02 Red-Black Trees and B+ Trees
1 Red-Black Trees#
Target: balanced BST
1.1 Definition#
- 每个节点红或黑
- 根是黑色
- 每个叶子(NIL)都是黑色,NIL 是一个共享的没有 key 的叶子节点
- 红色节点的两个孩子都是黑色,不能有两个连续的红色节点
- 每个节点到叶子的路径上黑色节点数量相同,same black height
Attention
- Black height 计算时不算自己,算 NIL
- 所有有 key 的节点都是 internal node
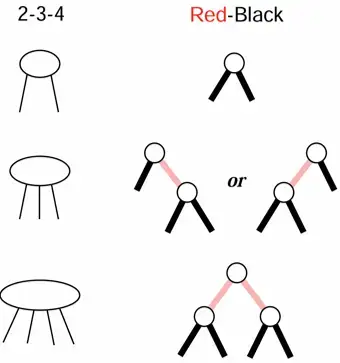
Red-Black Trees are just a way of representing 2-3-4 trees!
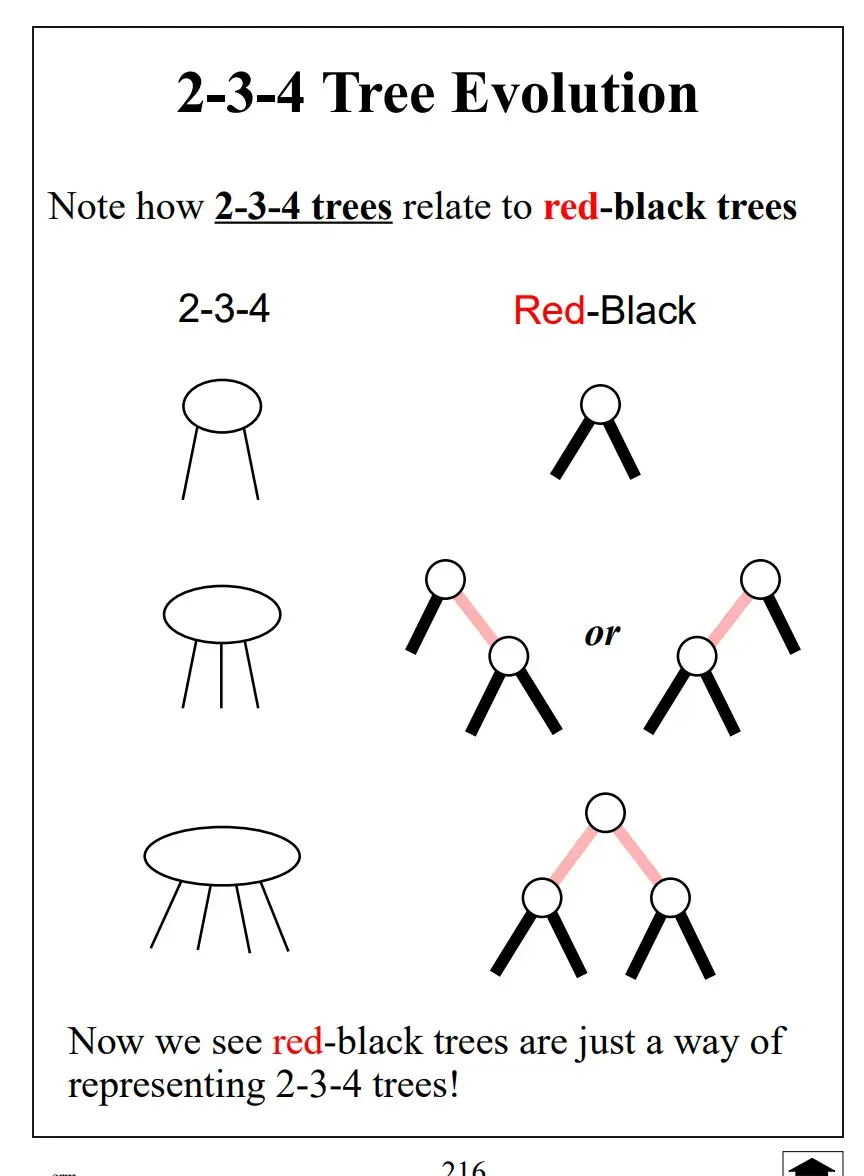
1.2 Black Height#
\(Lemma\): A red-black tree with \(N\) internal nodes has height at most \(2\ln(N+1)\), 因此它是平衡树
\(Proof\): 数学归纳,即证 \(N\ge 2^{h/2}-1\)
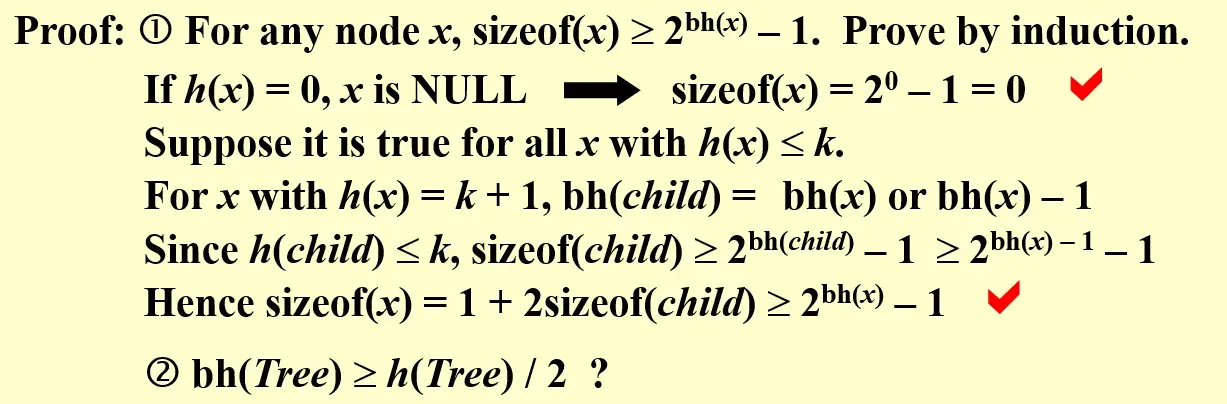
