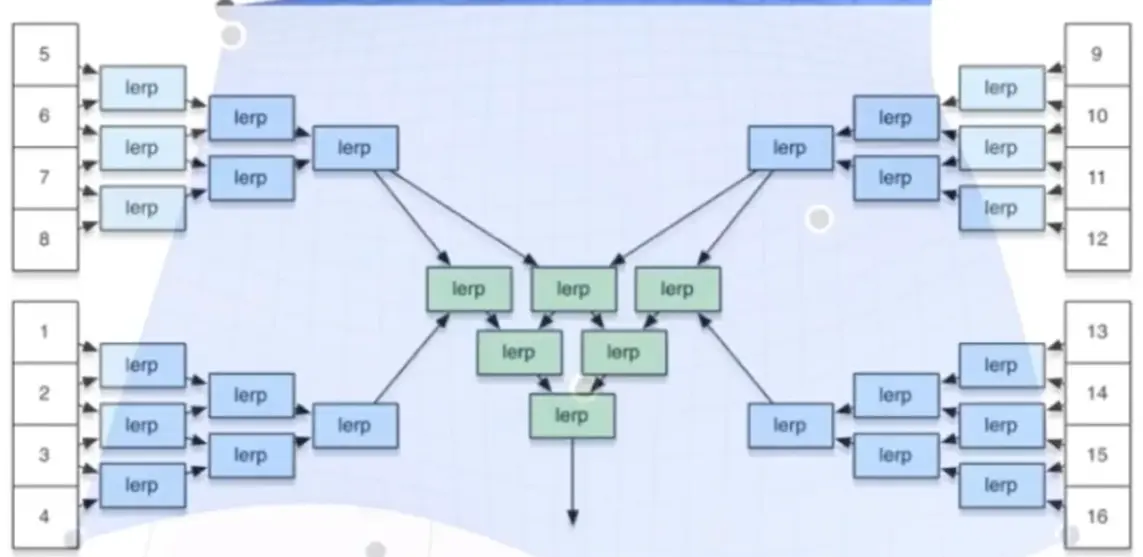
Mesh#

- mesh subdivision 网格细分
- mesh simplification 网格简化
- mesh regularization 网格正规化
Subdivision#
Loop Subdivision (triangle mesh)#
Note
- 划分三角形
- 调整顶点位置使模型更连续
