08 Dynamic Programming
1 Fibonacci Numbers#
\(F(N)=F(N-1)+F(N-2)\)
- trouble-maker:如果使用递归,那么一共要遍历 \(O(F(N))\) 个节点,这个复杂度是指数级的
- Solution:循环代替递归
| Fibnocci Number (iter ver) | |
|---|---|
这样,时间复杂度就变成了 \(T(N)=O(N)\)
2 Ordering Matrix Multiplications#
Question
一系列矩阵相乘时,不同的结合顺序开销不同,如

试图找到最优的结合方法?
2.1 定义问题规模#
Let \(b_{n}=\) the number of differrent ways to compute \(M_{1},M_{2},\dots M_{n}\), we have \(b_{2}=1, b_{3}=2, b_{4}=5 \dots\)
每个 \(n\) 问题,都可以拆分成两个较小的部分,且有不同的拆分方法 \(b_{n}=\sum_{i=1}^{n-1}b_{i}b_{n-i}\)
这里的 \(b_n\) 就是 Catalan number,渐进表达为 \(b_{n}=O(\frac{4^n}{n \sqrt{ n }})\)
2.2 Solution#
这里的 \(M\) 序列顺序不可调换,设 \(m_{i,j}\) 为解决 \(M_i\times M_{i+1}\times\dots \times M_{j}\) 的最小乘法次数,\(M_i\) 的形状为 \(r_{i-1}\times r_{i}\),那么递推式为:
也就是,考虑分割成的子序列中原有计算开销 \(m_{i,j}+m_{l+1,j}\) 以及合并开销 \(r_{i-1}r_{l}r_{j}\) 之和最小的,这样,如果子问题的解是最优的,一定能够保证 \(m_{i,j}\) 是最优的。
显然,\(T(N)=O(N^3)\)
3 Optimal Binary Search Tree#
Question
静态 BST,考虑搜索总开销为 \(T(N)=\sum_{i=1}^Np_{i}(1+d_{i})\),其中,\(p_i\) 是 \(Key_{i}\) 的搜索频率,\(d_i\) 是 \(Key_{i}\) 的深度。
如何找到最佳的树结构?显然,任何平衡树都不一定是最佳的
3.1 Solution#
首先假设 \(Key\) 已经按照升序排列好,令 \(c_{i,j}\) 表示 \(Key_{i}, Key_{i+1}, \dots Key_{j}\) 组成的最佳树结构的开销,用 \(w_{i,j}\) 表示 \(\sum_{k=i}^jp_{k}\),如果在 \(c_{{i,j}}\) 中选择 \(Key_{k}\) 为根,则:
那么显然就能得到递推公式:
3.2 Complexity#
显然要进行一个三角阵遍历,而且每个 entry 都是 \(O(N)\) 的,\(T(N)=O(N^3)\)
3.3 An \(O(N^2)\) algorithm#
introduction to algorithm 10.33 p.419 ?
4 All-Pairs Shortest Path#
Question
For all pairs of \(v_i\) and \(v_{j}\) (\(i\neq j\)), find the shortest path between.
4.1 Method 1: Dijkstra#
Single-source for \(|V|\) times,每一次就能找到一个点到所有点的最短距离
- 若使用简单数组,一次要 \(O(|V|^2)\),\(T=O(|V|^3)\),对于稀疏图很快
- 若使用堆,一次要 \(O((|V|+|E|)\log|V|)\),\(T=O(|V|(|V|+|E|)\log|V|)\)
4.2 Method 2: Floyd#
4.2.1 Definition#
- 定义 \(D^k[i][j]=min\{\text{length of path }i\to\{l\leq k\}\to j\}\),意思是从 \(v_{i}\) 经过中间节点集合 \(\{v_{m}|\,0\leq m\leq k\}\) 到达 \(v_{j}\) 的最短路径长度
- 定义 \(D^{-1}[i][j]=cost[i][j]\) 为初始情况:如果 \((v_{i},v_{j}) \in E\),那么初始化为这条边的长度;反之,初始化为 \(+\infty\)
- 于是,\(v_i\) 到 \(v_j\) 的最短路径长一定等于 \(D^{N-1}[i][j]\)
4.2.2 Solution#
从 \(D^{-1}\) 开始逐步计算得到 \(D^{N-1}\),假设 \(D^{k-1}\) 已经得到,那么如果通过 \(v_k\) 的路径更短,则更新最短路径长度:
\(T(N)=O(N^3)\), where \(N\) is the number of vertices.
