04 Resterization
Perspective Projection Cont.#
near plane#
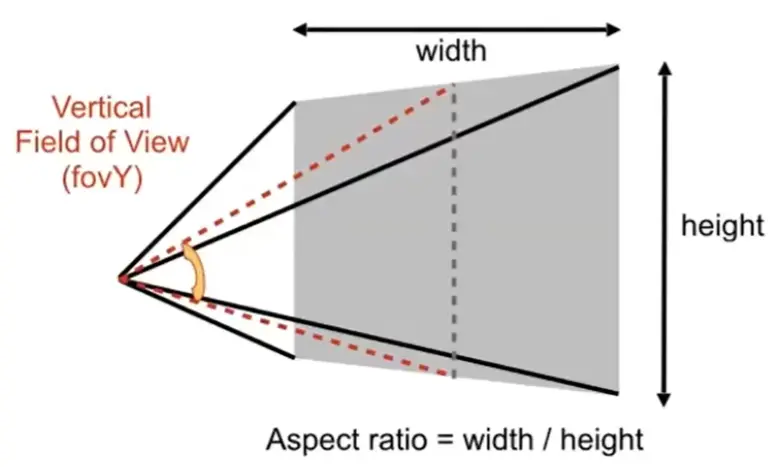
- width, height, aspect ratio
- field of view: vertical (fovY), horizontal (fovX)
- 通常,取原点对称
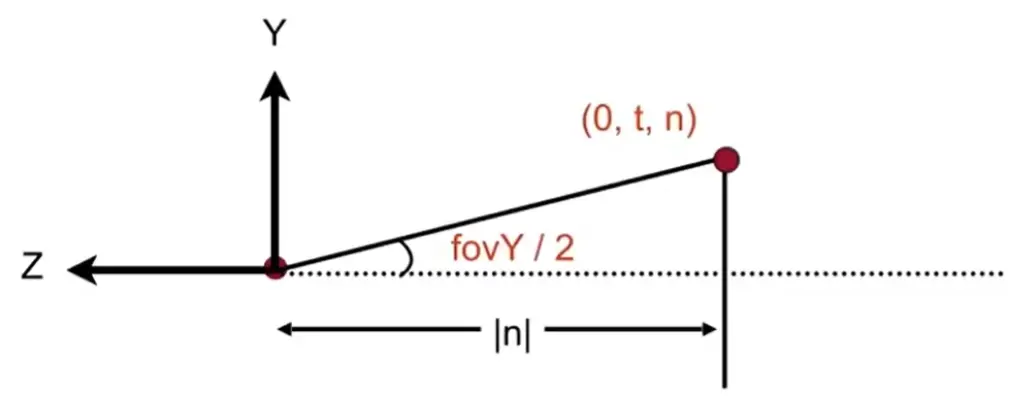
- \(\tan\frac{fovY}{2}=\frac{t}{|n|}\)
- \(\text{aspect}=\frac{r}{t}\)
Canonical Cube to Screen#
screen#
- an array of pixels
- resolution
- a typical raster display
pixel#
- r g b
- 定义左下角是原点,向右是 X,向上是 Y
- pixel \((x,y)\) is centered at \((x+0.5,y+0.5)\)