显而易见,没有连续的红色节点,所以 \(bh(x)\ge h(x)/2\),证毕,原命题证毕
1.3 Insertion#
1.3.1 Basic: Bottom-Up Insertion#
Note
优先选择红色:不用改变 bh,有几率不需要做任何其他操作;但如果出现红色相邻,就要进行以下调整
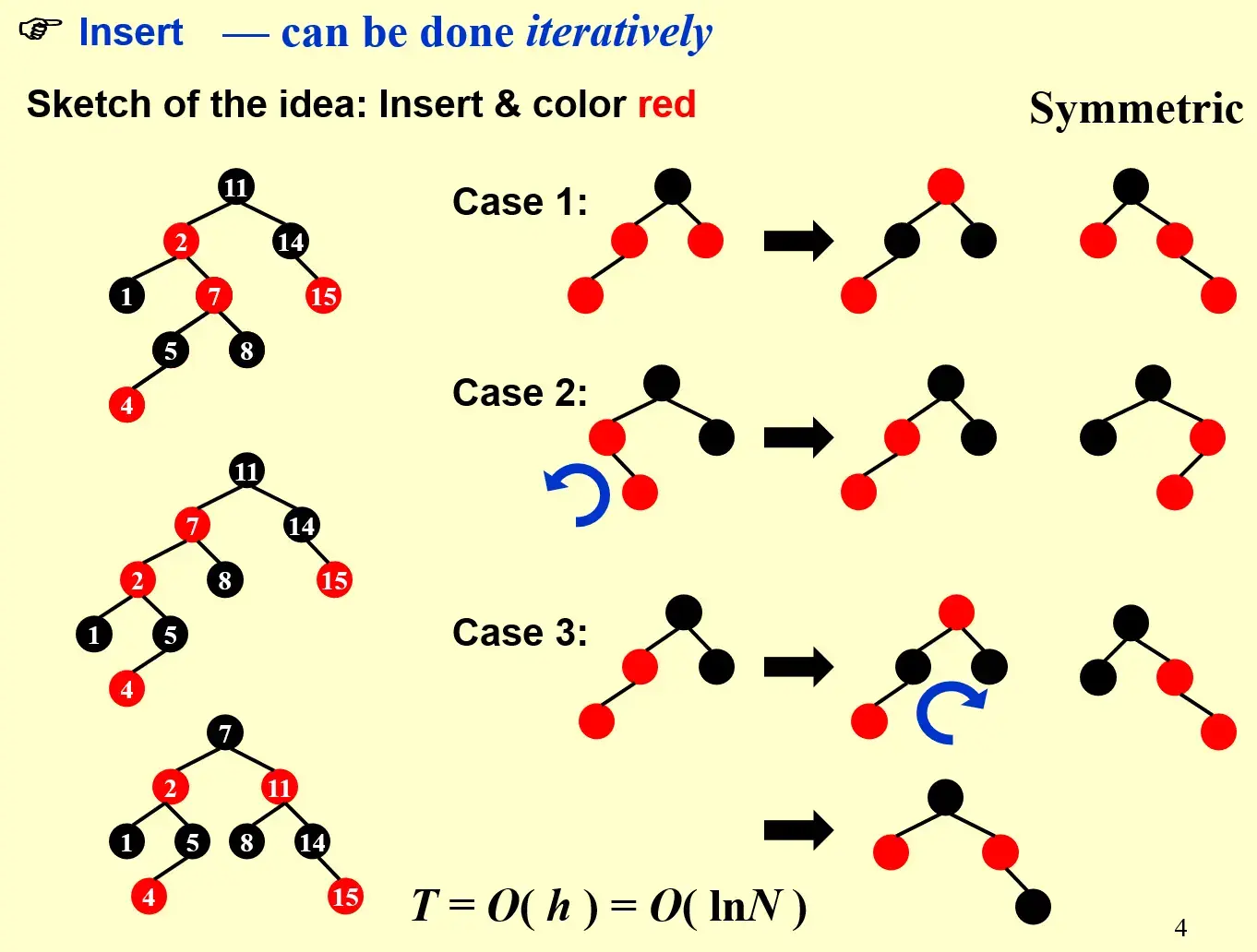
- Case 1: 解决局部问题,向上递归
- Case 2: 旋转,归纳为 Case 3
- Case 3: 更改颜色,为了修正 bh,需要旋转,Case 3 修正后就完成了,不需要向上传递
状态机
flowchart TD
A[Case 1] -->|C| A
C[Case3] -->|C&R| D(End)
A -->|C| B[Case2]
B -->|R| C
A -->|C| C
A -->|C| D- 其中
C为染色,R为旋转 - 可以发现旋转操作最多也就 2 次
Dicussion
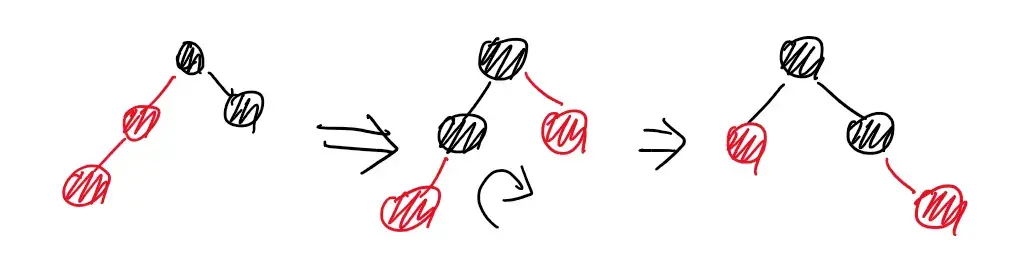 为什么不行?
为什么不行?
- 最右侧节点直接换红色可能导致出现红色节点连续
- P.right 子树的 bh 可能改变
1.3.2 Advanced: Top-Down Insertion#
Question
Q1:为什么使用 Top-Down
A1:为了减少 rotation 的次数,不进行 percolate up
