01 Introduction
Purpose#
File-processing system 的缺陷#
- Data reducdancy and inconsistency
- Difficulty in accessing data
- Data isolation
- Integrity problems
- Atomicity problems
- Concurrent-access anomalies
- Security problems
View of Data#
Data Models#
- Relational Model
- 使用多张表存储数据和数据的关系,tables are also known as relations
- an example of record-based model, fixed-format records of several types, each table contains records of a particular type
- columns 对应的是 attributes of the record type
- Entity-Relationship(E-R) Model
- a collection of basic objects, called entities
- widely used in database design
- Semi-structured Data Model
- individual data items may have different sets of attrs
.jsonand.xml
- Object-Based Data Model
- allows procedures to be stored and executed
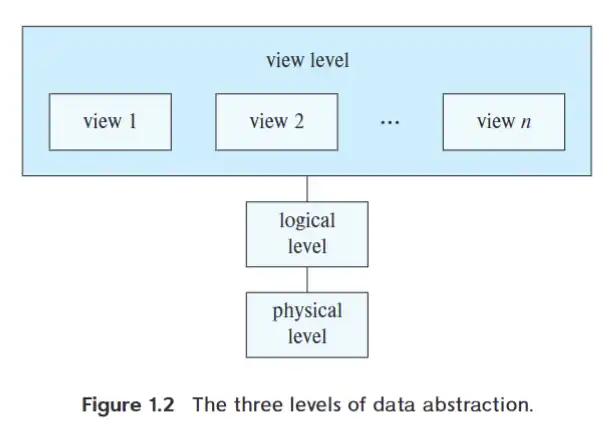
Data Abstraction#
- Physical level
- low-level 的数据结构,文件等
- describe how the data are actually stored
- Logical level
- describe what data are stored in db, and what relationships exist among those data
-
@Physical data independence: logical level 的用户无需关注 logical level 的简单结构在 physical level 的实现有多么复杂
- View level
- DBMS may provide many views for the same database
- 客户不会需要查看 db 里的所有信息,所以只展示部分信息
Instances and Schemas#
-
@instance: The collection of information stored in the database at a particular moment is an instance of the database
- 数据库的快照
-
@Schema: The overall design of the database
- physical schema: design at physical level
- hidden beneath the logical schema
- usually can be changed easily without affecting application programs
-
logical schema: design at logical level
- most important
- subschemas: at view level
- physical schema: design at physical level
Database Languages#
- Data-Definition Language (DDL): 表述 schema
- data storage and definition
- integrity constrs
- domain constr
- referential integrity
- authorization
- read
- insert
- update
- delete
- Data-Manipulation Language (DML): 表述 query 和更新操作
- Procedural DML
- Declarative DML
- 二者并非独立,而是结合成 SQL language
- 非 turing complete
Database Design#
- logical
- physical
Database Engine#
- storage manager
- query processor
- transaction management