适用范围
- 能够处理负的权重
- 无法处理负权重环
5 Product Assembly#
Question
- 两条生产线
- 每个 stage 使用了不同的技术,因此有不同的时间开销
- 部件可以在 stage 之间更换生产线
- 求最小的组装时间?
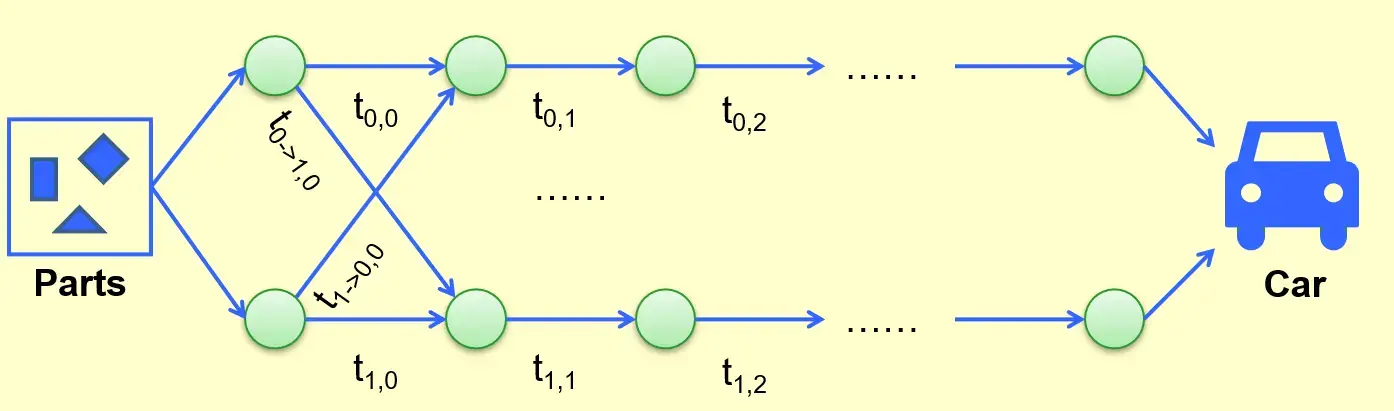
- Characterize an optimal solution
- 首先分析,显然最优解中一定含有子问题最优解
- Recursively define the optimal values
- 到 \(stage\) 的最优解取决于到 \(stage-1\) 的最优解
f[line][stage] = min(f[line][stage-1] + t_process[line][stage-1],f[1-line][stage-1] + t_transit[1-line][stage-1]);
- Compute the values in some order
- 显然,因为是线性的,只需要遍历 stage 维度,每次都更新 line 维度就好
- \(O(N)\text{ time }+O(N)\text{ space}\)
- Reconstruct the solving strategy
- 需要另一个数组来存放一个路径
6 Conclusion#
如何设计 DP 算法
- 找到一种符合题意的部分最优解
- 找到递推式、初始条件
- 按照合适的顺序计算最优解目标函数
- 重构最优解
7 Discussion %% fold %%#
Question
A palindrome is a nonempty string over some alphabet that reads the same forward and backward. Examples: civic, racecar, and aibohphobia (fear of palindromes).
Give an efficient algorithm to find the longest palindrome that is a subsequence of a given input string. For example, given the input character, your algorithm should return carac.
Notice the subsequence does not have to be consecutive.
8 Questions#
8.1 Q8#
8.1.1 Optimal BST's Root#
The root of an optimal binary search tree always contains the key with the highest search probability. (T/F)
Answer
F
完全不一定,例如 aaaaa 也可能是频率最高的词,但是会导致树非常不平衡,从而不是最优解
但是在 Huffman Coding 中可以这样贪心求解
8.2 HW8#
8.2.1 dp 遍历顺序问题#
Given a recurrence equation \(f_{i,j,k}=f_{i,j+1,k}+\min_{0\leq l\leq k} \{f_{i−1,j,l}+w_{j,l}\}\). To solve this equation in an iterative way, we cannot fill up a table as follows:
A. for k in 0 to n: for i in 0 to n: for j in n to 0
B. for i in 0 to n: for j in 0 to n: for k in 0 to n
C. for i in 0 to n: for j in n to 0: for k in n to 0
D. for i in 0 to n: for j in n to 0: for k in 0 to n
Answer
B 关键在于 \(j\) 依赖于 \(j+1\),所以一定不能出现 for j in 0 to n
8.2.2 Programming Contest#
Question
Bob will participate in a programming contest. There are altogether n problems in the contest. Unlike in PAT (Programming Ability Test), in a programming contest one can not obtain partial scores. For problem i, Bob will need time[i] to solve it and obtains the corresponding score[i], or he may choose not to solve it at all. Bob will be happy when he obtains a total score no less than happy_score. You are supposed to find the minimum time needed for Bob to be happy. The function need_time must return the minimum time, or -1 if it is impossible for Bob to obtain a score no less than happy_score.