Q2:Top-Down 如何保证插入时最多只用 rotate 一次?
A2:在 search 的过程中进行操作,保证了插入节点的叔叔节点是黑色,直接来到 Case 3
1.3.2.1 Procedure#
- Top-Down search 的过程中,如果发现一个节点
X有两个红色孩子,那么将X染成红色,孩子染成黑色,注意此时X的父亲和叔叔不可能都是红色,否则它们将已经都被染成黑色- 若
X的父亲是红色,其叔叔节点必为黑色,则进入 Case ⅔ 进行修正,不会产生递归
- 若
- 到了插入位置
- 若父亲是红色,叔叔必为黑色,进入 Case ⅔,结束
- 若父亲为黑色,结束
Example
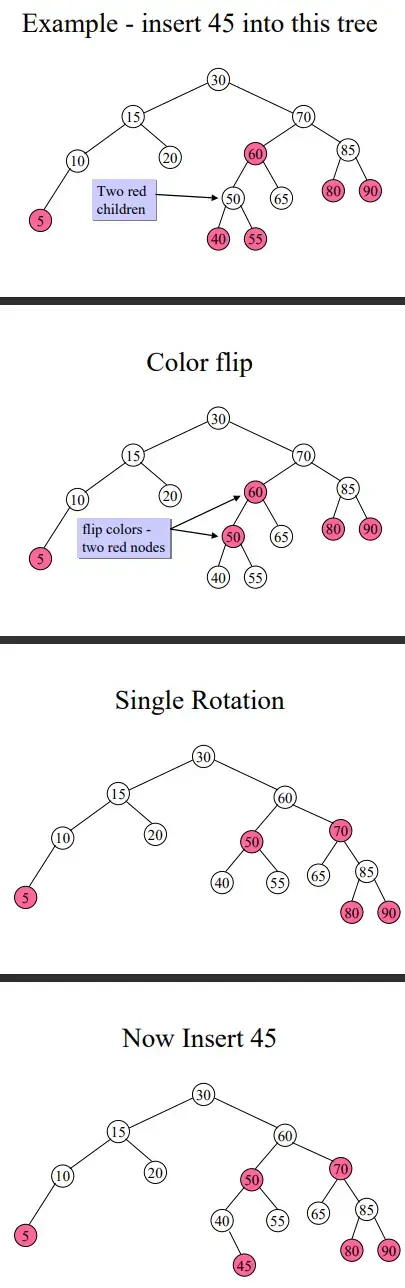
1.4 Deletion#
1.4.1 Basic: Bottom-Up Deletion#
1.4.1.1 Step 1. 查找并删除#
- Delete a leaf node: 这个节点就是
x,将父亲指向 NIL。如果这个节点是红色,进入 Step 2,否则,结束 - Delete a degree 1 node:
- 先分析一下,如果这个节点是 degree 1,那么它的 bh = 1,它的孩子一定是红色,否则 bh 不相等,所以这个节点一定是黑色
- 用子节点替代待删除节点,并染成黑色,结束
- Delete a degree 2 node: 将前驱(后继)的值 copy 过来并尝试删除前驱(后继),递归
