02 Intro to the Relational Model
Structure of Relational Databases#
- 很多 tables,table 也称为 relations
- tuple 是表的一行,代表了 a relationship among a set of values
- attribute 指的是表的一列
- relation instance 表的快照
- domain: 每个 attribute 的允许值的集合
- domain is atomic: domain 的每一个元素都具有原子性
- null value 是 domain 中一个特殊的值
Database Schema#
- a relation schema consists of a list of attributes and their corresponding domains.
- \(A_{1},A_{2},\dots A_{n}\) 是 attr
- \(R=(A_{1},A_{2},\dots A_{n})\) 是 relation schema
- \(r(R)\) 是 \(R\) 中的一个 relation instance
- \(t\in r\) 是快照中的一行,一个 tuple
- e.g.
department(dept_name, building, budget)
Keys#
- Superkey(超键):足够用来唯一确定一个元组
- e.g. {ID, name} 和 {ID} 都可以是超键
- Candidate Key(候选键):最小的超键
- e.g. {ID}
- 可以有多个
-
并非元素最少的集合,而是不能缩小的集合,是极小值
- Primary Key(主键):从候选键中选出来的一个
- Foreign Key(外键):其值必须在另一张表中出现

图中下划线标记的是主键
Schema Diagrams#
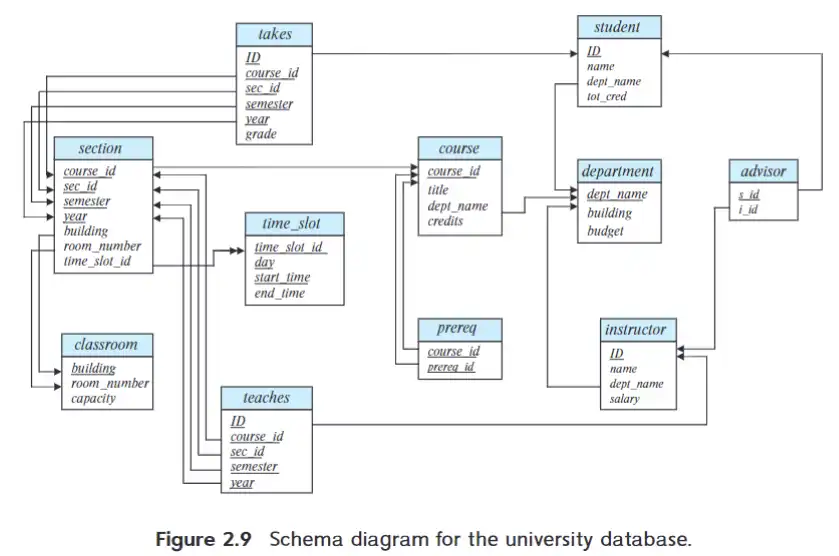
drawDB | Online database diagram editor and SQL generator
Relational Query Languages#
- select: \(\sigma\)
- project: \(\Pi\)
- union: \(\cup\)
- set diff: \(-\)
- Cartesian product: \(\times\)
- rename: \(\rho\)
Select Operation#
- Notation: \(\sigma_{p}(r)\)
- where \(p\) is predicate(谓词)
- e.g. \(\sigma_{\text{dept\_name="Physics"}}(\text{instructor})\)
- 允许在 predicate 中使用 \(=,\geq,\leq,\neq,>,<\) 和逻辑运算符
- e.g. \(\sigma_{\text{dept\_name}=\text{"Physics"}\land\text{salary}>90000}(\text{instructor})\)
- 允许在不同 attr 间进行比较
Project Operation#
- Notation: \(\Pi_{A_{1},A_{2},\dots A_{k}}(r)\)
- 表示只保留这些 attr
- 因为删除了一些列,可能会出现完全相同的行,但是因为 relations are sets,只会输出一个
- composition of relational operations
- \(\Pi_{\text{name}}(\sigma_{\text{dept\_name="Physics"}}(\text{instructor}))\)
Cartesian-Product Operation#
- Notation: \(\text{instructor}\times\text{teaches}\)
- 将 A 中所有 tuple 和 B 中所有 tuple 连缀组合
- 重命名,instructor.ID, teaches.ID
- 结果会很大,且大部分 tuple 没有意义,但是一些查询需求的基础运算
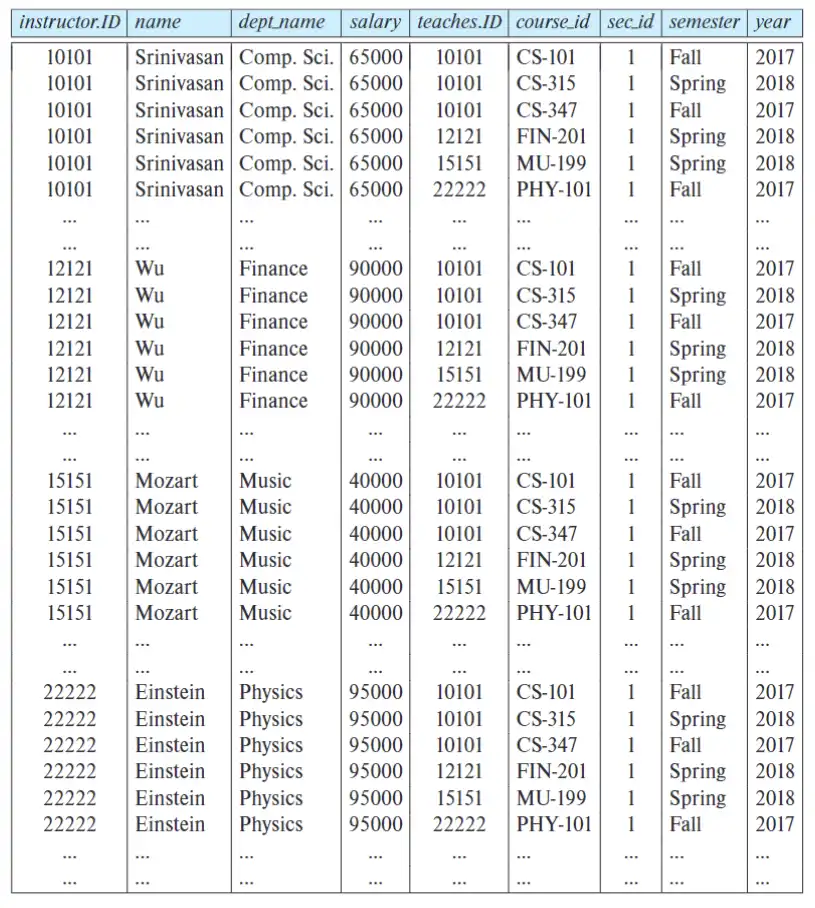
表格中
