14 Indexing
Basic Concepts#
- search key: 可以是单个或多个属性
- index file: 每个 entry 包含
[search_key, pointer] - basic kinds of indices
- ordered
- hash: 通过 hash 将数据均匀分布在 buckets 中
Index Evaluation Metrics#
- access types
- point query
- range query
- access time
- insertion time: 索引插入的维护时间
- deletion time: 索引删除的维护时间
- space overhead
Ordered Indices#
- Clustering index: 聚集索引/主索引/primary index,search key 和 record 的顺序一样
- Secondary index: 辅助索引/nonclustering index,search key 定义的顺序和 record 顺序不同
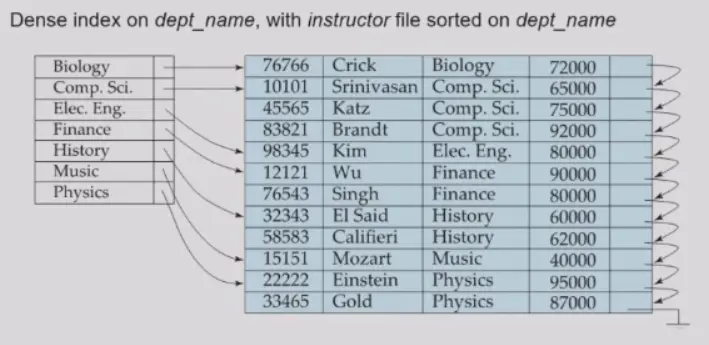
Dense Index Files#
- 表示所有的 search key 都出现在了索引文件中
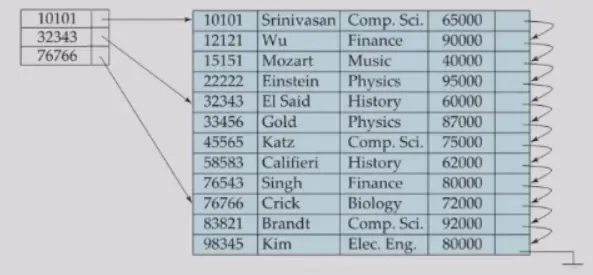
Sparse Index Files#
- 只包含了部分 search key
- 减少空间占用
- 减少维护成本
- 查询时间更长了
- Good pracitce
- 对于 clustered index,将 index 分 block,然后将每个 block 中保存最小的 search key
- 对于 unclustered index,sparse index 必须是 dense index 的上层索引
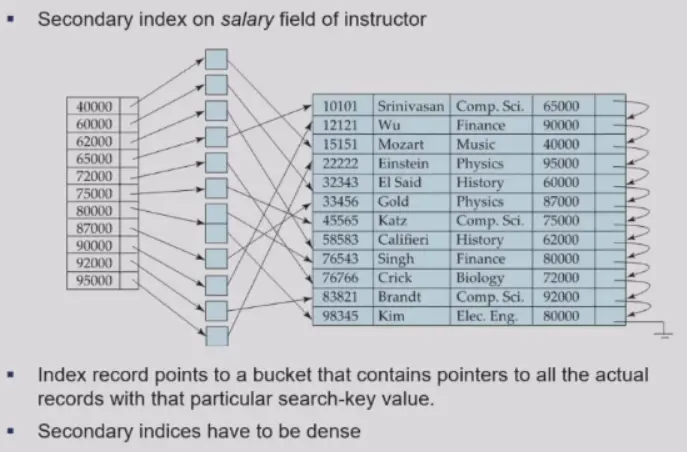
- more views
- clustered index,顺序检索
- secondary index,非顺序检索,跳读,导致 io 花销增大
Multilevel Index#
如果索引文件仍然很大,也无法放在内存中
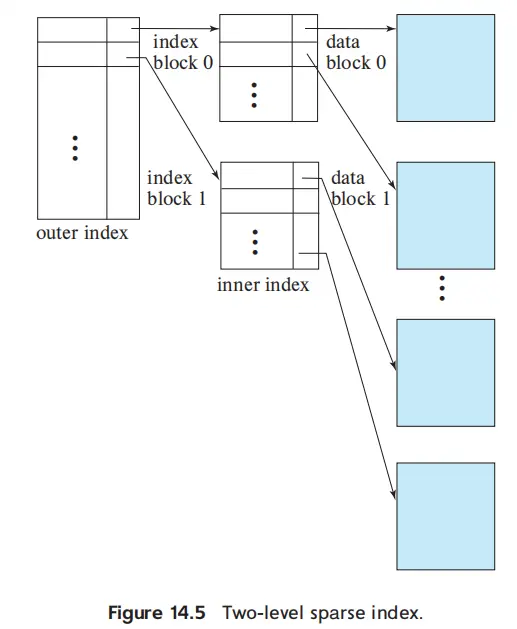
- inner index - basic index file
- outer index - a sparse index of the basic index
- 维护成本增大
- e.g. B+Tree
Index Update#
Deletion#
如果 index 中的 search key 对应的数据项被删除了,那么 index 中也需要删除
- dense index,直接删除
- sparse index
- 如果下一个 search key 不在 index 中,则用其替换
- 如果已经在 index 中,直接删除
Insertion#
- single-level
- dense index
- 需要创建新的空间并插入,可能需要添加 overflow blocks
- sparse index
- 如果是 block of file 的 index,只有创建新的 block 时才插入
- dense index
- multilevel: 类似 single-level