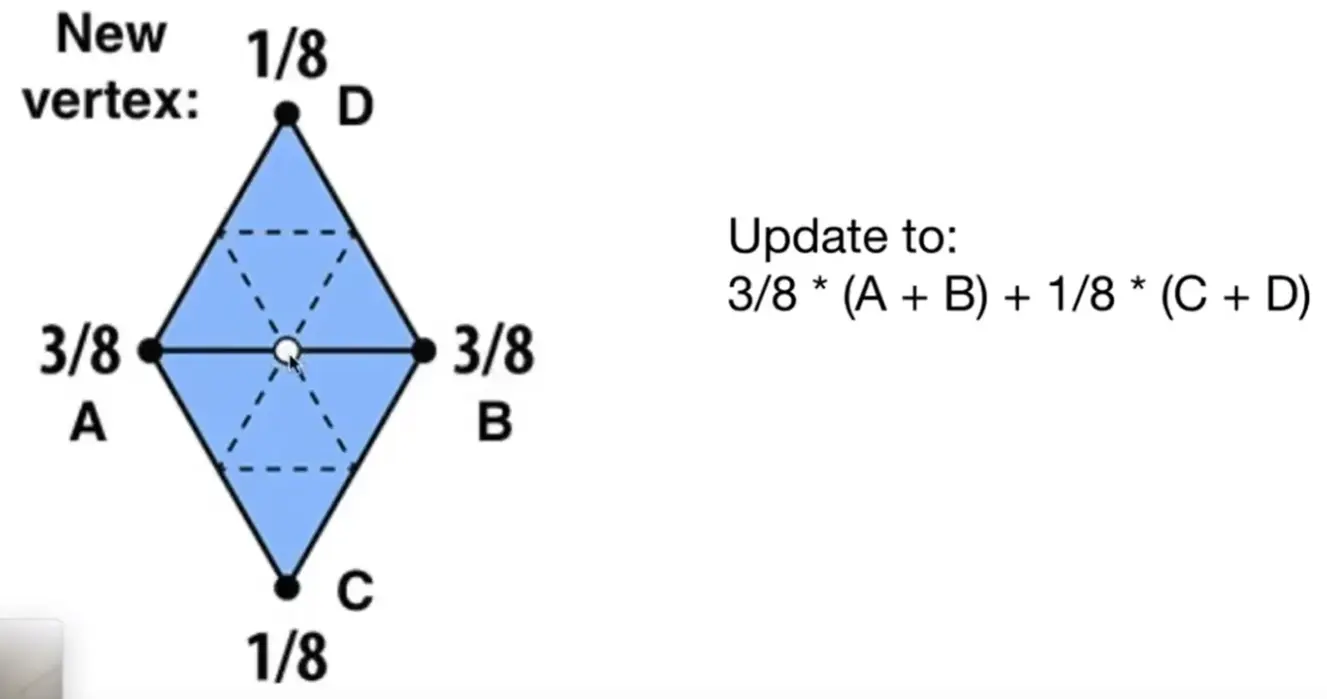
\[
N=\frac{3}{8}(A+B)+\frac{1}{8}(C+D)
\]
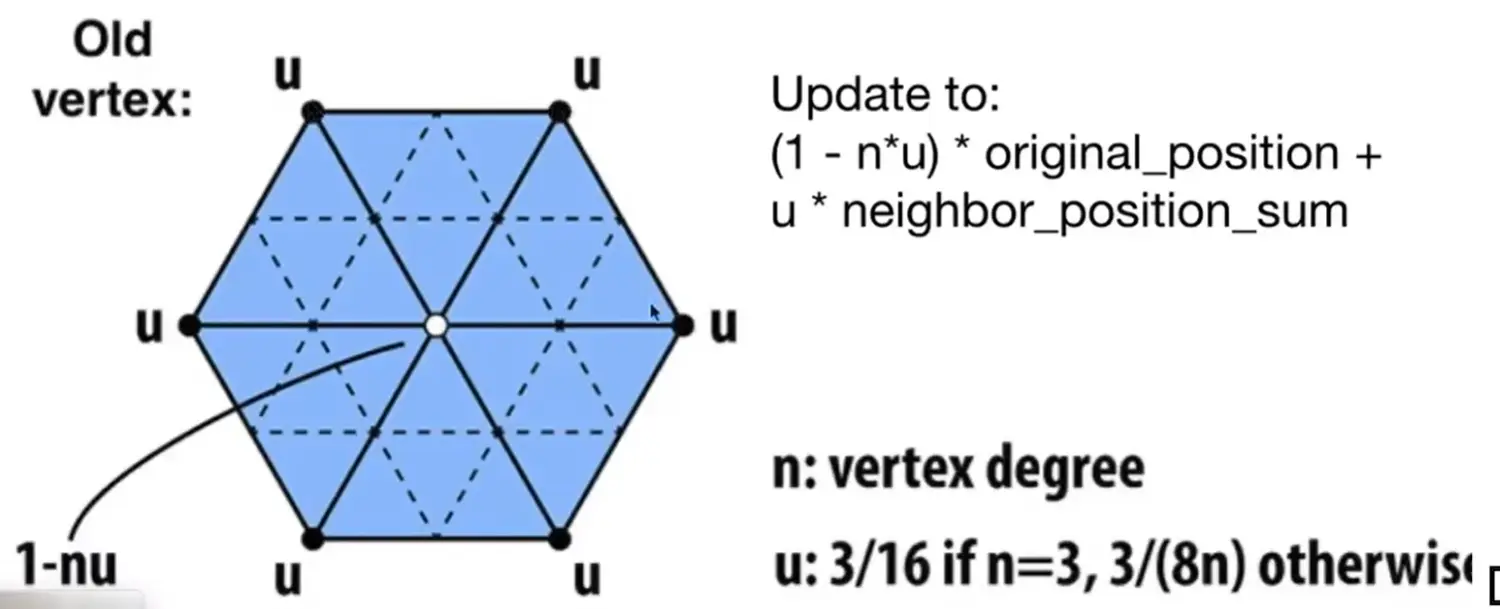
\[
\begin{align}
O'&=(1-\text{deg}(O)\cdot u)O+u\cdot \sum_{V_{i}\in \text{neighbor}(O)}V_{i} \\