找到 key 之后的流程图
flowchart TD
A[To delete leaf] -->|is red, delete|B{End}
A -->|is black, delete|D[Step 2: adjust black height]
C[To delete degree 1 node] -->|replace, recolor| B
E[To delete degree 2 node] -->|copy, recur| Z{Begin}
Z ---> |is leaf|A
Z --->|is degree 1| C
Z ---> |is degree 2|E1.4.1.2 Step 2. 调整 Black Height#
Target
x 是黑色叶子节点,让 x 所在的路径 bh+1 以保持平衡
1.4.1.2.1 Case 1 x 有红色邻居#
Target
将邻居换成黑色,化归为其他 Case
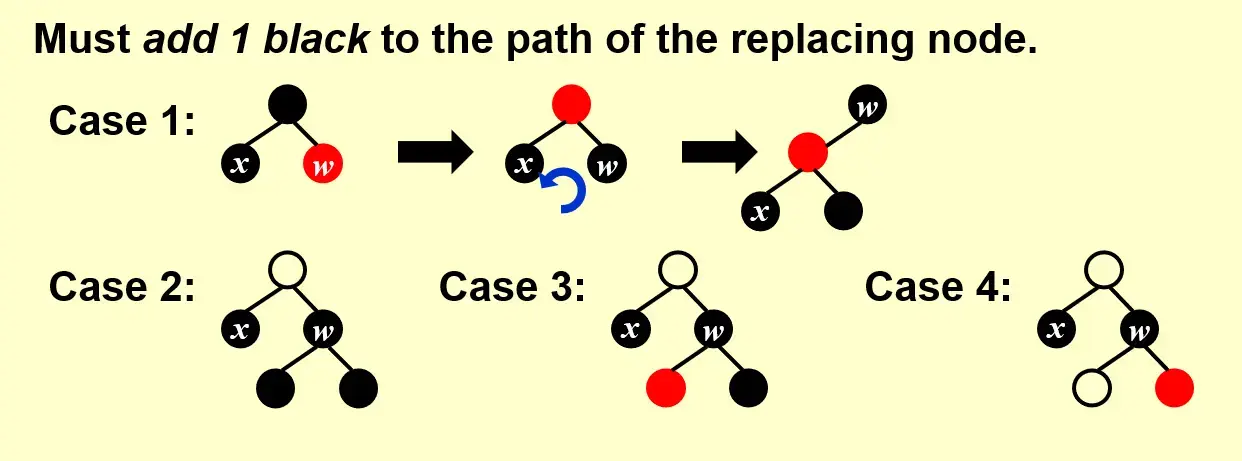
- 由于
w是红色的,必有两个黑色孩子 考虑NIL - 进行染色,左侧 bh-1,右侧 bh 不变
- 进行旋转,左侧 bh+1,右侧 bh 不变
- 最终实现:
- 不改变左右的 bh
- 将
x的邻居变成黑色,化归为其他 Case
1.4.1.2.2 Other cases x 有黑色邻居#