indices on multiple keys
multiple keys, e.g. (name, ID), 通过字典序排列
- query
nameor(name, ID)都可以 - 查
ID时索引无效,因为ID是乱的,可能还不如顺序扫描
可见 index 在有些情况下并没有用
B+ Tree Index Files#
- indexed-sequential files 的维护代价比较大,需要周期性重组织
- B+ Tree 能够在 insert delete 时以较小的代价调整 index file 结构
- 会有 perf overhead,但 minor
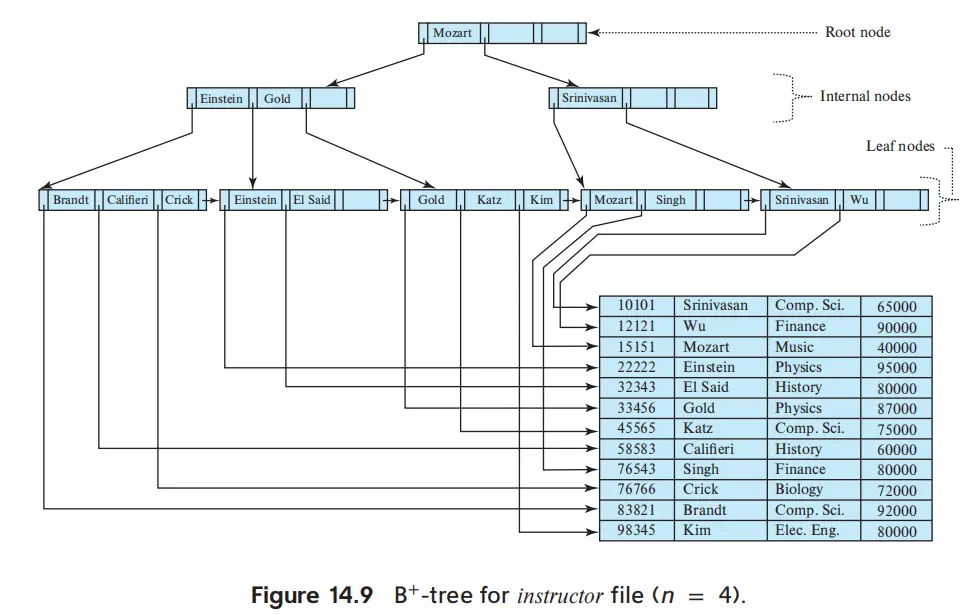
- order \(n\),结构性质
- 根节点
- 孩子数量 \([2,n]\)
- 作为叶子,\([0,n-1]\) value
- 中间节点
- 孩子数量 \([\lceil n/2 \rceil, n]\)
- key 是右边指针指向的最小值
- 叶子节点(非根)
- 对应 entry 数量 \([\lceil (n-1)/2\rceil,n-1]\)
- 记忆:二分之一向上取整
- 最后一个指针指向下一个叶子节点
- key 是左边指针指向的 entry 值
- 对应 entry 数量 \([\lceil (n-1)/2\rceil,n-1]\)
- 根节点
- \(Height\leq\lceil \log_{\lceil n/2\rceil} K\rceil\),\(K\) 是文件的 search key value 数量
Non-Unique Keys#
- 如果一个 key \(a_i\) non-unique,添加一个 key \(A_p\) 使得 \((a_i,A_p)\) 是唯一的
- 查找 \(a_i=v\) 相当于范围查找 \([(a_i, -\infty),(a_i, +\infty)]\)
- 但是会导致更多的 I/O
- clustering,sequential
- non-clustering,每个 record access 可能都需要一次 i/o
Complexity#
- Worst case \(O(\log_{\lceil n/2\rceil} K)\)
- n 和 K 确定后,树的高度和插入顺序有关
- insert in sorted order,每次都会导致一个 leaf full,分裂成 half full,就不会继续插入了,所以 occupancy = 0.5
- insert in random order,occupancy = ⅔

B+ Tree Extensions#
- file organization: 需要考虑 leaf node 的合并,可能一次要考虑更多的 leaf node
- secondary index
- 辅助索引也需要更新,且代价很大
- 也可以 secondary index 只保存 search key,查询的时候,通过 secondary index 找到 search key,再去 B+ tree 中查询对应的指针
- indexing strings
- varible fanout,因为 string 是变长度的
- string 还可以前缀压缩,减少空间占用
- B+ Tree disadvantages
- 大量插入时,每次插入都需要多于一次 i/o,如何解决?
