Ch.04 Trees
1 Preliminaries#
1.1 Definition#
- A tree is a collection of nodes. The collection can be empty, which is sometimes denoted as A. Otherwise, a tree consists of a distinguished node r, called the root, and zero or more (sub)trees T 1, T 2, . . . , Tk, each of whose roots are connected by a directed edge to r.
- 这是一个递归的定义
- Note
- subtrees must not connect to each other
- there are N-1 edges in a tree with N nodes
- Degree
- for a node, degree(node) = the number of its children node
- for a tree, it is the maximum of degree of its node
- Parent, children, sibilings, leaf 都是特殊定义的节点
- Path: the path from node A to node B is unique in a tree 只能是从上到下走
- Length of path: 路径中边的个数
- Depth: the length of the path from root to this node, Depth(root)=0
- Height the length of the longest path from this node to a leaf, height(leaf)=0
- height(depth) of a tree = height(root) = depth(deepest leaf)
- Ancestors: all the nodes along the path from this node up to the root
- descendants: all the nodes in its subtrees
1.2 Implementation#
1.2.1 List Representation#
- 可以用 (A(B(E,F),C,D)) 的线性结构来表示
- 可以用链表来表示
- 劣势:tree 在生长的时候每个节点需要几个 pointer 不好确定
- 如果提前知道了 degree,也会浪费空间
- 劣势:tree 在生长的时候每个节点需要几个 pointer 不好确定
1.2.2 FirstChild-NextSibiling Representation#
- 每个 node 都有两个 pointer,第一个指向 firstchild,第二个指向 nextsibiling
- 表达不唯一,子节点的顺序是不重要的
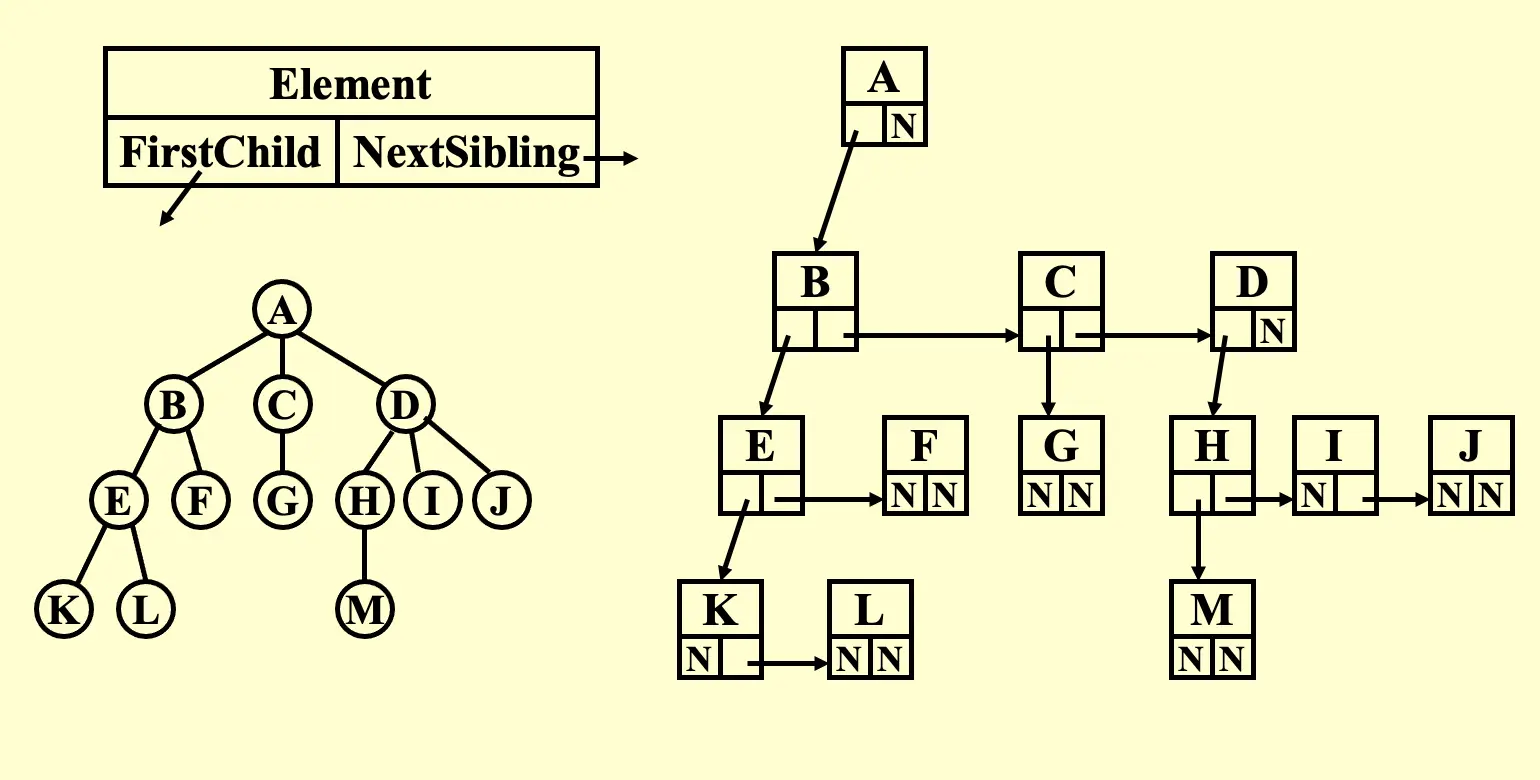
general tree can be converted into a Binary Tree
2 Binary Tree#
2.1 Definition#
- 每个节点最多只能有两个子节点
- 相当于 general 的 firstchild-nextsibiling 表达旋转 45°
2.2 Applications#
2.2.1 Expression Tree (syntax trees)#
- review: postfix expression -> stack
- constructing an Expression Tree from postfil expression
- operand, push
- operatior, operator 指向栈顶两个元素,push operator 的指针
2.3 Tree Traversels#