Target
Add 1 black to the path of x, not to change others
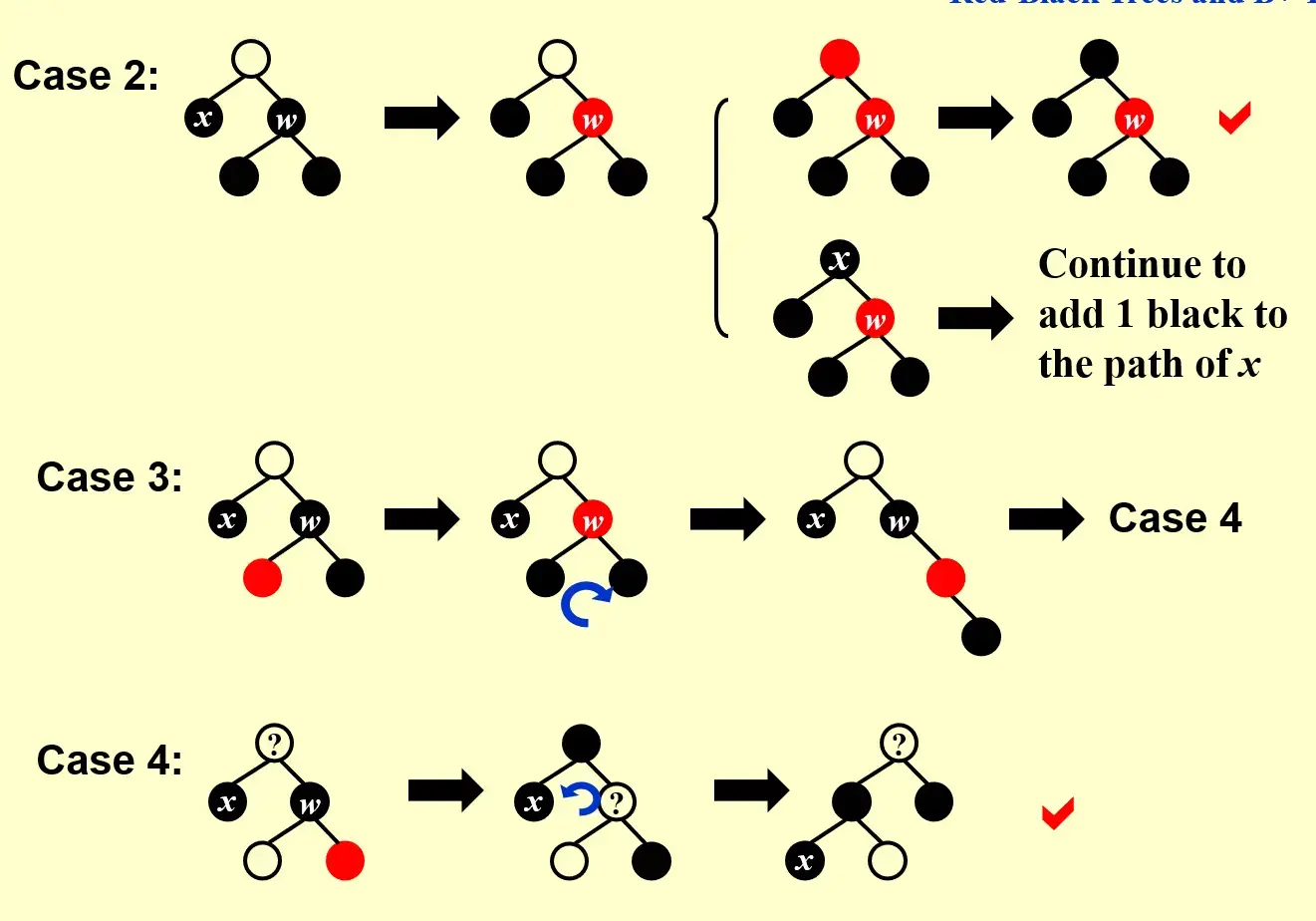
- 最多旋转次数为 3,
Case 1 -> Case 2 -> Case 4 -> End
Example
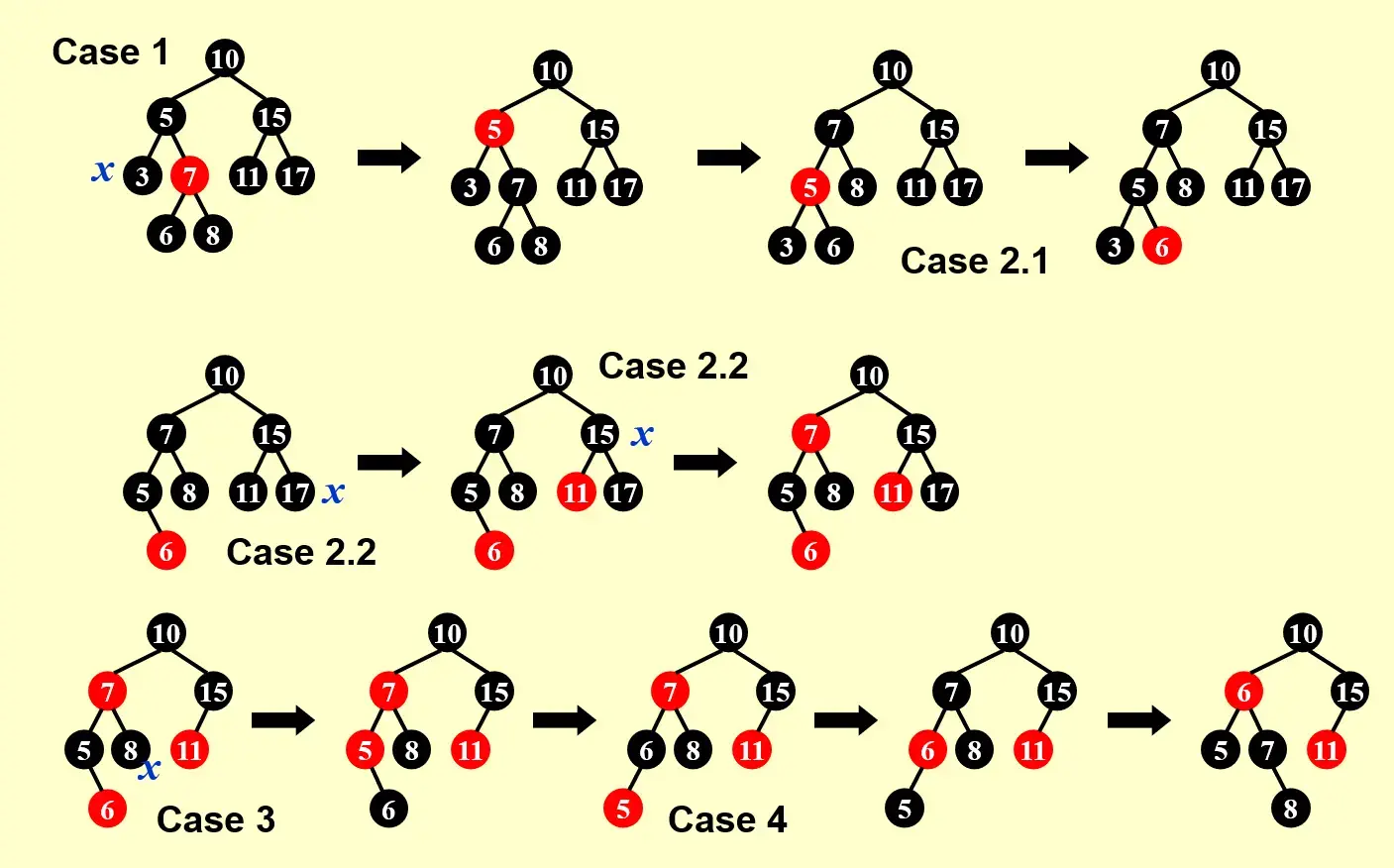
1.4.2 Advanced: Top-Down Deletion#
Bug
并没有找到相关的资料?& 不知道和前面的 Bottom-Up 有什么具体区别?
1.5 Advantage#
| Number of rotations | AVL | RBT |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion | \(\le 2\) | \(\le 2\) |
| Deletion | \(O(\log N)\) | \(\le 3\) |
2 B+ Trees#
2.1 Definition#
- 根是叶子或有 \([2, M]\) 个孩子
- 所有非叶子节点(除了根)都有 \([\lceil M/2\rceil, M]\) 个孩子
- 所有叶子的深度相同
Important
- 所有数据都在叶子上
- 每个中间节点有 \(M\) 个 ptr,\(M-1\) 个 key value
