04 Leftistf Heaps and Skew Heaps
1 Intro#
- Leftist heaps -> AVL 依靠规则维持平衡
- Skew heaps -> splay 依靠随机性维持平衡
1.1 Heaps#
- definition
- almost complete binary tree
- Max/min heap
- implementation
- array representation
- operations
- findMin
- insert
- deleteMin
- createHeap
- heapify
- merge(meld)
1.2 how to merge bin-heap?#
- 最快也是 \(O(N_1+N_2)\),也就是直接合并然后建堆
- 为了更快地合并堆,需要引入 Leftist Heap
2 Leftist Heaps#
Target
Speed up merging to \(O(\log N)\)
- order property - same as bin heap
- structure property - binary tree, but unbalanced
2.1 Null Path Length 零路径长#
\(Definition\): The null path length, \(Npl(x)\), of any node X is the length of the shortest path from x to a node without 2 children. Define \(Npl(NULL)=-1\)
\(Definition\): The leftist heap property is that for every node X in the heap, the null path length of the left child is at least as large as that of the right child.
\(Property\): Leftisit Heaps 的右路径节点数 \(\le \lfloor \log(N+1) \rfloor\)。
换一种说法就是,右路径上有 \(r\) 个节点的 Leftist Heaps 至少有 \(2^r-1\) 个节点。
Hint
We can perform all the work on the right path, which is guaranteed to be short.
2.2 Merge#
| Declaration | |
|---|---|
2.2.1 Recursive version#
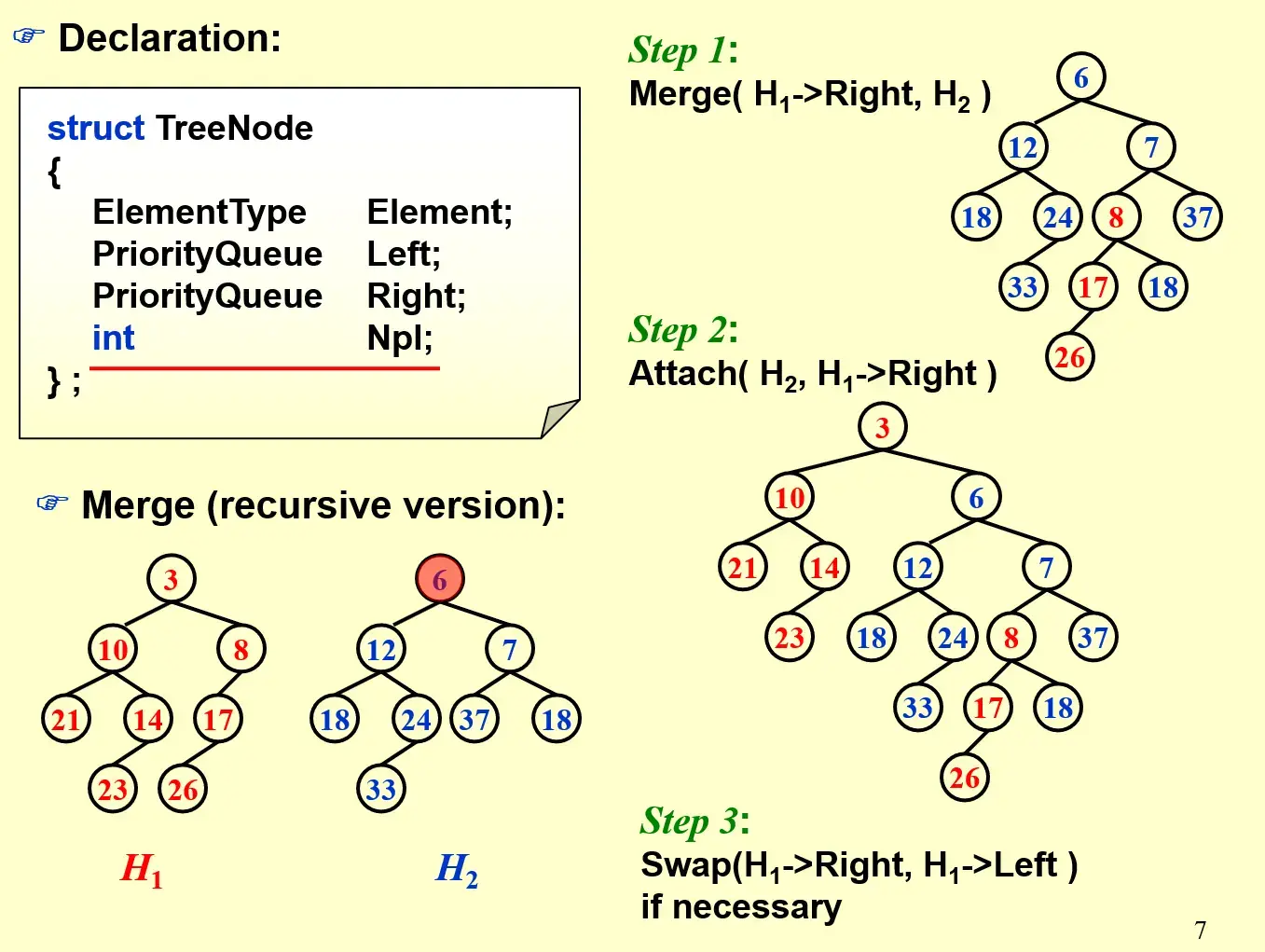
进行如下递归的操作 Merge
- Merge 两个根,本质上是选择一个子树,然后 call merge 剩余部分
- 进行 attach,更新子树
- 根据
Npl,检查是否需要交换
关于 if (H1->=Left == NULL) H1->Left = H2;
如果其中一个堆已经没有左孩子了,那么根据 \(Npl\),它一定没有右孩子,这时候为了维护 \(Npl\) 只需要将另一个堆当作其左孩子
