15 Query Processing
Overview#
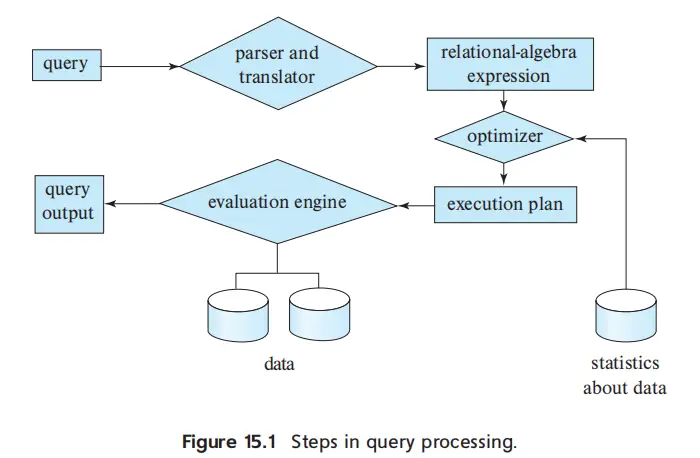
- exec-plan: annotated expr specifying detailed evaluation strategy
- e.g. use an index on salary to find instructors with salary < 75000
Measures of Query Cost#
- factors
- disk, cpu, network
Disk#
- factor: num of seeks/blocks read/block written
- 为了简单,用 seek 和 block transfer 来分析
- \(bt_T+St_S\)
- \(t_T, t_S\) 和硬件有关
- 进行 worst case 分析,假设初始 buffer 中没有任何数据
Selection Operation#
Using File Scans and Indices#
A1: Linear Search#
- linear search: \(t_S+b_r t_T\)
- linear search, equality on key: \(t_S+(b_r/2)t_T\)
A2: Clustering B+-tree Index, Equality on Key#
- \((h_i+1)(t_T+t_s)\)
- 需要找到叶子节点,并读取数据所在 block,每次都要寻址和读
A3: Clustering B+-tree Index, Equality on Non-key#
- \(h_i(t_T+t_S)+t_S+bt_T\)
- 找到位置后,顺序读 \(b\) 个块
A4: Secondary B+-tree Index#
- equality on key: \((h_i+1)(t_T+t_S)\)
- 和 clustering 差不多
- equality on non-key: \((h_i+n)(t_T+t_S)\)
- \(n\) 是取到的 record 数量,每个 record 都可能在不同且不连续的 block 上,所以认为每次都要寻址和传输
Selections Involving Comparisons#
A5: Clustering B+-tree Index, Comparison#
- \(h_i(t_T+t_S)+t_S+bt_T\)
- 找到第一个满足的 key,然后顺序读 \(b\) 个块
- 和 A3 比较像
A6: Secondary B+-tree Index, Comparison#
- \((h_i+n)(t_T+t_S)\)
- 找到第一个满足的 key,然后读 \(n\) 个 record
- 和 A4 比较像
Implementation of Comploex Selections#
- 考虑多个 selection condition 的逻辑运算,包括 conjunction, disjunction, negation
A7: Conjunctive Selection Using One Index#
- 首先检查是否有能通过 A2-A6 进行计算的简单条件,如果有则先用成本最低的方法运算
- 剩下的部分,从前面的结果中 fetch and check
A8: Conjucntive Selection Using Composite Index#
- 如果存在可用的复合索引,就使用 A2-A4 中的算法进行激素那
A9: Conjunctive Selection by Intersection of Identifiers#
- 索引有 record ptr,首先利用各个条件得到 sets of record ptrs
- 然后计算交集,再从文件中取
- 没有 index 的 condition 还是 fetch and check
A10: Disjunctive Selection by Union of Identifiers#
- 和 A9 类似,用并集
P.S. Negation
- linear search
- 如果有 index,而且满足 \(\neg\theta\) 的 record 数量非常少,可以用 index