projection#
xy coordinates: \([-1,1]^2\) to \([0,\text{width}]\times[0,\text{height}]\), viewpoint transformation
\[
M_{viewport}=
\begin{pmatrix}
\frac{width}{2} & 0 & 0 & \frac{width}{2} \\
0 & \frac{height}{2} & 0 & \frac{height}{2} \\
0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\
0 & 0 & 0 & 1
\end{pmatrix}\]
Rasterization#
raster displays#
- 阴极射线管:逐行扫描、隔行扫描
- Frame Buffer: pixel arrays in memory
a simple approach: sampling#
使用像素中心对模型进行采样,判断一个像素的中心是否在三角形内部
| sampling | |
|---|---|
实现 inside()#
- 进行向量叉积,从判断 \(\vec{P_{0}P}\) 和 \(\vec{P_{0}P_{1}}\) 的位置关系开始,在三条边的同侧则在三角形内部
- 刚好在三角形边上时,可以规定其属于左边或上边
bounding box#
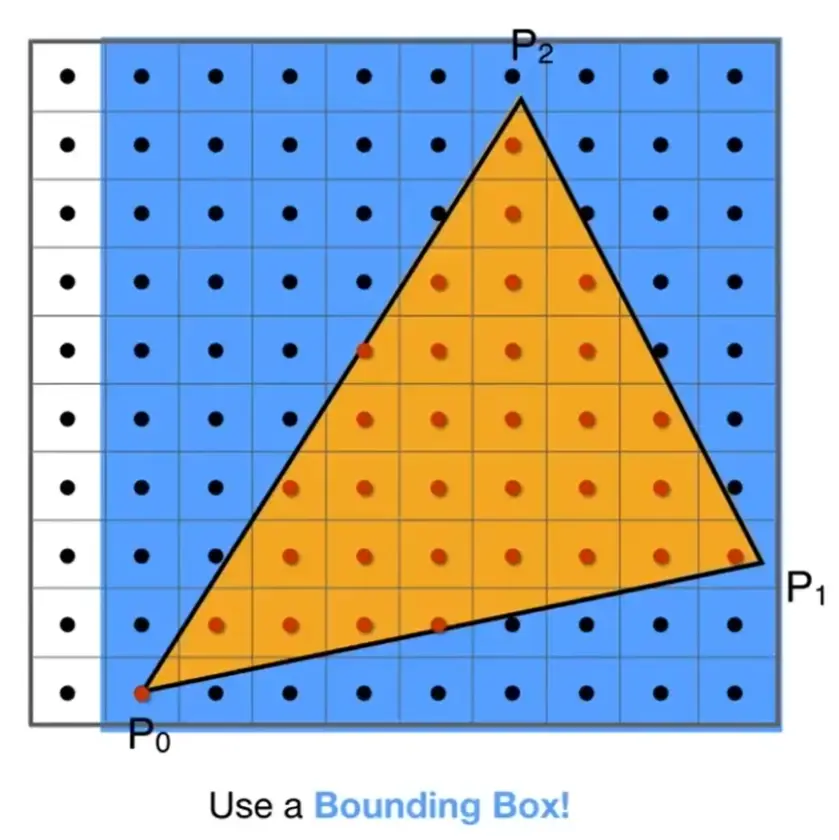
- 只有 bounding box 中的像素点才需要考虑
Question
采样精度小的时候,容易产生锯齿
Antialiasing#
recap: 锯齿,走样
intro#
- sampling artifacts
- jaggies - sampling in space
- moire patterns - undersampling images
- false motion - sampling in time
-
信号的变化太快,跟不上采样速度
idea: blurring(pre-filtering) before sampling#
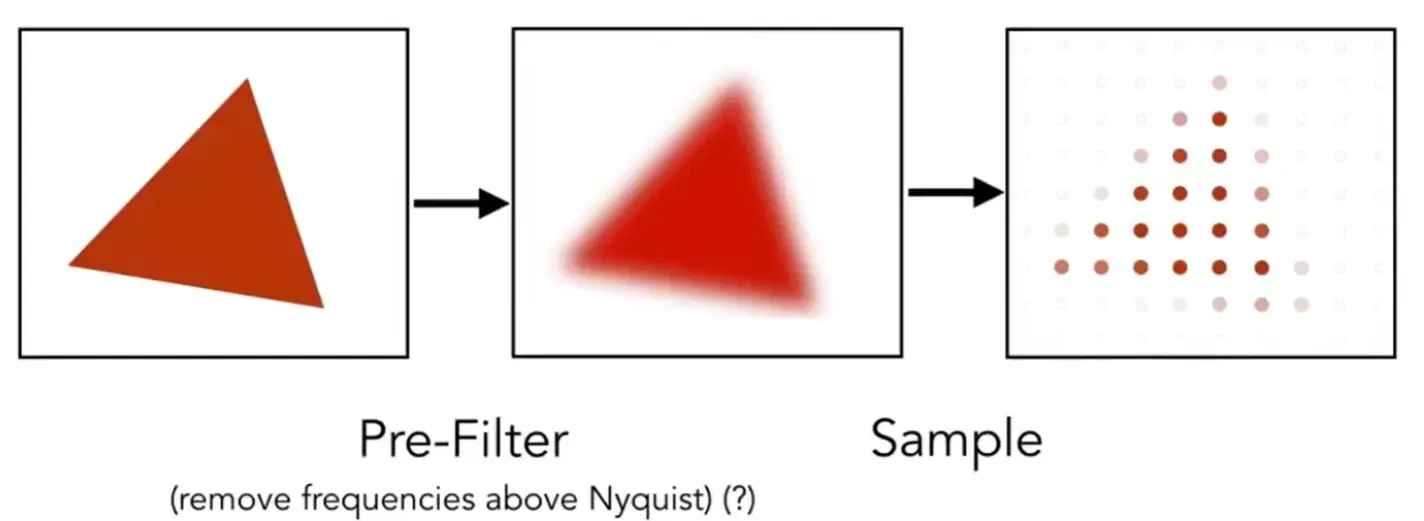