2.2.2 Iterative version#
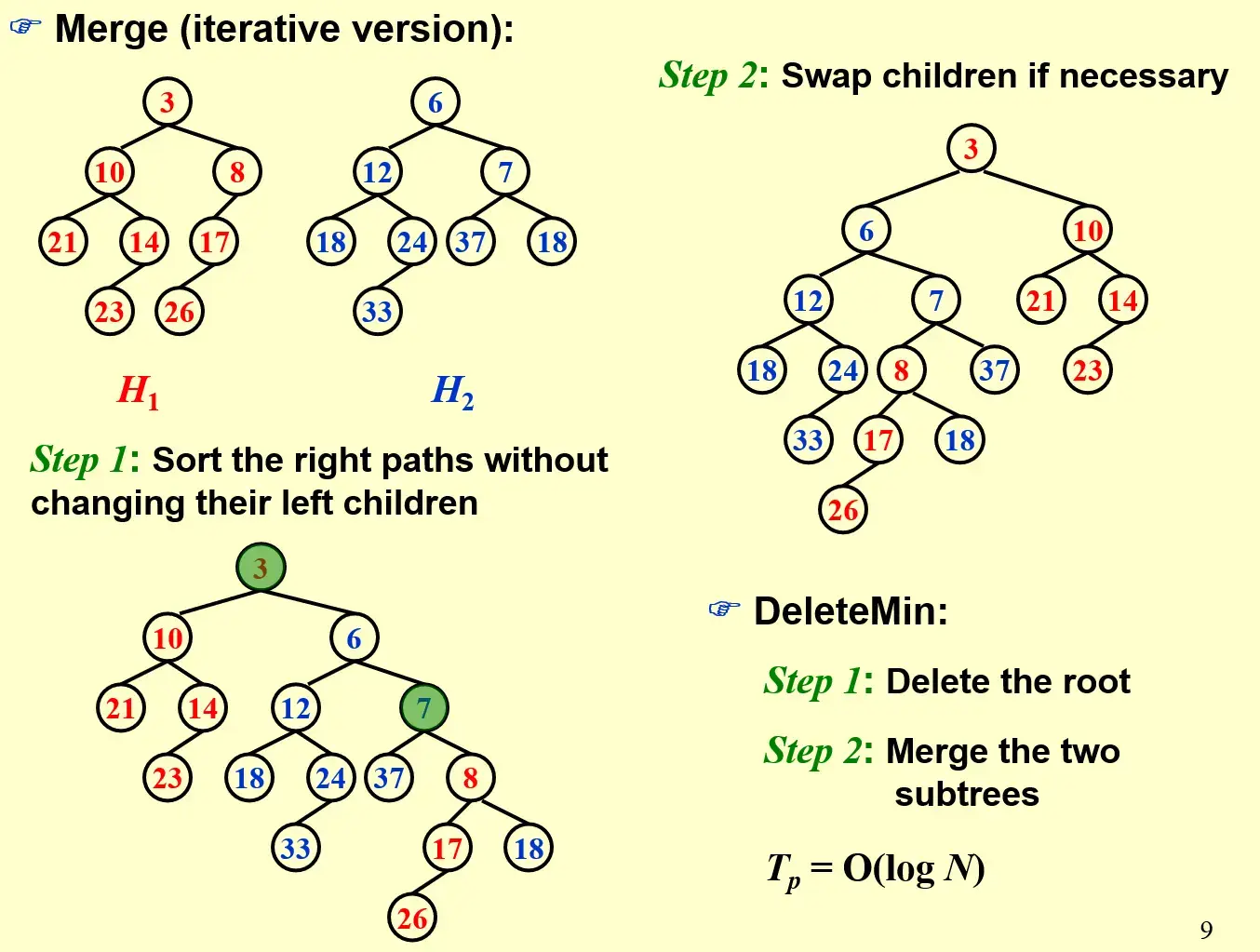
- 按照右路经排序(链表的合并)
- 沿着右路径从下往上检查是否需要交换
2.2.3 Conclusion#
由于都是沿着右路经的操作,所以 \(T(N)=O(\log N)\)
2.3 DeleteMin#
- 删除根节点
- 合并剩下的两个子树
3 Skew Heaps#
a simple version of the leftist heaps
Target
Any \(M\) consecutive operations take at most \(O(M \log N)\) time.
3.1 Merge#
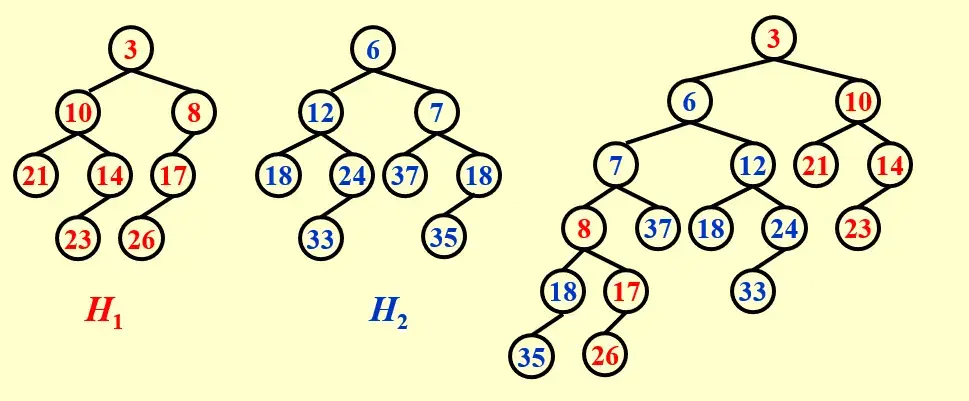
Always swap the left and right children except that the largest of all the nodes on the right paths does not have its children swapped. 始终交换左子树和右子树,除了在右路径上最大的节点不交换其子节点。
Note
- Skep Heap 的优势在于,无需多余的空间来记录路径长, 无需判断是否需要交换孩子
- It is an open problem to determine precisely the expected right path length of both leftist and skep heaps.