- preorder 先根遍历,根左右
- postorder 后根遍历,左右根
- levelorder 深度遍历
- 使用 queue 存储将要遍历的节点指针
- 每遍历一个节点,将它的子节点加入队列
- Inorder Traversal 中根遍历,左根右
- 先左子树,再根节点,再右子树
- 递推形式非常复杂,递归很好读
2.3.1 expression tree#
- 按照不同的遍历方式,能得到不同的表达式,这就是 expression tree 的作用
- perorder: prefix exp
- inorder: infix exp
- postorder: postfix exp
2.3.2 print directory#
- 使用 preorder 遍历,先打印根目录
- 记录 depth,用作 print 的缩进
2.3.3 Calculating the size of a directory#
- 使用 postorder,先计算子节点(文件或文件夹)的大小,在返回子节点
- \(T(N)=O(N)\)
2.4 Different Binary Trees#
2.4.1 Threaded Binary Trees 线索二叉树#
- 一个二叉树有 n 个节点,那么它就一定有 n+1 个空的指针,所以为了 避免浪费可以使用 threads
- Rules: 有一个 dummy head node
- 如果左指针空,替换为中序遍历的前驱
- 如果没有前驱,替换为 dummy head node
- 如果右指针空,替换为中序遍历的后继
- 如果左指针空,替换为中序遍历的前驱
- 便于从下面来往上遍历
2.4.2 Other binary trees#
- Skewed Binary Trees: 斜树,退化成线性结构 表达能力很弱,不如用 linear list
- Complete Binary Trees: 完全二叉树 ^bfe95b
- 除了最后一层,全都填满
- 最后一层从左往右填
2.5 Properties of Binary Trees#
- 第 i 层最大有 \(2^{i-1}\) 个节点
- k 层二叉树的最大节点个数为 \(2^k-1\)
- 完全二叉树中,叶子节点的个数比 2 度节点个数多 1 \(n_0=n_2+1\)
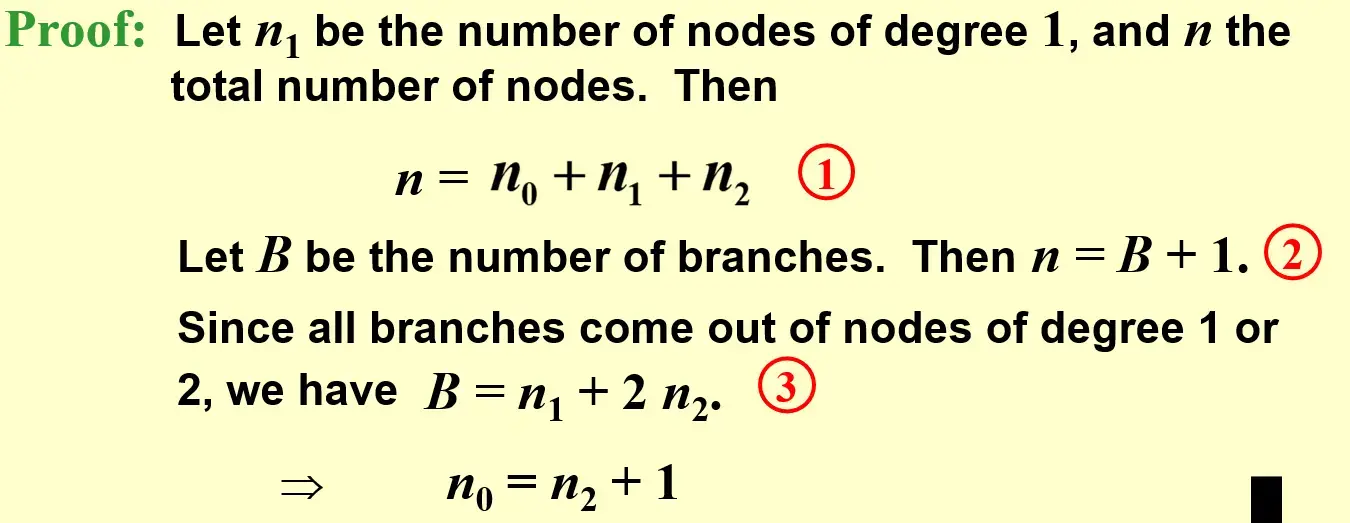
- 或者这样理解
- 如果没有二度节点,只会有一个叶子
- 每多一个二度节点,就能多一条支路,多一个叶子
3 The Search Tree ADT - Binary Search Tree#
3.1 Definition#
- 每个节点都有一个 key,为整数,每个 key 不同
- 左子树的 key 都小于 root
- 右子树的 key 都大于 root
- Binary Search Tree 的子树也是 Binary Search Tree
3.2 ADT#
- Objects: A finite ordered list with zero or more elements
- Operations
3.3 Implementations#
3.3.1 Find#
- 递归可以实现
- 由于是尾递归,可以优化为循环
- 时间复杂度,就是树的深度 d
3.3.2 FindMin/FindMax#
- 找到左下角/右下角的节点 循环解决
- 时间复杂度为 d
3.3.3 Insert#
- 找到待插入的位置(父节点)
- 进行和 Find 一样的操作
- 最后一个遇到的节点就是这个数的父节点
- 创建节点并返回指针
- 上一层调用中使父节点的指针等于这个新节点的指针
- \(T(N)=O(d)\)
3.3.4 Delete#
- delete leaf node: free 并将父节点指向空
- delete 1 degree node: 将它的子节点直接接到父节点上
- delete 2 degree node:
- 将这个节点替换为左子树中最大的,或右子树中最小的