Format of function
Here n (1≤n≤ MAXN) is the number of problems;
happy_score (1≤ happy_score ≤ MAXS) is the minimum score for Bob to be happy;
time[] is the array to store time[i] (1≤time[i]≤100) which is the time to solve problem i;
score[] is the array to store score[i] (1≤score[i]≤100) which is the score Bob gets for solving problem i.
Sample program of judge
Sample Input
Sample Output
8.2.2.1 View 1 %% fold %%#
A naive solution
- 设
dp[i]为得到i分的最小耗时,是 一维动态规划问题 - 对于
dp[i]遍历所有题目,计算上一个分数i-score[j]- 如果
i-score[j] < 0,那么dp[i] = min(dp[i], time[j] - 如果
i-score[j] >= 0,而且j在dp[i-scorep[j]]中没有标记完成,那么dp[i] = min(dp[i], dp[i-score[j]] + time[j])
- 如果
- 所以,还需要一张
happy_score * n的布尔表,来标记每个分数最好情况下做过的题目
上面的 solution 虽然能够 AC,但是复杂度太高了,因为要记录做过哪些题目,但是,如果换做按照题目遍历,就不用这么麻烦了
A better solution
- 定义
dp[i]为恰好获得i分的最小耗时 - 对于所有题目
problemIdx- 从
MAXS到score[prbIdx],更新得到此分数的最短用时dp[thisScore] = min(dp[thisScore], dp[thisScore - score[prbIdx]] + time[prbIdx]) - 倒着遍历,就不需要考虑这道题目是否在子问题中被选中做过,因为
dp[thisScore - score[proIdx]]还没有来得及被更新
- 从
8.2.2.2 View 2#
- \(dp[i]\) 是达到 \(i\) 分数的最小时间
- 遍历所有题目,每次,对于每个题目,对于每个总分,向前搜索未做题目的总分
- 由于是从地址低的位置向高的位置写入,必须使用逆序
- 最后,满足题意的是,达到
>=happy_score的某个分数的最短时间,找到输出即可
8.3 Midterm Review#
8.3.1 dp 的指数复杂度#
If a problem can be solved by dynamic programming, it must be solved in polynomial time. (T/F)
Answer
F 虽然动态规划能够将问题限制在一个张量所有 entry 的遍历中,但是这个张量的规模可能是指数级的,一个有意思的例子是动态规划版本的 TSP,使用 Held-Karp 算法:
GPT 的解释
旅行商问题(TSP)的动态规划解法通常使用 Held-Karp 算法,其时间复杂度为 \(O(n^2 \cdot 2^n)\)。以下是对这一复杂度的详细解释:
问题描述
旅行商问题要求找到一条最短路径,使得每个城市都被访问一次,并最终返回到起始城市。假设有 \(n\) 个城市。
动态规划解法
- 状态定义:
- 用 \(dp[S][j]\) 表示从起始城市出发,经过一组城市 \(S\)(其中 \(S\) 包含城市 \(j\)),最终到达城市 \(j\) 的最短路径长度。
- \(S\) 是一个集合,包含了当前访问的城市。
-
- 对于每个可能的城市集合 \(S\) 和每个城市 \(j\):
状态转移:
$$ dp[S][j] = \min_{i \in S, i \neq j}(dp[S - {j}][i] + d(i, j)) \(\(<br>这里,\)d(i, j)\) 是城市 \(i\) 到城市 \(j\) 的距离。
- 对于每个可能的城市集合 \(S\) 和每个城市 \(j\):
- 状态数:
- 集合 \(S\) 的数量是 \(2^n\),因为每个城市可以在集合中或不在集合中(总共有 \(n\) 个城市)。
- 对于每个集合 \(S\),需要遍历所有可能的目标城市 \(j\),共有 \(n\) 个城市。
- 复杂度计算:
- 由于我们需要填充一个大小为 \(2^n\) 的表格(每个集合对应一个状态),而对于每个状态需要遍历 \(n\) 个城市来计算最短路径,因此总的时间复杂度为:
$$ O(n^2 \cdot 2^n) $$
结论
因此,旅行商问题的动态规划版本由于需要处理所有可能的城市组合和每个组合中的所有城市,导致其复杂度为 \(O(n^2 \cdot 2^n)\)。这种复杂度在城市数量 \(n\) 较大时,计算量会迅速增加,表现出指数级的增长。