Sorting#
Exteranl Sort-Merge Algorithm
Stage 1. Run Sorting#
- 每次读取 \(M\) 个 block 到 buffer,进行 in-memory sorting
- 排好序的一组称为 run,保存为 run file \(R_i\)
- run file 的保存有两种策略
- early materialization: 存储实际数据
- late materialization: 存储 sort key 和 ptr(record ID)
Stage 2. Merge#
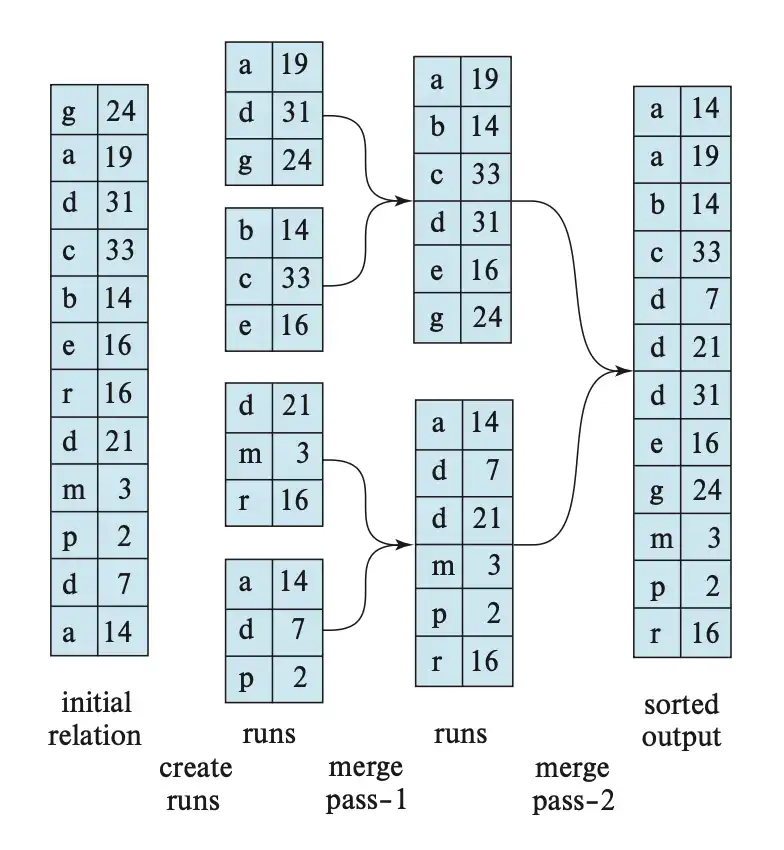
- 假设一共有 \(N\) 个 run file,考虑 output buffer,每趟最多将 \(M-1\) 个 run 作为输入
- 若 \(N<M\),每个 run 都能分配到一个 input buffer,进行一次 N-way merge 即可
- 但一般情况下 \(N>M\),此时要用多趟合并
- 每一趟最多将 \(M-1\) 个 run 合并为 1 个 run,也就是 run 数量减少到 \(\frac{1}{M-1}\)
- 可以将初始创建 run 的过程视作 pass 0,pass 数量的计算方法为:\(\text{\# passes}=1+\lceil \log_{M-1} \lceil N/M\rceil\rceil\)
Cost Analysis#
- 假设 relation 有 \(b_r\) 个 block,为了减少 seek 数量,每次读写 \(b_b\) 个 block,忽略最终结果写回的任何开销
- block transfer
- run sorting: \(2b_r\),因为需要读取并写回这么多数据
- merge
- 每一趟合并了 \(\lfloor M/b_b-1\rfloor\) 个 run
- 总合并趟数 \(\lceil \log_{\lfloor M/b_b-1 \rfloor} (\frac{b_r}{M})\rceil\)
- 每趟都需要读写整张表大小的数据,所以 \(2b_r \lceil \log_{\lfloor M/b_b-1 \rfloor} (\frac{b_r}{M})\rceil\)
- 考虑忽略最终结果的写回操作开销 (\(-b_r\)),则总 block transfer \(b_r(2 \lceil \log_{\lfloor M/b_b-1 \rfloor} (\frac{b_r}{M})\rceil+1)\)
Note
如果使用 LIMIT 语句,只查询 top-N,可以维护一个大小为 N 的 heap,并使用线性扫描
Join Operations#
- \(r\bowtie_{r.A=s.B} s\)
- 同样忽略最终结果的任何开销
Nested-Loop Join#
- 假设 \(r\) 是外层关系
- 最好情况下,内存能容纳两张表
- block transfer: \(b_r+b_s\)
- seek: \(2\)
- 最坏的情况下,内存只能为每个关系保存一个块
- block transfer: \(b_r+n_r b_s\)
- seek: \(b_r+n_r\)
- 如果内存能保存一个完整的关系,最好将内层关系完整保存,也是最好的
- block transfer: \(b_r+b_s\)
- seek: \(2\)
Block Nested-Loop Join#
- 按照块读取关系,节省块的访问次数
- 最好情况下,内存能够容纳内层关系
- block transfer: \(b_r+b_s\)
- seek: \(2\)
- 最坏情况下,仍然只能各容纳一块
- block transfer: \(b_r+b_rb_s\)
- seek: \(2b_r\)
- 一般情况下,每次从外层循环读取尽量多的内存块,减少内层的读取次数
- block transfer: \(b_r+\lceil\frac{b_r}{M-2}\rceil b_s\)
- seek: \(2\lceil\frac{b_r}{M-2}\rceil\)
Indexed Nested-Loop Join#
- 对于外层关系 r 的每一个元组,都对 s 的索引进行一次查找