- 对被换过来的这个节点递归进行 delete 操作
3.3.4.1 Lazy Deletion#
- 使用一个 flag 来标记这个节点是否 active,标记为 deleted 就可以,用于减少 free 操作
- 如果二叉树比较平衡的话,使用 lazy deletion 只会使搜索的时间复杂度增加一点点
3.4 Average-Case Analysis#
- 建立一个 n 个节点的 binary search tree
- \(height(bst)\in[h-1,\lceil\log_2(n+1)\rceil-1]\)
4 HW 4#
- There exists a binary tree with 2016 nodes in total, and with 16 nodes having only one child. F
- 去除所有的单个孩子的节点,剩下 2000 个节点的完全二叉树,但 2000 不是 2 的次方数
- Given a tree of degree 3. Suppose that there are 3 nodes of degree 2 and 2 nodes of degree 3. Then the number of leaf nodes must be ____.
- 如果所有的 degree 都是 1,那么只有一个叶子节点
- every extra degree add 1 leaf node
- 1+3+2*2=8
- If a general tree T is converted into a binary tree BT, then which of the following BT traversals gives the same sequence as that of the post-order traversal of T?
- left right root
- the sequence of M H I J D
- T preorder = BT preorder; T postorder = BT inorder
- Among the following threaded binary trees (the threads are represented by dotted curves), which one is the postorder threaded tree?
- threaded binary tree 空指针的替换规则可以是 postorder, inorder, preorder
4.1 函数题:Isomorphic 同构树#
4.1.1 Idea 1#
- 需要使用递归,每次判断一层,然后拆成子树再次判断
- degree 不相等直接返回 0
- 对于 degree = 2 节点在本层,判断下一层的 value 是否对应
- 对应,则对应递归调用
- 不对应,则返回 0
- 对于 degree = 1 节点在本层,判断下一层的 value 是否对应
- 对于 degree = 0 的节点返回 1
- 对于 degree = 2 节点在本层,判断下一层的 value 是否对应
4.1.2 Idea 2#
- 判断值是否相等,不相等返回 0
- 判断 degree
- not equal return 0
- = 2
- if tree 1 left == tree 2 left
- iso(left, left)
- iso(right, right)
- else
- iso(left, right)
- iso(right, left)
- if tree 1 left == tree 2 left
- =1
- 相应调用
4.1.3 易错点、改进建议#
- 需要考虑对两个空树调用的情况
- 使用 bitmap 来统一表示,可以稍微减少判断的问题
4.2 编程题:ZigZagging on a Tree#
4.2.1 Question#
- how to build a tree from inorder array and postorder array?