Warning
一定是 filter then sample,不能用 sample then filter,否则效果会更差
Frequncy Domain 频域#
intro#
- \(f=\frac{1}{T}\)
- Fourier Transform: spatial domain (时域) -> frequency domain (频域)
- 频率高,需要的采样频率也更高
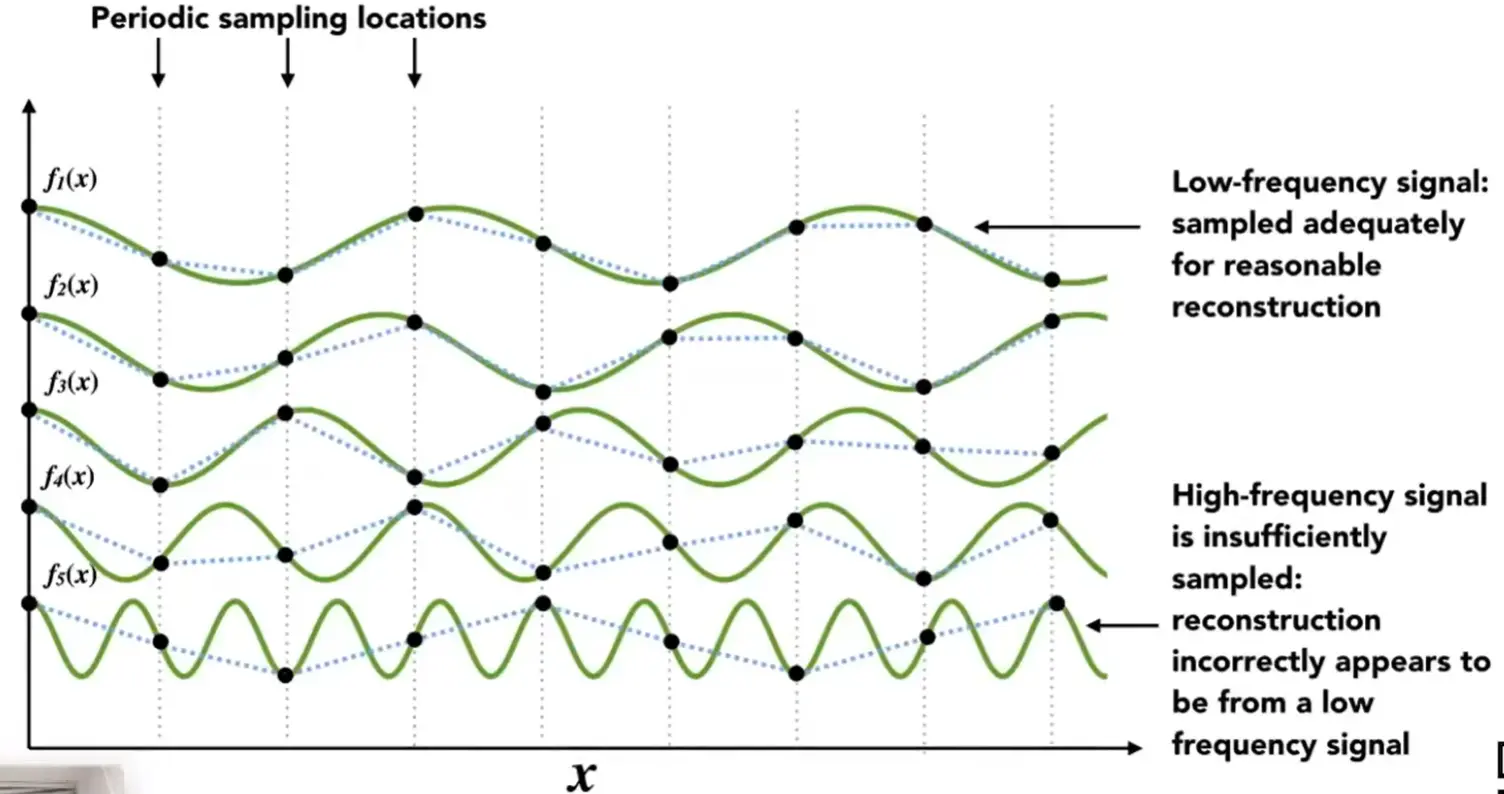
Aliases#
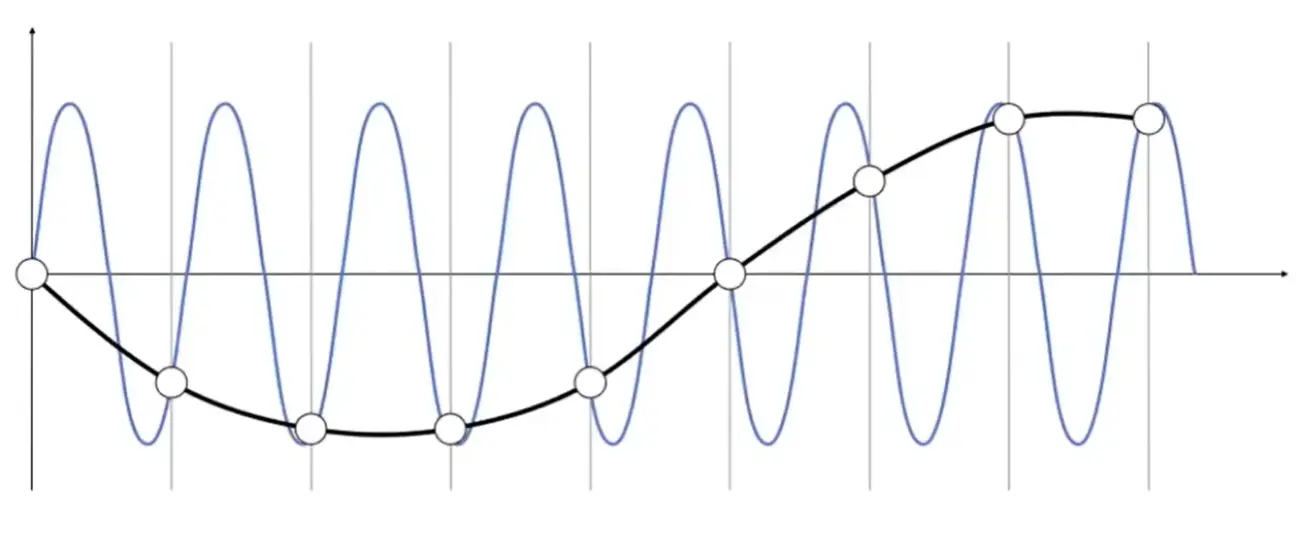
高频信号经过 undersampling 得到的结果失真(和某种低频信号产生相同的结果)
Filtering#
about high/low freq.#
= Getting rid of certain freq. contents 去掉一系列频率
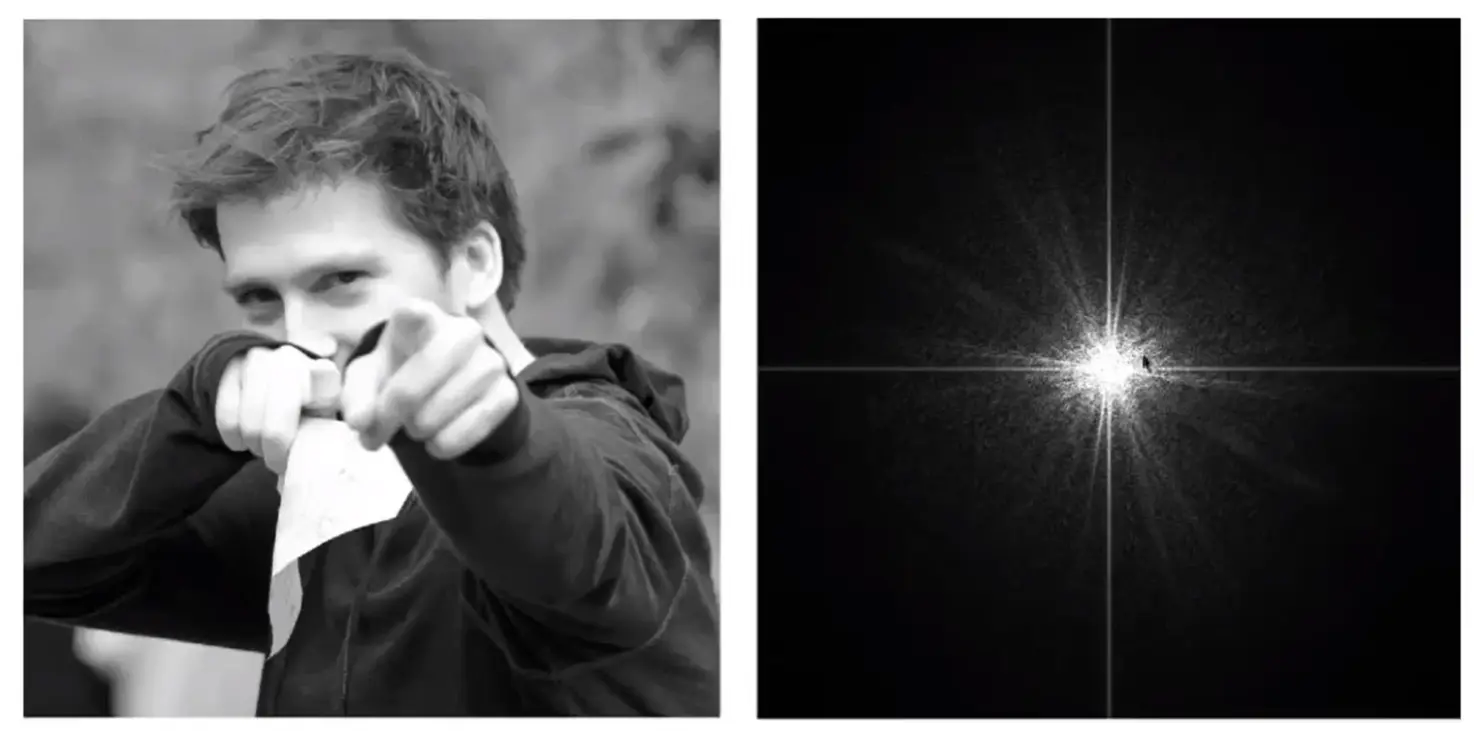

右侧是频域可视化
- 中间为低频,说明低频信息比较丰富