- 每个叶子节点有 \(M\) 个 key 和 \(M\) 个 ptr,这里的 ptr 指向实际的数据结构而不是其他节点
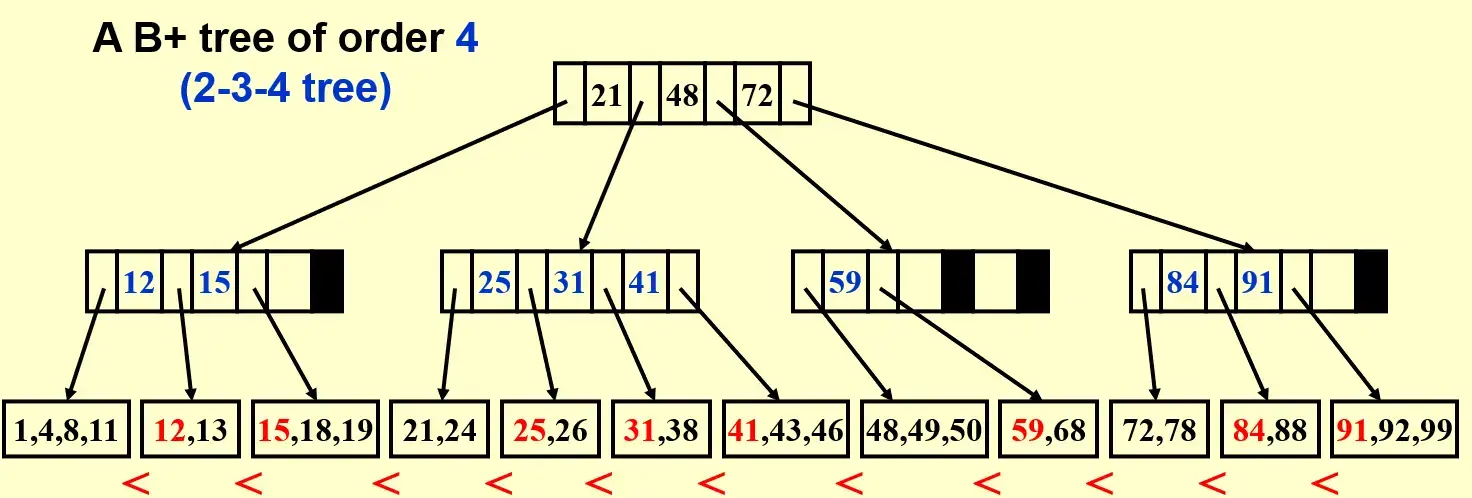
2.1.1 复杂度分析#
考虑 \(M\) order B+ tree 有 N 个数据
- \(Depth(M, N)=O(\lceil \log_{\lceil M/2\rceil} N\rceil)\)
- \(T_{find}=Depth(M, N) \times O(\log M)=O(\log N)\)
2.2 Insertion#
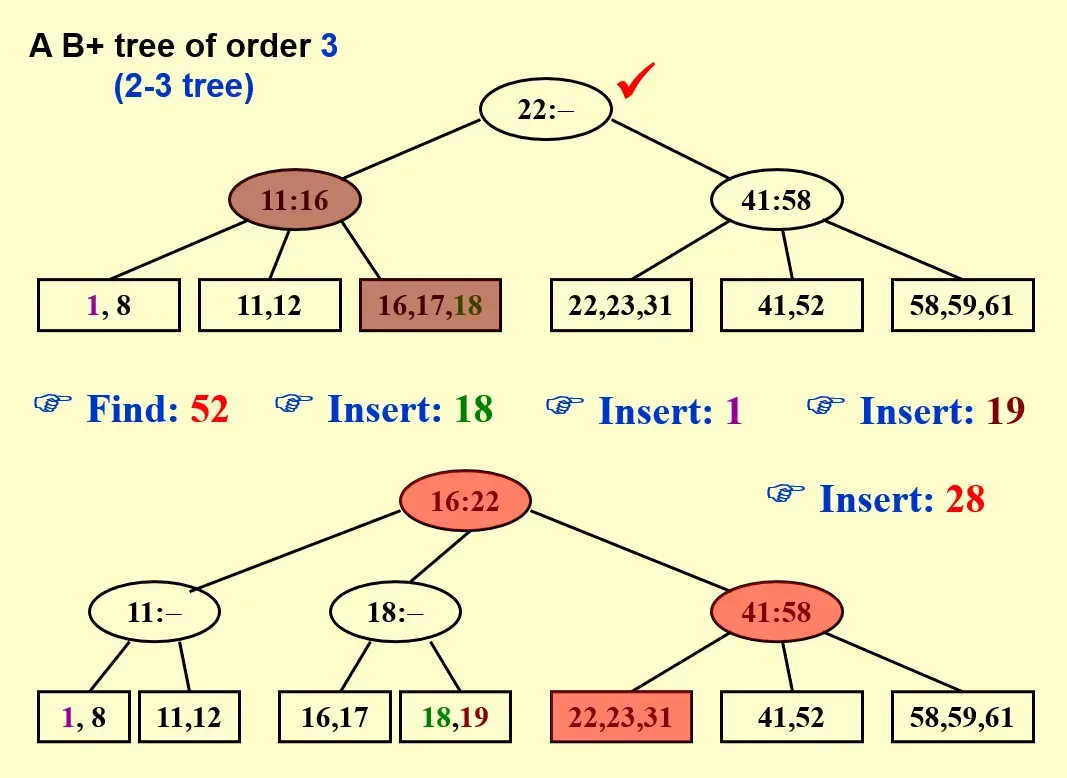
- 找到要插入的位置,直接插入
- 如果插入节点已满
- 可以查看同层的邻居还有没有位置,可以进行调整(如上图,其实可以匀一个位置出来,但这样的实现比较复杂)
- 进行分裂,并向上传递
Note
\(M\) 最好的选择是 3 或 4,但在数据库中经常选几千的
2.3 Deletion#
类似 Insertion,当父节点只有一个孩子时,需要移除
A RB tree corresponds to a 2-3-4 tree
3 Questions#
3.1 Q2#
3.1.1 2-3 Tree 插入#