instructor.ID == teaches.ID是有意义的,所以先笛卡尔积然后选择
Join Operation#
- 连接算子,其实就是笛卡尔积再选择
- Notation: \(r \bowtie_{\theta}s=\sigma_{\theta}(r\times s)\)
- e.g. \(\sigma_{\text{instructor.ID}=\text{teaches.ID}}(\text{instructor}\times\text{teaches})=\text{instructor}\bowtie_{\text{instructor.ID}=\text{teaches.ID}}\text{teaches}\)
Union Operation#
- Notation: \(r\cup s\)
- 要求
- must have the same arity 元数 (same number of attrs)
- domains must be campatible
- e.g. \(\Pi_{\text{course\_id}}(\sigma_{\text{semester}=\text{"Fall"}\land\text{year}=2017}(\text{section}))\cup\Pi_{\text{course\_id}}(\sigma_{\text{semester}=\text{"Spring"}\land\text{year}=2018}(\text{section}))\)
Intersection Operation#
- e.g. \(\Pi_{\text{course\_id}}(\sigma_{\text{semester}=\text{"Fall"}\land\text{year}=2017}(\text{section}))\cap\Pi_{\text{course\_id}}(\sigma_{\text{semester}=\text{"Spring"}\land\text{year}=2018}(\text{section}))\)
- 交集不是基本算子,因为可以通过并集和差集得到
Set Diff Operation#
- e.g. \(\Pi_{\text{course\_id}}(\sigma_{\text{semester}=\text{"Fall"}\land\text{year}=2017}(\text{section}))-\Pi_{\text{course\_id}}(\sigma_{\text{semester}=\text{"Spring"}\land\text{year}=2018}(\text{section}))\)
Assignment Operation#
- e.g. find all instructor in physics and music department
- \(\text{Physics}\leftarrow \sigma_{\text{dept\_name}=\text{"Physics"}}(\text{instructor})\)
- \(\text{Music}\leftarrow \sigma_{\text{dept\_name}=\text{"Music"}}(\text{instructor})\)
- \(\text{Physics}\cup\text{Music}\)
Rename Operation#
- Notation: \(\rho_{x}(E)\)
- 返回被命名为 \(x\) 的,表达式 \(E\) 的结果
- Notation: \(\rho_{x(A_{1},A_{2},\dots,A_{n})}(E)\)
- 会将 attrs 也进行重命名
Equivalent Queries#
- \(\sigma_{\text{dept\_name}=\text{"Physics}}(\text{instructor}\bowtie_{\text{instructor.ID}=\text{teaches.ID}}\text{teaches})\)
- \((\sigma_{\text{dept\_name}=\text{"Physics}}\text{instructor})\bowtie_{\text{instructor.ID}=\text{teaches.ID}}\text{teaches})\)
- 直观来看,第二种会更快,但是考虑到索引之类的优化方法就不一定了