u&=\begin{cases}
\frac{3}{16}\text{, if }n=3 \\
\frac{3}{8n}\text{, otherwise}
\end{cases}
\end{align}\]
Catmul-Clark Subdivision (general mesh)#
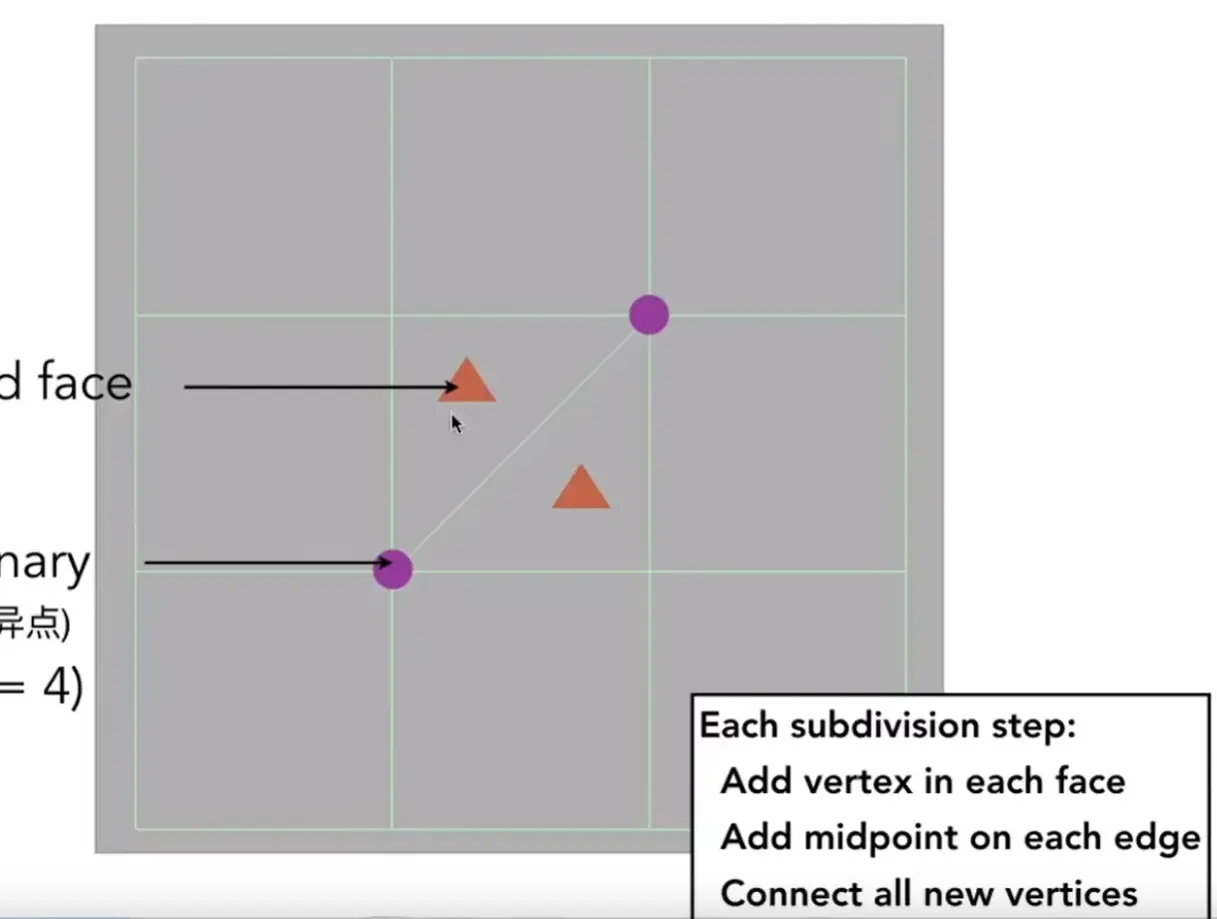
concepts