- 可以忽略水平和竖直的两条线
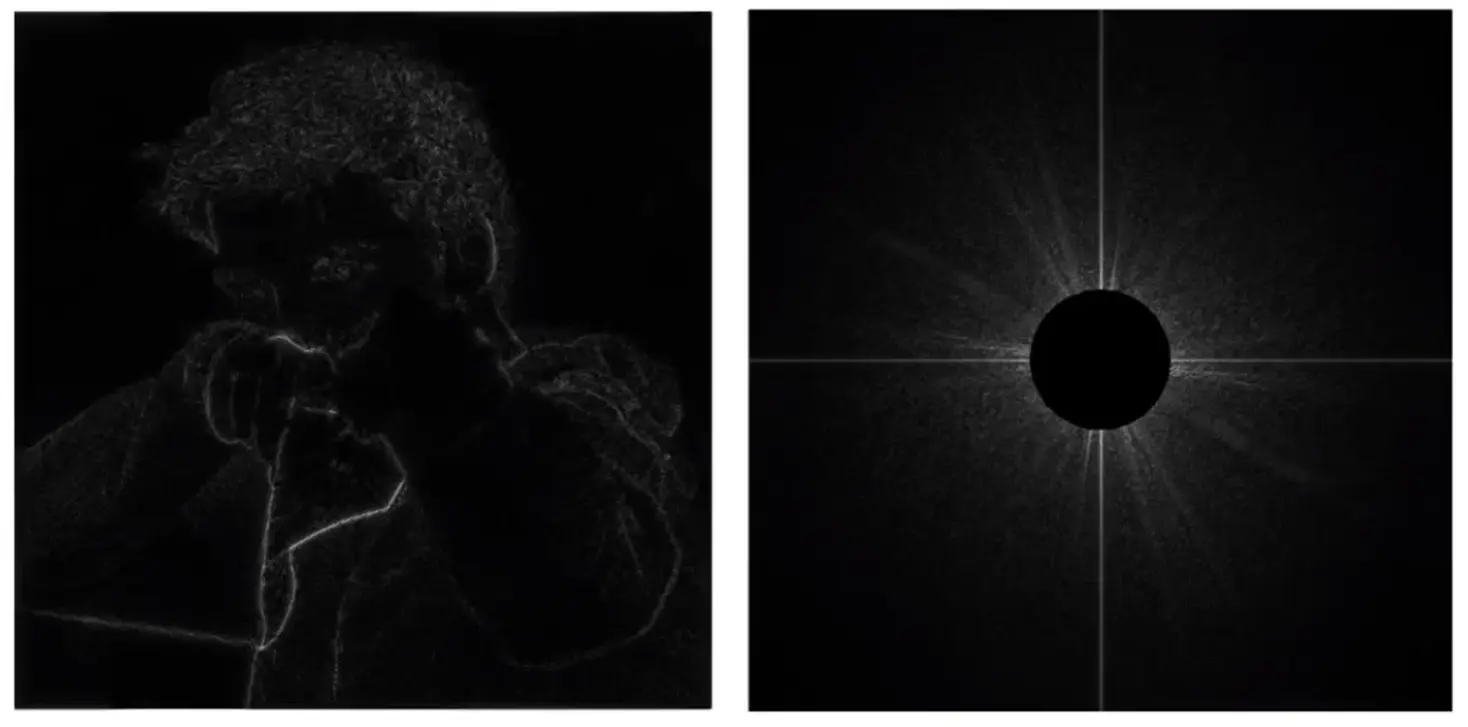
Note
- 高频信息对应图像的边界
- 低频信息对应图像内部平滑的部分
with convolution#
= Average = Convolution
- Convolution in the spactial domain is equal to multiplication in the freq. domain, and vice versa
- option1: filter by convolution in spatial doamin
- option2:
- transform to freq. domain (Fourier)
- multiply by Fourier transform of convolution kernel
- transform back to spatial domain (inverse Fourier)
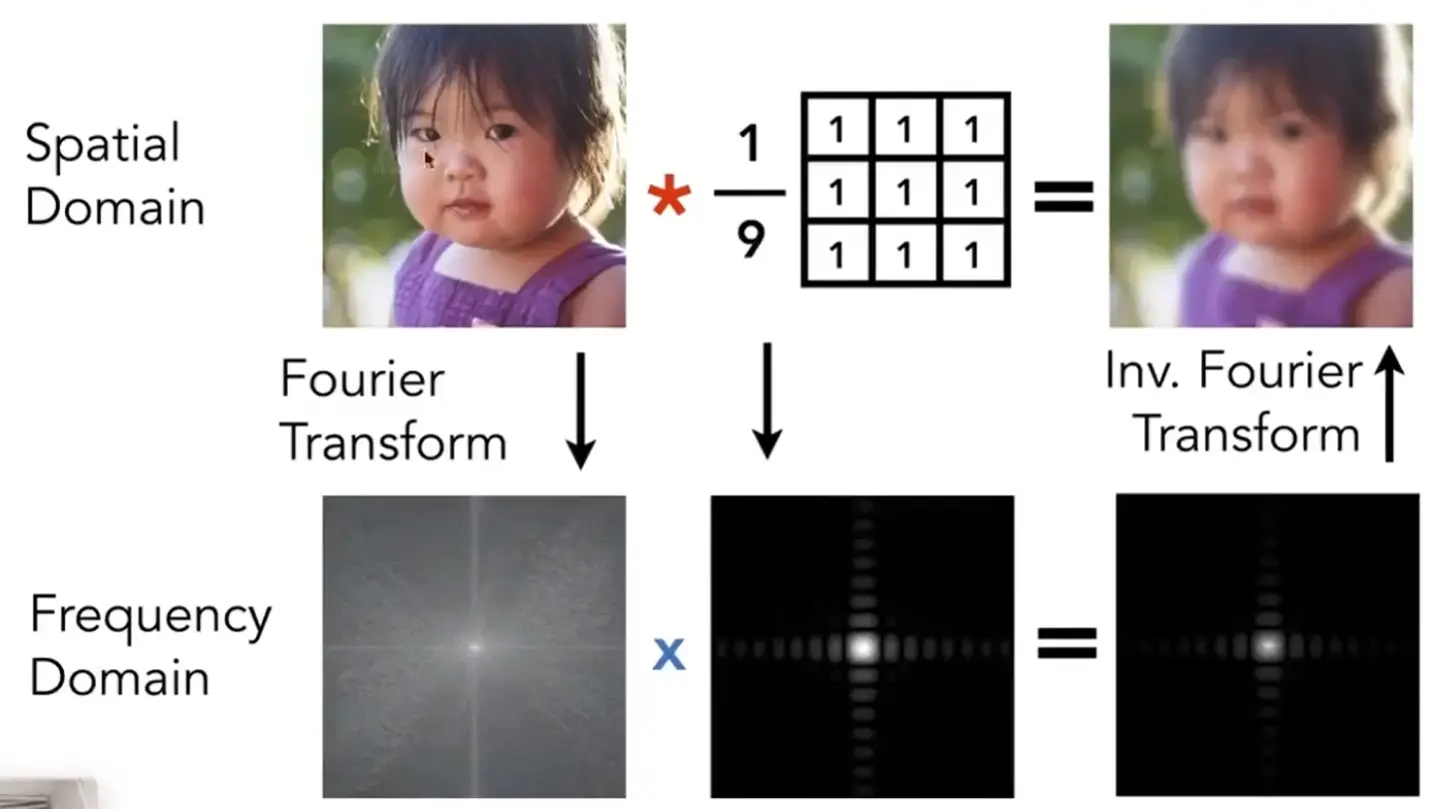

Note