When insert three keys into a non-empty 2-3 tree, and if the tree gains height when the first key is in, then it is possible that the 2-3 tree will gain more height after the insertions of the next two keys. (T/F)
Answer
F,因为如果树高增大的话,至少是从单个满的叶子节点(3keys)变成一根 2 叶子(4keys),这样完全可以容纳剩下的两个 key 而一定不会增加树高
3.1.2 Validity of a RBTree#
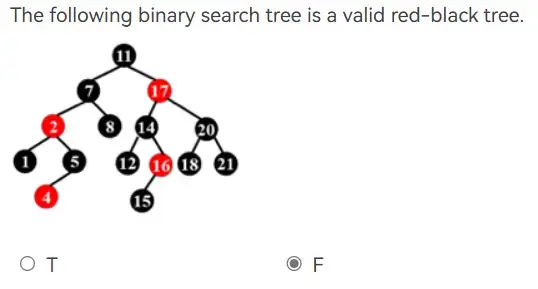
Answer
F,16 节点的 NIL 叶子黑高少一,总结为红色一度节点出现就非法
3.2 HW2#
3.2.1 2-3 Tree 最多 key 数量#
A 2-3 tree with 3 nonleaf nodes must have 18 keys at most. (T/F)
Answer
T
一定是一个根两个中间节点,所以 3*6=18
3.2.2 2-3 Tree 结构和插入详解#
Insert 3, 1, 4, 5, 9, 2, 6, 8, 7, 0 into an initially empty 2-3 tree (with splitting). Which one of the following statements is FALSE?