- Non-quad face: 非四边形面
- Extraordinary vertex (奇异点): \(\text{deg}(v)\neq 4\)
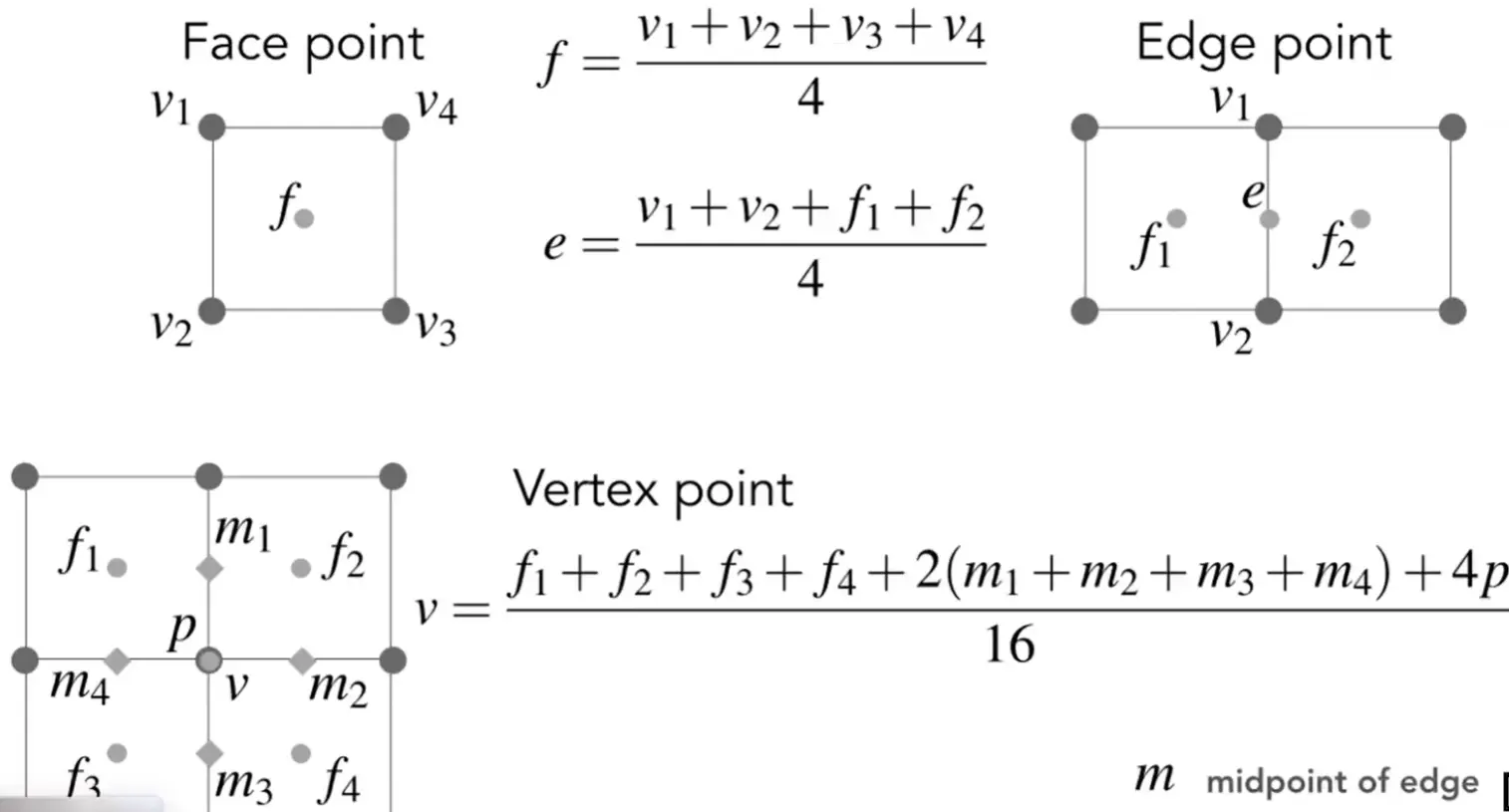
method
- 每个面中间取一个点
- 每条边取中点
- 连接
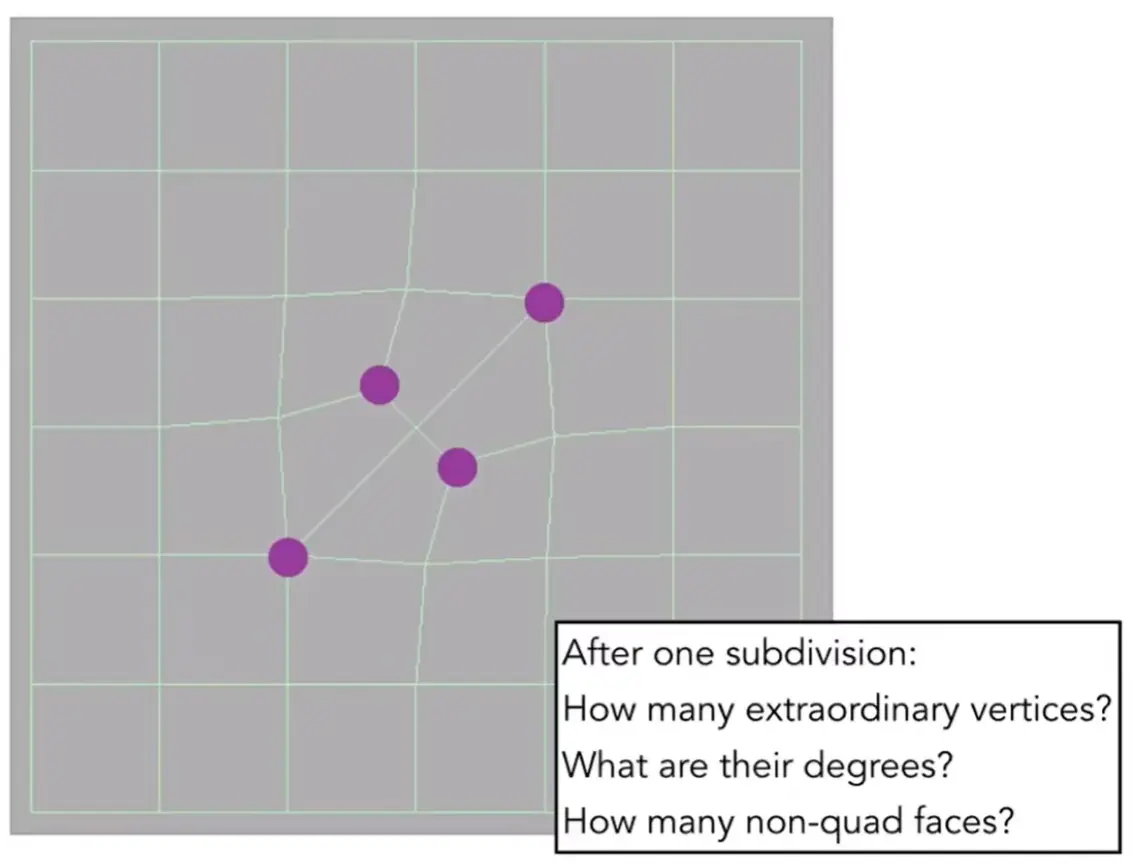
property
- 三角形中新的点是奇异点