卷积核越大,得到的图像越平滑,频域越低
Sampling#
= repeating freq. contents,就是在复制
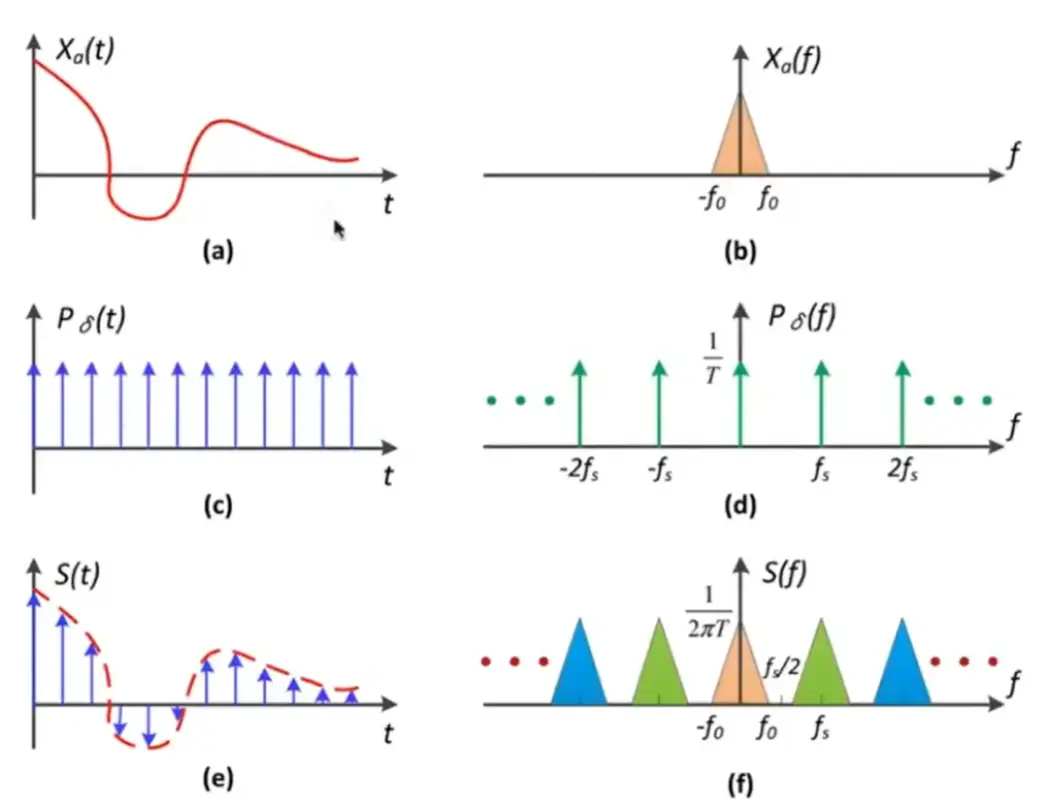
Note
- 左图中的箭头是冲击函数,对应采样点
- 频域上的来看就是卷积,将原有的频谱复制了很多份
- 时域上的乘积对应频域上的卷积
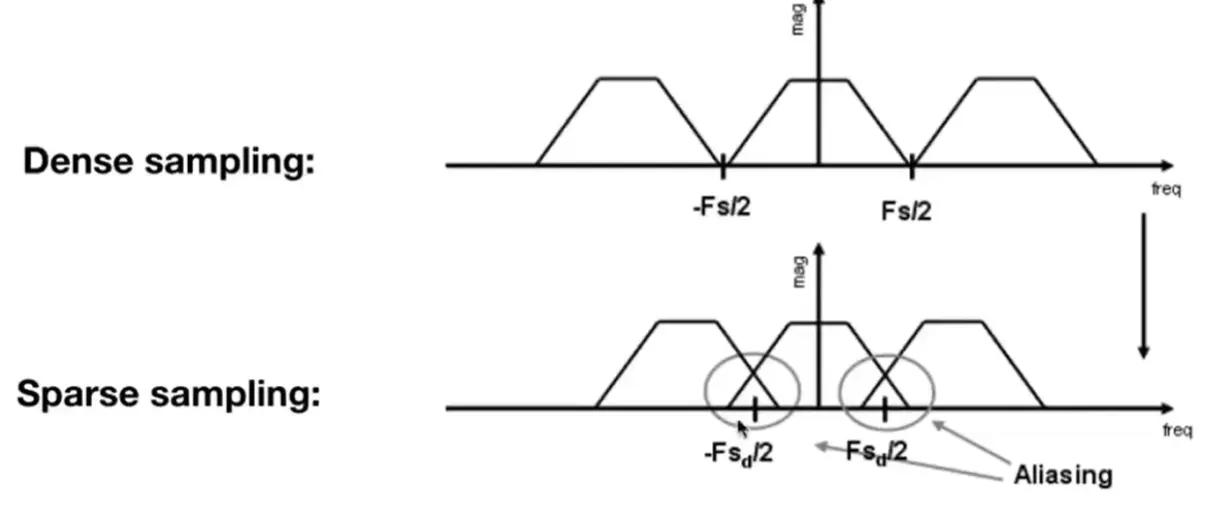
Note
- 采样越稀疏,频谱越密集,会产生混叠,导致 aliasing
Antialiasing#
- option1: 提高采样率 costly
- option2: antialiasing
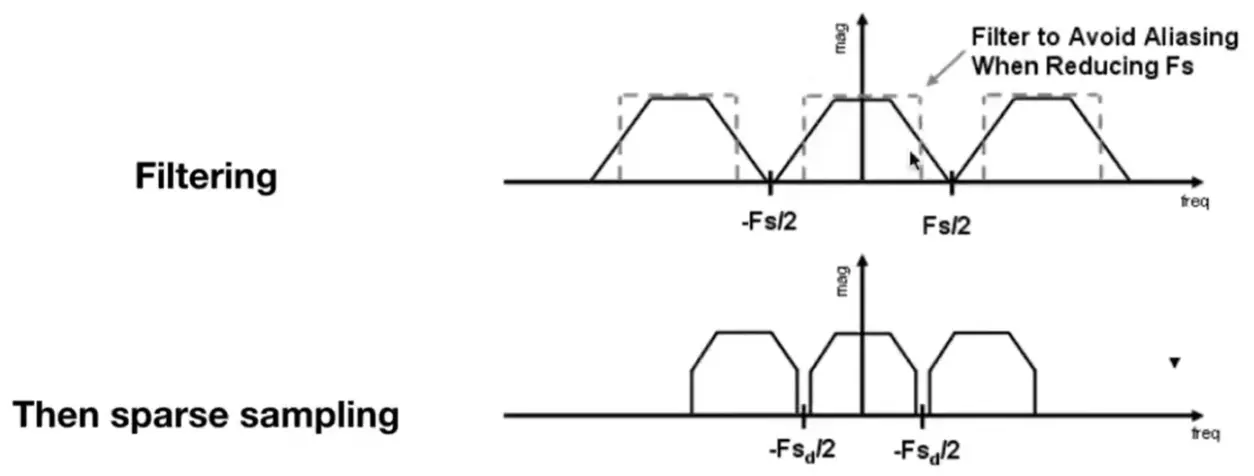
Note
减少高频信号,在采样率低时也不会产生混叠
solution: computing average pixel value#
- convolve: 每个像素取平均值
- sampling: 对每个像素中心进行采样
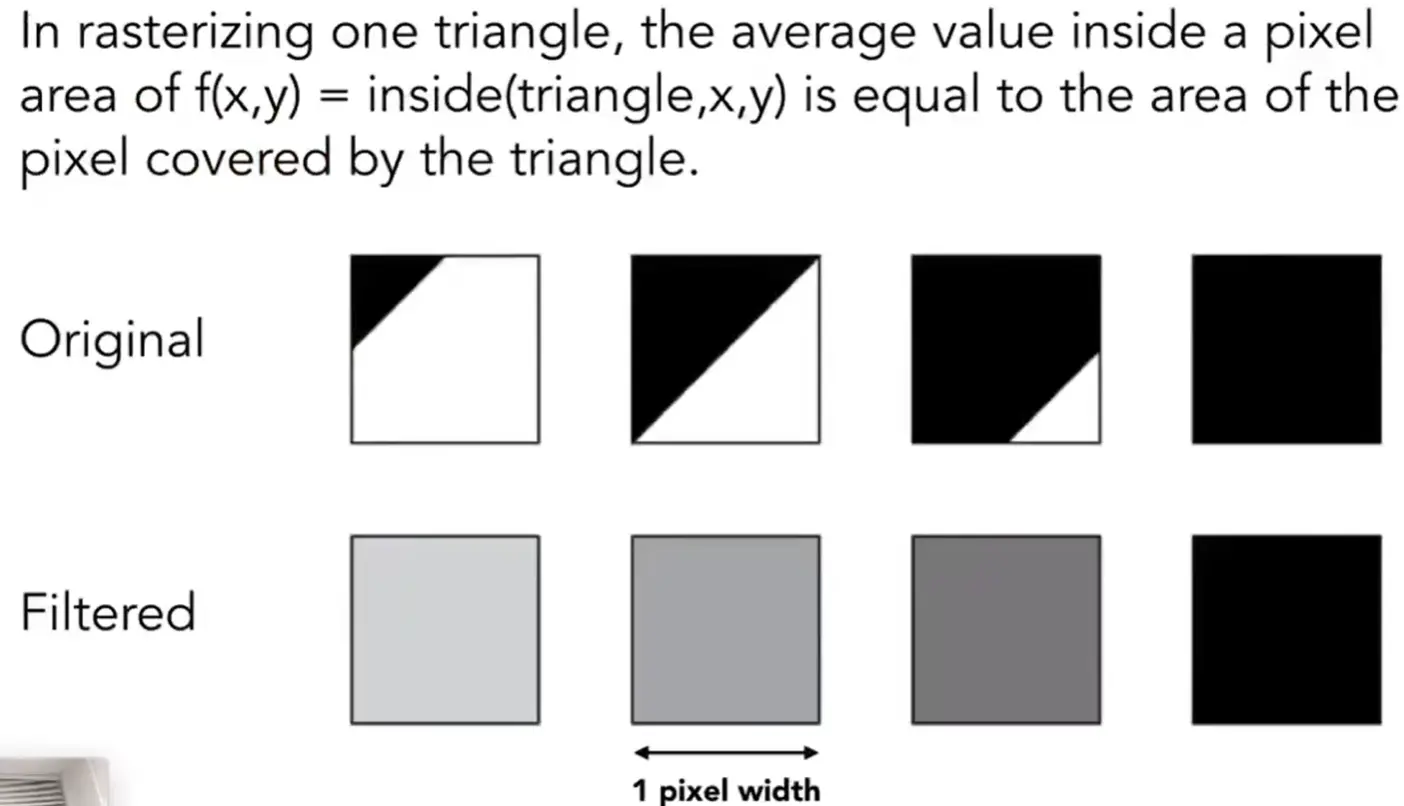