- 最坏情况下,仅容纳 r 的一个块和 index 的一个块,链接成本为 \(b_r(t_T+t_S)+n_rc\),其中 \(c\) 是从 s 中进行索引和数据读取的开销
Merge Join#
- 流程
- r 和 s 先按照 join attr 排好序
- 使用双指针法判断是否需要 join,并写入 result
- 假设为了减少随机 I/O,分配了 \(b_b\) 个缓存块
- block transfer: \(b_r+b_s\)
- seek: \(\lceil b_r/b_b\rceil+\lceil b_s/b_b\rceil\)
Hybrid Merge-Join#
如果一个关系已经排序了,另一个在 join attr 上有 secondary index:
- 将 sorted relation 和 B+tree leaf entries 进行 merge
- 对来自 index 的 tuple 的物理地址进行排序
- 按照顺序访问这个 relation,减少 I/O,得到结果
Hash Join#
- 类似 merge,都是进行局部的判断来减少比较次数,进行 equi-joins 和 natural join
- 内存分配
- 假设划分为 \(n_h\) 个 bucket,考虑到希望每个 bucket 都能一次性读入内存,所以 \(n_h\) 要足够大,至少为 \(\lceil b_s/M\rceil\)
- 又希望内存里能够放下 \(n_h\) 个 buffer,这样不用递归划分,所以至少 \(M>n_h\)
- 综上 \(M^2>b_s\) 的时候不用递归划分
- 这里的 \(b_s\) 可以选择比较小的一张表
- Partitioning
- 对于 \(s,r\) 中的元组,进行 hash 划分,得到 \(n_h\) 个 \(H_s\) 和 \(H_r\) buckets
- 在 \(M^2<b_s\) 的情况下,由于 \(n_h>M\),第一轮的 bucket 存的可能不是单一 hash value 而是 hash value 在一个区间内的值,所以需要递归划分
- 无论怎样,确保最终一个 bucket 能够放在内存中 \(n_h\geq \lceil b_s/M \rceil\)
- 但即使满足了这个等式,也可能出现偏斜划分,导致部分 bucket 大小超出内存容量,所以一般划分数量要再多 20%
- 无论怎样,确保最终一个 bucket 能够放在内存中 \(n_h\geq \lceil b_s/M \rceil\)
- join
- 每次从 \(H_s\) 中取一个 bucket 放入内存,取 \(r\) 对应的 bucket(不一定都能放入内存)
- Cost
- 如果不用递归划分
- 划分需要 \(2(b_r+b_s)+2n_h\) 次传输,join 需要 \(b_r+b_s+2n_h\) 次传输,总共 \(3(b_r+b_s)+4n_h\) 次传输,其中 \(4n_h\) 基本可以忽略
- 假设缓冲区大小是 \(b_b\),划分需要寻道 \(2(\lceil b_r/b_b\rceil+\lceil b_s/b_b\rceil)\) 次,join 需要 \(2n_h\) 次,一共 \(2(\lceil b_r/b_b\rceil+\lceil b_s/b_b\rceil)+2n_h\) 次
- 需要递归划分
- 每次递归,划分数量增加 \(\lceil M/b_b-1\rceil\) 倍,一共需要 \(\lceil \log_{\lfloor M/b_b -1\rfloor}\frac{b_s}{M}\rceil\) 趟
- 总传输次数 \(2(b_r+b_s)\lceil \log_{\lfloor M/b_b -1\rfloor}\frac{b_s}{M}\rceil +b_r+b_s\)
- 总寻道次数 \(2(\lceil b_r/b_b\rceil+\lceil b_s/b_b\rceil)\lceil \log_{\lfloor M/b_b -1\rfloor}\frac{b_s}{M}\rceil\)
- 都已经忽略了 bucket 多余一些和 bucket 寻道的少量开销
- 如果不用递归划分
Query Processing in Memory#
Cache-Conscious Algorithms#
目标是减少 cache miss
- sorting -