- 第一次细分之后,所有的非四边形消失,增加了非四边形面数个奇异点
- 后续奇异点不会增加
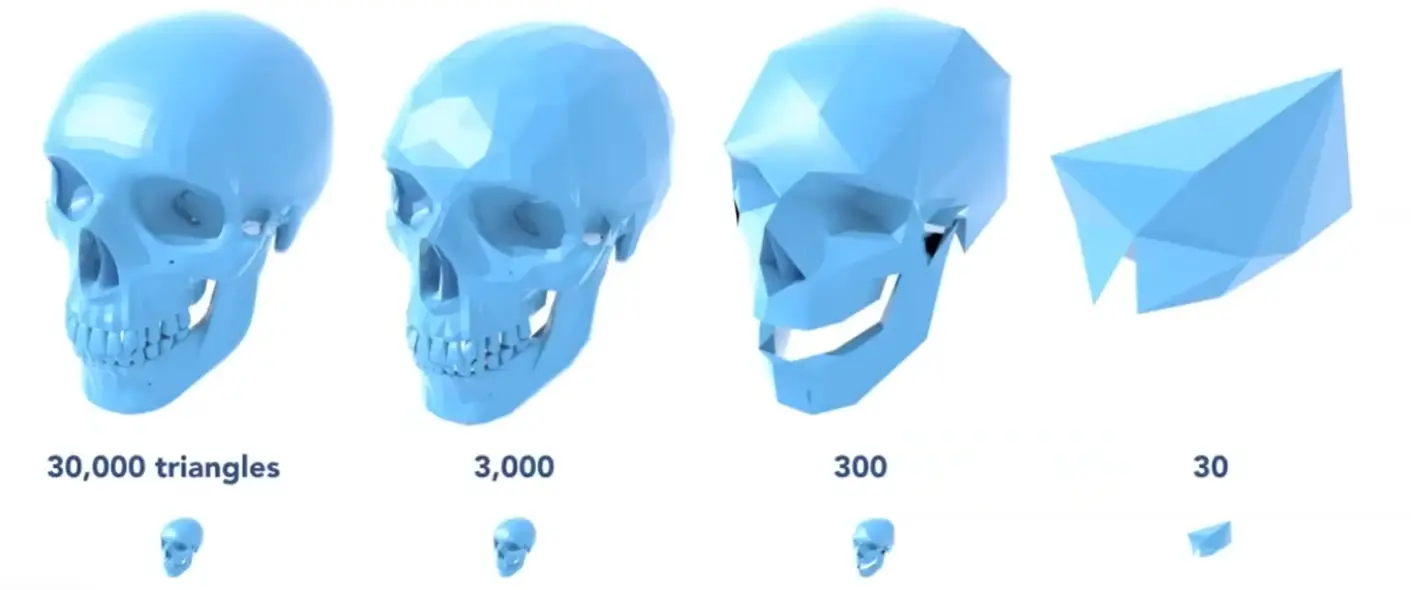
Simplification#

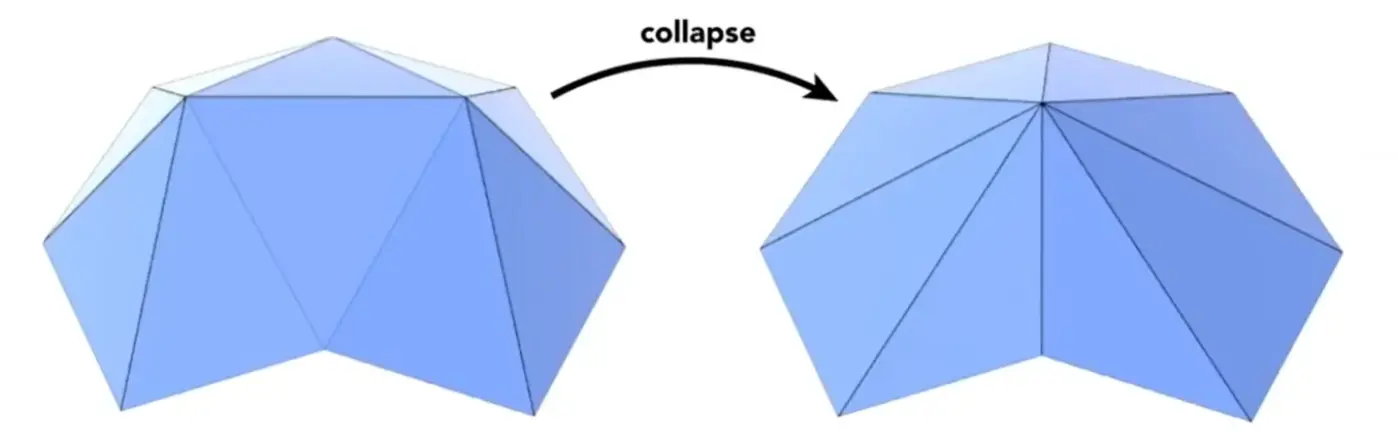
collapse edges to point
Quadric Error Metrics#