practice: by supersampling (MSAA)#
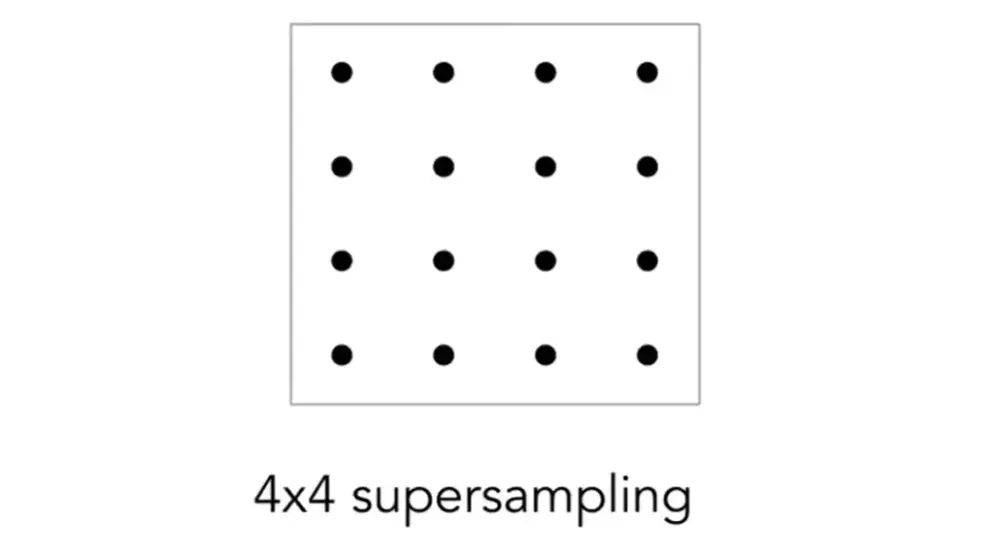
- 每个像素内部选多个采样点,并取平均
Antialiasing today#
- 使用不规则采样点分布来减少计算量
- 其他的抗锯齿方法
- FXAA(Fast Approximate AA) 将有锯齿边替换为无锯齿边
- TAA(Temporal AA) 复用上一帧的结果
- 超分辨率 super resolution
- resolution low to high,会导致锯齿
- DLSS(Deep Learning Super Sampling)
Visibility/Z-Buffering#
Painter's Algorithm#
- 先画出远的物体,再画出近的物体
-
不需要考虑遮挡关系,\(O(n\log n)\)
-
可能无法进行排序互相遮挡
Z-Buffer 深度缓冲#
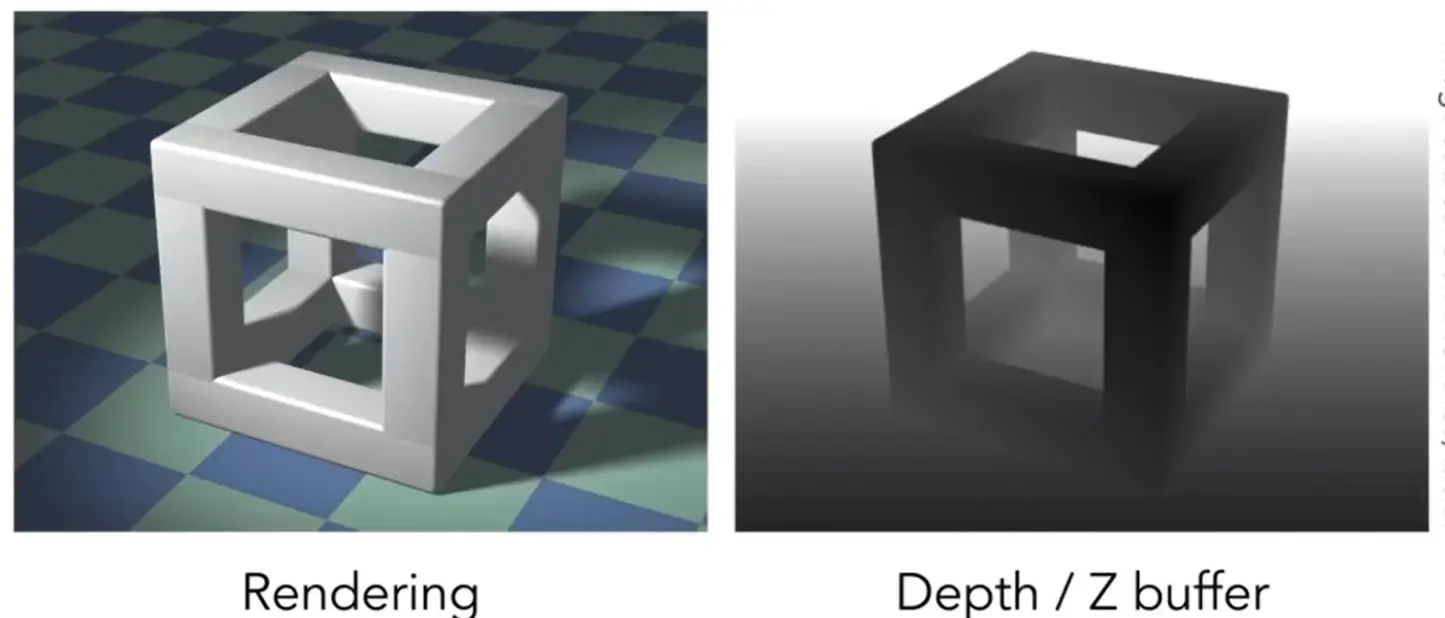