- how to traversal this binary tree in required form?
- build binary tree
- traversal it
4.2.2 idea 1: abandoned 空间太大了,其实操作很简单,真正建立树的结构没有用#
4.2.2.1 建立树#
- 拿到 postorder 的最后一个元素作为 pivot
- 在 parent 下建立这个节点
- 在 inorder 中找到这个 pivot,查询左右子树长度
- 递归调用,分别传入 root 的左右指针
- 当 size = 1 时,建立这个节点,递归出口
4.2.2.2 遍历树#
4.2.3 idea 2#
- 使用一个二维数组 inorder 标记每个数字的深度?
- 需要用到遍历,每次取 postorder 的最后一个数字为 pivot,设置这个 pivot 的深度,并递归求子树元素的深度
- 然后直接交叉遍历数组?
4.2.3.1 评价:非常好,一遍过!很省空间#
- 最后换成单独的 depths 数组,维护起来比较方便
4.2.3.2 建议#
- 注意输出格式的限制,末尾是否允许有多余的空格
- 注意这是 C 语言,不是 python
- 三目运算符
int max = a>b?a:b;
5 HW#
- There exists a binary tree with 2016 nodes in total, and with 16 nodes having only one child. F
- 根据 2.5 Properties of Binary Trees 进行推导得出 \(2n_2=1999\) 除不尽,所以不可能
- In a binary search tree which contains several integer keys including 4, 5, and 6, if 4 and 6 are on the same level, then 5 must be their parent. F
- False: 可以是三层的树,5 为根,4 为右孩子,6 为左孩子
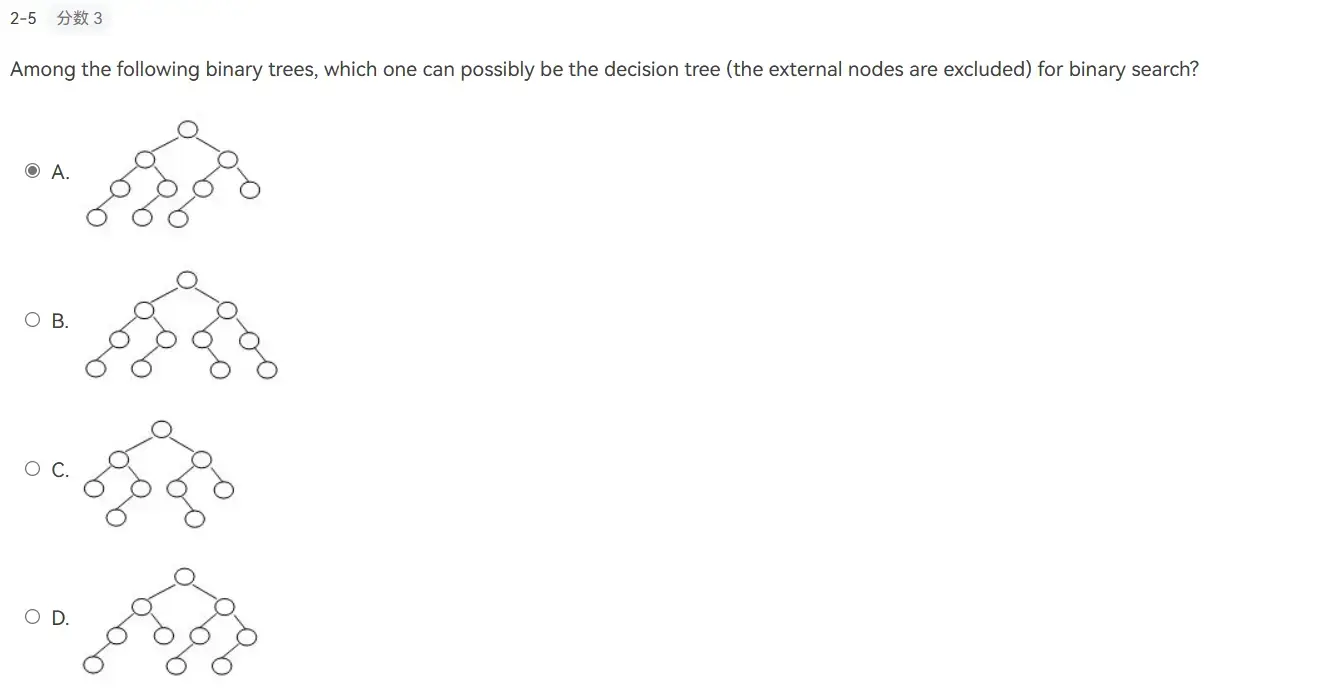
6 Review#
- The time comlexity of Binary Search will be the same no matter we store the elements in an array or a linked list.
- F, idkw