Attention
- 必须完整遍历右路径,即使一个堆已经空了也需要遍历另一个堆余下的右路经,以此保证进行交换
- 最后一个合并的节点,其一定没有右孩子,且不进行子树交换
3.2 Amortized Analysis for Skew Heaps#
Question
\(T_{amortized}=O(\log N)\) ?
- \(D_{i}=\) the root of the resulting tree
- \(\Phi(D_{i})=\) number of heavy nodes
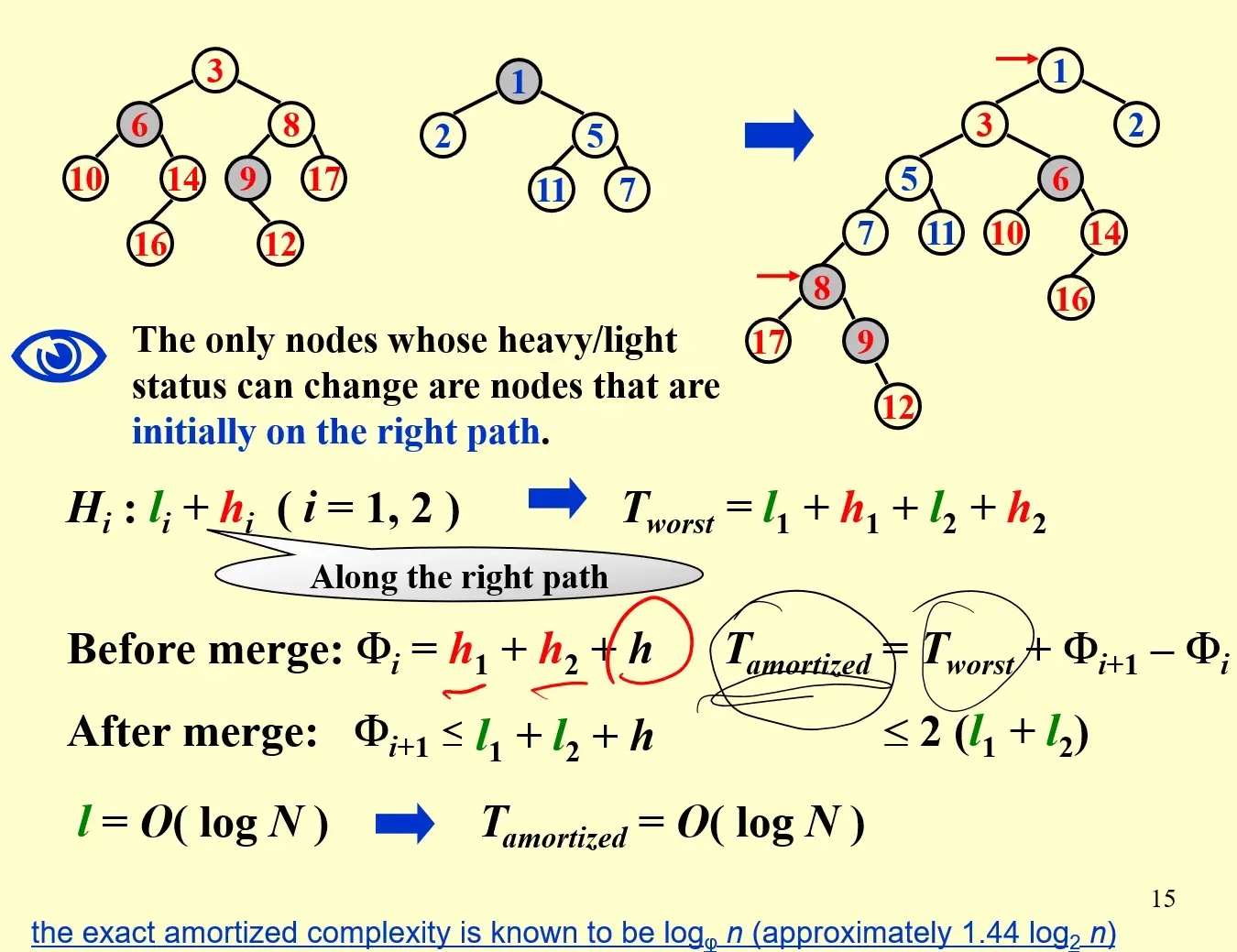
\(definition\): 某一节点的后代(包括自己)中,其右子树内的大于等于一半,则其为 heavy node,反之为 light。也就是 \(R\geq \frac{L+R+1}{2}\)
Important
每次合并,只有原本在右路经上的节点才有机会改变轻重状态
考虑 \(H_{i}\) 的右路经上有 \(l_i\) 个轻节点,\(h_i\) 个重节点,合并的最坏情况就是遍历了两个右路径
令两棵树中右路径除外的节点中还有 \(h\) 个不会改变的重节点,则 merge 之前有
Merge 后,由于 heavy 一定变成 light,light 可能变成 heavy1
所以
又 \(l=O(\log N)\),因此 \(T_{amortized}=O(\log N)\)
4 Conclusion#
| Operation | FindMin | DeleteMin | Insert | DecreaseKey | Merge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binary | \(\Theta(1)\) | \(\Theta(\log n)\) | BuildHeap in \(O(n)\) | \(O(\log n)\) | \(\Theta(n)\) |
| Leftist Heap | \(\Theta(1)\) | \(\Theta(\log n)\) | \(\Theta(\log n)\) | \(O(\log n)\) | \(\Theta(\log n)\) |
| Skew Heap | \(\Theta(1)\) | \(\Theta(\log n)\) | \(\Theta(\log n)\) * | \(O(\log n)\)* | \(\Theta(\log n)\)* |
*is amortized time.
5 Questions#
5.1 Q4#
A leftist heap with the null path length of the root being r must have at least \(2^{r+1}-1\) nodes. (T/F)