- 先排序 external sort 再一个个插入,i/o 性能提升,但是大部分节点都 half full
- 先排序,bottom-up 构建 B+ tree
- 大量插入时,每次插入都需要多于一次 i/o,如何解决?
Hash Indices#
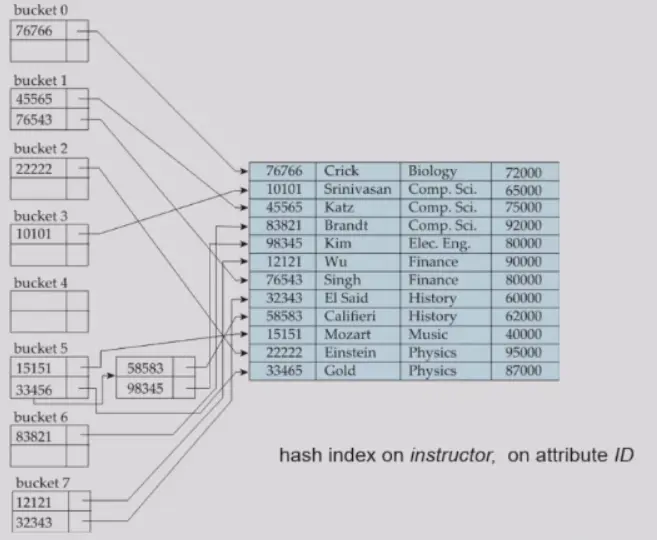
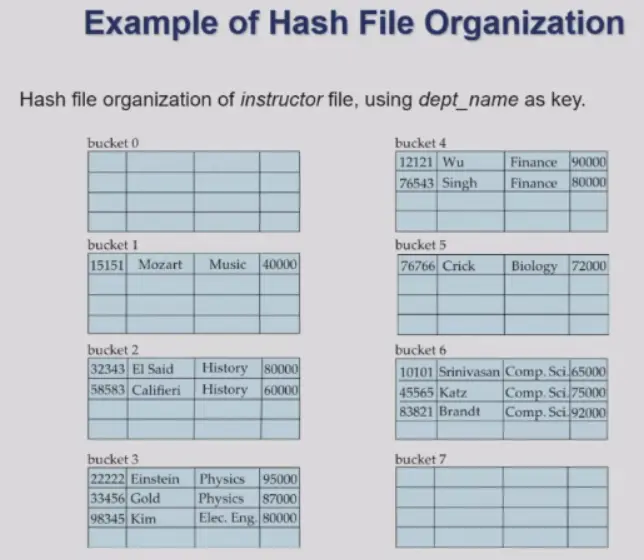
- hash function 的设计非常重要,与数据分布密切相关
Multiple-Key Access#
- 要进行
where dept_name = 'Finance' and salary = 80000查找时- 对 dept_name 做 index,然后检查 salary,或反之
- 同时索引,效果更好
where dept_name < 'Finance' and salary = 80000,这时(dept_name, salary)的索引就失效了
Other Features#
- covering indices
- 索引中可以有除了 search-key 之外的一些属性,且只保存在叶子节点中
- 部分查询不需要取数据
Creation of Indices#
- 外键索引
- 大多数数据库并不会自动创建
- \(takes \bowtie \sigma_{name=Shankar}(student)\),根据 student 查询到 id,然后用 id 查询 takes,如果有外键索引,效率会高很多
Write-Optimized Index Structures#
- B+ tree 在随机插入时性能很低
- 如果树过大,叶子节点的数量大于内存容量,每次随机访问叶子节点都很可能会导致 io
- 参考 bottom-up b+ tree construct,就是顺序 io,关键在于将随机 io 变成顺序 io
- lsm tree:
- buffer tree: lazy writes, bulk processing
LSM Trees#
支持高吞吐更新、写集中
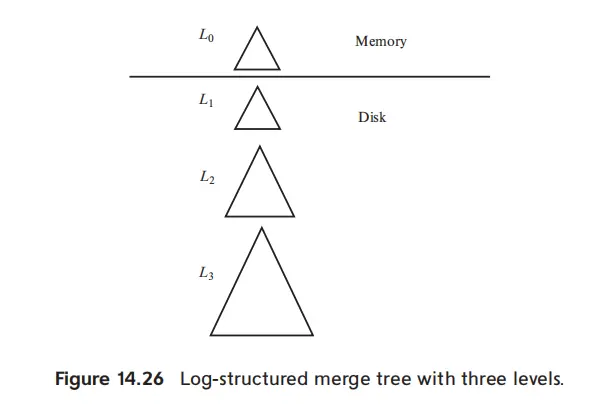
Insert#
- 所有的 insert 都先插入到 L0
- 当 L0 满了,整个合并到 L1