- A. 7 and 8 are in the same node
- B. the parent of the node containing 5 has 3 children
- C. the first key stored in the root is 6
- D. there are 5 leaf nodes
Question: 2-3 树与 B+ 树的区别是什么,数据只在叶子节点还是在所有节点?
- 按照 2-3 Trees | (Search, Insert and Deletion) - GeeksforGeeks 所给的定义,2-3 树的每个节点都最多能有 2 keys, 3 pointer,并且数据不全在叶子上
- 所教的 2-3 树则更像是 B+ 树,所有数据全都在叶子节点上,中间节点最多 2 keys, 3 ptrs,叶子节点最多 3 keys
Answer
A1
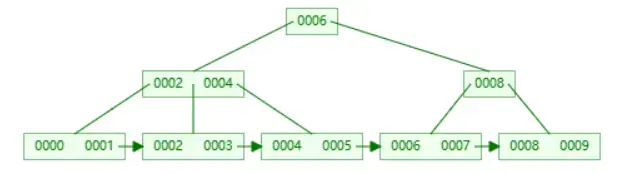
3.2.3 2-3 Tree 删除#
After deleting 9 from the 2-3 tree given in the figure, which one of the following statements is FALSE?
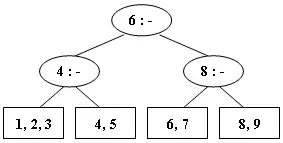
- A. the root is full
- B. the second key stored in the root is 6
- C. 6 and 8 are in the same node
- D. 6 and 5 are in the same node
Answer
D1
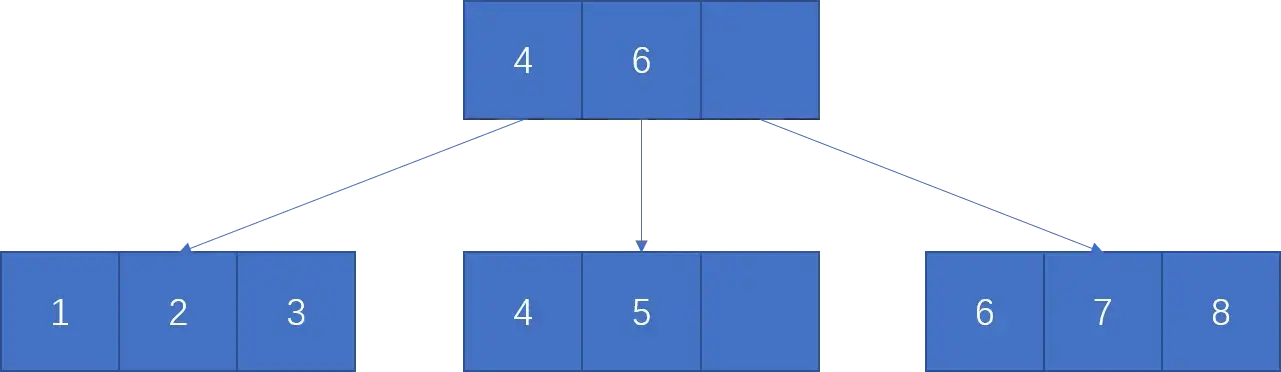
3.2.4 Self-printable B+ Tree %% fold %%#
- 实现
OEDER = 3的 B+ 树插入和打印即可
3.3 Midterm Review#
3.3.1 BPTree least 2-degree node#
A B+ tree of order 3 with 21 numbers has at least __ nodes of degree 2.
Answer
0 这题不能~贪心,~认为 2 度节点最少的情境下就是叶子节点最少;事实上,如果有 9 个叶子,就可以没有 2 度节点了 所以贪心方案应该是尽量构建全是 3 度节点的树
3.4 Midterm#
3.4.1 RBTree Insert#
After inserting { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 } into an initially empty red-black tree, then the number of black nodes in the red-black tree is 4. (T/F)
Answer
T 建议再尝试一次