Answer
T 由于 \(Npl(x)=min\{Npl(x.left), Npl(x.right)\}+1\),如果 \(Npl(root)=r\),那么意味着不存在小于 \(r\) 的 shorter path,极端情况是高为 \(r\) 的满二叉树,最少有 \(2^{r+1}-1\) 个节点 注意与 右路经上有 \(r\) 个节点,则 Leftist Heap 至少有 \(2^r-1\) 个节点 区分
5.2 HW4#
5.2.1 Skew Heap 插入自然数#
The result of inserting keys 1 to \(2^k-1\) for any \(k>4\) in order into an initially empty skew heap is always a full binary tree.
Answer
T,MinHeap 也是这样的
5.2.2 Leftist Heap Build#
We can perform BuildHeap for leftist heaps by considering each element as a one-node leftist heap, placing all these heaps on a queue, and performing the following step: Until only one heap is on the queue, dequeue two heaps, merge them, and enqueue the result. Which one of the following statements is FALSE?
- A. in the \(k\)-th run, \(\lceil N/2^k \rceil\) leftist heaps are formed, each contains \(2^k\) nodes
- B. the worst case is when \(N=2^K\) for some integer \(K\)
- C. the time complexity \(T(N)=O(\frac{N}{2}\log 2^0+\frac{N}{2^2}\log 2^1 + \frac{N}{2^3}\log 2^2+\dots+\frac{N}{2^K}\log 2^{K-1})\) for some integer \(K\) so that \(N=2^K\)
- D. the worst case time complexity of this algorithm is \(\Theta(N\log N)\)
Answer
D
- A. 可能错误,错误点在于 \(2^k\) 过于绝对,但如果指的是渐进就对了
- B. 可能是因为刚刚好形成完美配对?