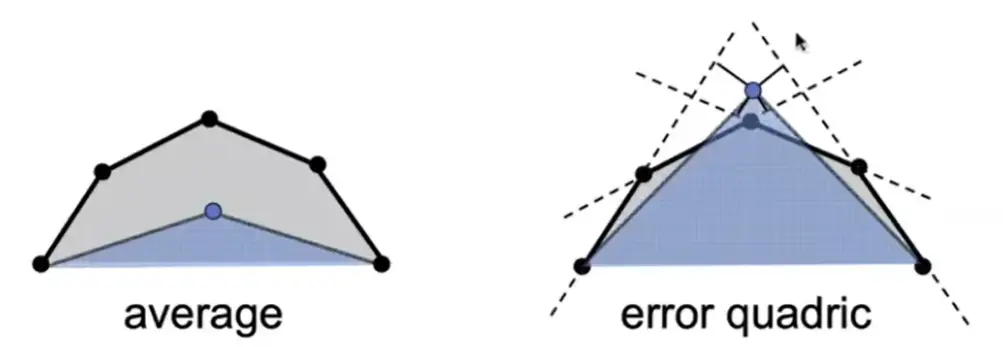
Note
- 使用平均值,会导致模型塌陷
- 使用二次误差度量:最小化新顶点到原来的三角形面的距离平方和
Simplification#
如何找到应该坍缩的边?
- 将模型中所有的边坍缩的误差算出来
- 每次取误差最小的进行坍缩
- 一条边坍缩之后,会改变相邻的几条边的坍缩误差,需要更新
- 使用优先队列来维护,方便找到最小误差的边
- 一个贪心算法,只是近似解