保存一个像素当前最浅的深度
For simplicity we suppose
- z is always positive
- smaller z -> closer
| z-buffering | |
|---|---|
- \(O(n)\)
- 不同顺序绘制的结果是一样的
- 在 GPU 中硬件实现
-
透明物体不适用
Shadows#
Shadow Mapping#
如果视野中的一个点能被光源看到,那么就有光照
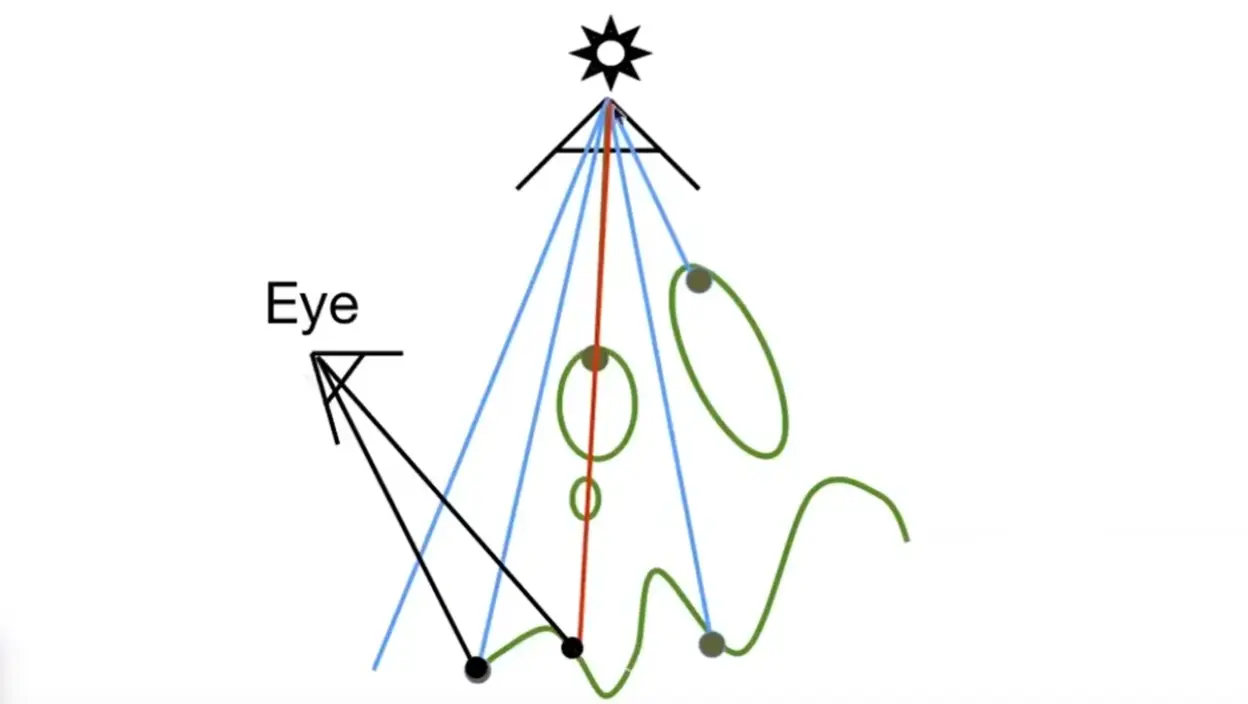
method
- 光源视角下记录深度图
- 对于相机看到的一个像素点,映射到光源的深度图上,如果像素到光源的距离和深度图的深度一致,那么被照亮
problems
- 浮点数相等的判断有精度问题,需要允许一个小的 bias,但也不能从根本上解决问题
- 光源深度图的分辨率不能太小,否则会形成锯齿
- 开销很大,需要渲染两遍
Hard Shadow v.s. Soft Shadow#
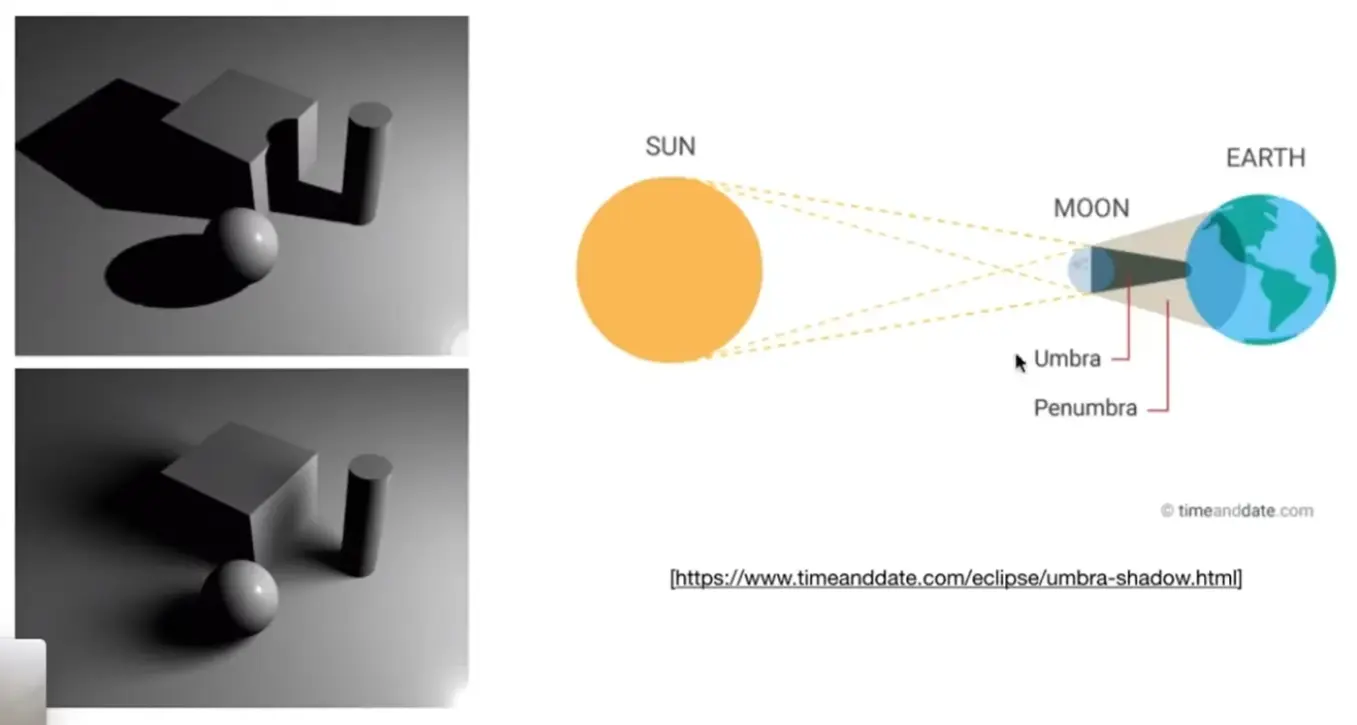
因为光源有一定大小