- C. 如果 \(N=2^k\),那么第 \(r\) 次 run 有 \(N/2^r\) 个堆需要合并,每个合并的复杂度是 \(\log size(heap)=\log 2^r=r\)
- D. 建堆算法一定是线性的,从 C 也可以得出 \(\Theta(N)\),因为 \(\sum_{i=1}^K \frac{i-1}{2^i}\) 的结果是常数
5.3 Ex4#
5.3.1 Skew Heaps Merge#
Merge the two skew heaps in the following figure. How many of the following statements is/are FALSE?
- the null path length of 8 is the same as that of 12
- 40 is the left child of 18
- the depths of 18 and 33 are the same
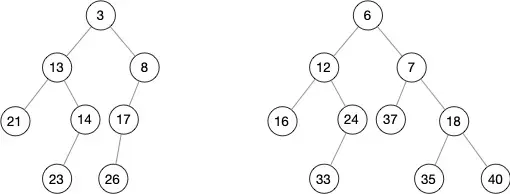
Answer
0 注意参考 3.1 Merge 中的说法,即使一个堆空了,另一个堆的右路经也是要进行遍历交换的,所以最后 35 是 18 的右孩子,40 是左孩子
5.3.2 Analyzing Self-Adjusting Structures#
In typical applications of data structures, it is not a single operation that is performed, but rather a sequence of operations, and the relevant complexity measure is not the time taken by one operation but the total time of a sequence. Hence instead of imposing any explicit structural constraint, we allow the data structure to be in an arbitrary state, and we design the access and update algorithms to adjust the structure in a simple, uniform way, so that the efficiency of future operations is improved. We call such a data structure self-adjusting. For example skew heaps and splay trees are such kind of structures.
Which one of the following statements is FALSE about self-adjusting data structures?
- A. They need less space, since no balance information is kept.
- B. Their access and update algorithms are easy to understand and to implement.
- C. In an amortized sense, ignoring constant factors, they can be at least as efficient as balanced structures.
- D. Less local adjustments take place than in the corresponding balanced structures, especially during accesses.
Answer
D
- A. 确实,由于不存储 \(Npl\),\(BF\) 等辅助信息
- B. trivial
- C. trivial
- D. 自平衡结构正是依靠局部调整来实现 amortized 意义上的高效,而 balanced 由于可以依赖辅助信息,局部调整只在违反了性质时进行
5.4 Midterm Review#
5.4.1 Right path length of Skep Heaps#
The right path of a skew heap can be arbitrarily long. (T/F)
Answer
T
5.4.2 Which is more balanced?#
With the same operations, the resulting skew heap is always more balanced than the leftist heap. (T/F)
Answer
F skew heap 更不平衡的例子可以很容易举出;从另一个角度想,leftist 由于有平衡约束条件,肯定在更多情况下比随机的更加平衡
5.5 Midterm#
5.5.1 Heavy Nodes?#
Consider the following merge algorithm for skew heaps. A merge is perfomed using a simple routine: merging two skew heaps A and B, if the top of A is less than or equal to the top of B, A becomes the skew heap, its children are swapped and B is merged with the left sub-heap of the root of A. If the left sub-heap is empty, B is assigned to the left sub-heap of A.
A node p is heavy if the number of descendants of p’s right subtree is at least half of the number of descendants of p, and light otherwise.
The potential function is defined to be the number of heavy nodes. Let heap A and heap B be a n-node tree.
Which of the following is FALSE?
- A. There are at most \(O(\log n)\) light nodes in the right path of a n-node tree.
- B. The amortized running time of merge is \(O(\log n)\).
- C. The only nodes whose heavy/light status can change are nodes that are initially on the right path.
- D. All heavy nodes in the right path of A and B will become the light nodes after merging.
Answer
D 这题不应该出的,这里修改了 skew heap 合并的定义了,如果按照正确的定义,所有右路经上的节点都会进行 swap children,这样所有的 heavy nodes 都会变成 light,否则就无法进行复杂度证明