- 使用 bottom-up build 来进行 merge
- 将 L1 的叶子读入内存,建树,写回 disk
- L1 超过一定 threshold,则合并到 L2
Pros and cons#
- pros
- 插入全都在内存操作,效率更高
- io 都是顺序的
- 叶子总是满的
- cons
- 查询时需要遍历所有树
- 合并时 copy 很多次
- stepped-merge index
- 达到 threshold 才进行 merge,也就是每一层都有 k 个位置
- bloom filter,树有一些标记,可以在查询时跳过部分树
Delete#
- 加入一个特殊的 delete entry
- 在进行 merge 的时候可以同时遇到原 entry 和 delete entry,删掉这个 entry
Buffer Tree#
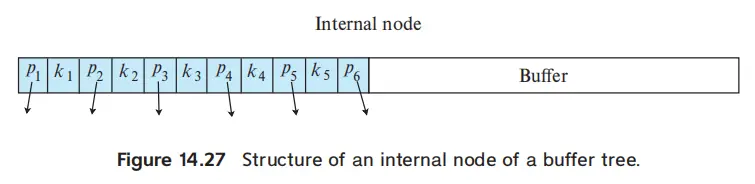
- 每个中间节点,包括根,都附带一个 buffer
- 插入
- 找到最近的 buffer,记录在 buffer 里,buffer 中按 key 排好序
- 当 buffer 满了再下推,也就是分发到孩子的 buffer 中
- leaf 没有 buffer,就是执行正常的插入
- leaf 分裂可能让 internal node 分裂,此时 buffer 也要分裂
- 查找
- 相比普通的查找,多了一个检查叶子缓冲区的步骤
- 同样可以使用范围查找(internal node 和 buffer 双指针完成)
- 删除和更新
- 和 LSM 一样,通过加入 key 一样的删除和更新项来进行
最坏情况下,buffer tree 的 I/O 次数上界比 LSM 更低;读操作 buffer tree 更快,写操作 buffer tree 更差,因为需要更多的随机 I/O,寻道时间更多。因此,写操作多用 LSM tree,读操作多用 buffer tree
Bitmap Indices#
方便进行多个条件的搜索
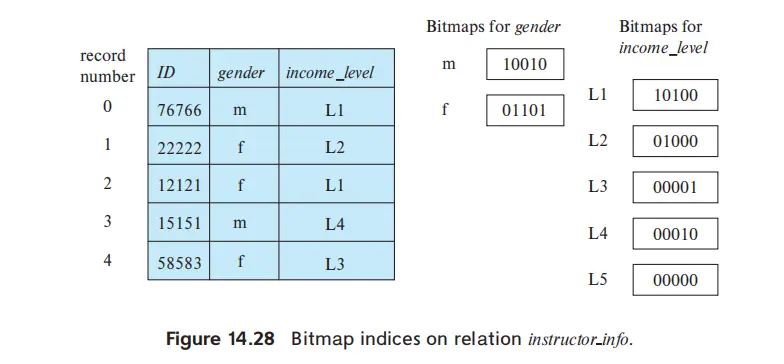
- 和 attr 的 domain 有很大关系
- enum 比较方便编码
- 连续的可以划分 level
- and or 都能直接进行位运算,sum 也可以直接计算 1 的数量