Ch.02 Algorithm Analysis
1 Complexity: Asymptotic Notation#
- \(T(N)=O(f(N))\) if there are positive constants \(c\) and \(n_0\) such that \(T(N)\le cf(N)\) for all \(N\ge n_0\)
- Big O 代表一种上界,小于等于
- \(T(N)=\Omega(g(N))\) if there are positive constants \(c\) and \(n_0\) such that \(T(N)\ge cg(N)\) for all \(N\ge n_0\)
- Big Omega 代表一种下界,大于等于
- \(T(N)=\Theta (h(N))\) if and only if \(T(N)=O(h(N))\) and \(T(N)=\Omega(h(N))\)
- Big Theta 代表上下界同阶,是确界
- \(T(N)=o(p(N))\) if \(T(N)=O(p(N))\) and \(T(N)\ne \Theta(p(N))\)
- Small o 代表严格渐进上界,严格小于
1.1 Rules of Asymptotic Notation#
- \(T_1(N)=O(f(N))\,\, T_2(N)=O(g(N))\)
- \(T_1(N)+T_2(N)=\mathrm{max}(O(f(N)),O(g(N)))\)
- \(T_1(N)*T_2(N)=O(f(N)*g(N))\)
- \(log^kN=O(N)\) for any constant \(k\), logarithms grow very slowly
1.2 General Rules#
if/else- 上界是不同选择中 runtime 最大的
- Recursions
- 使用递推数列来计算
- for example: Fibonacci number
- \(T(N)=T(N-1)+T(N-2)+2\)
- \((\frac{3}{2})^N\le Fib(N) \le (\frac{5}{3})^N\) grows exponentially
2 Compare the Algorithms#
2.1 MaxSubsequenceSum problem#
2.1.1 Divide and Conquer#
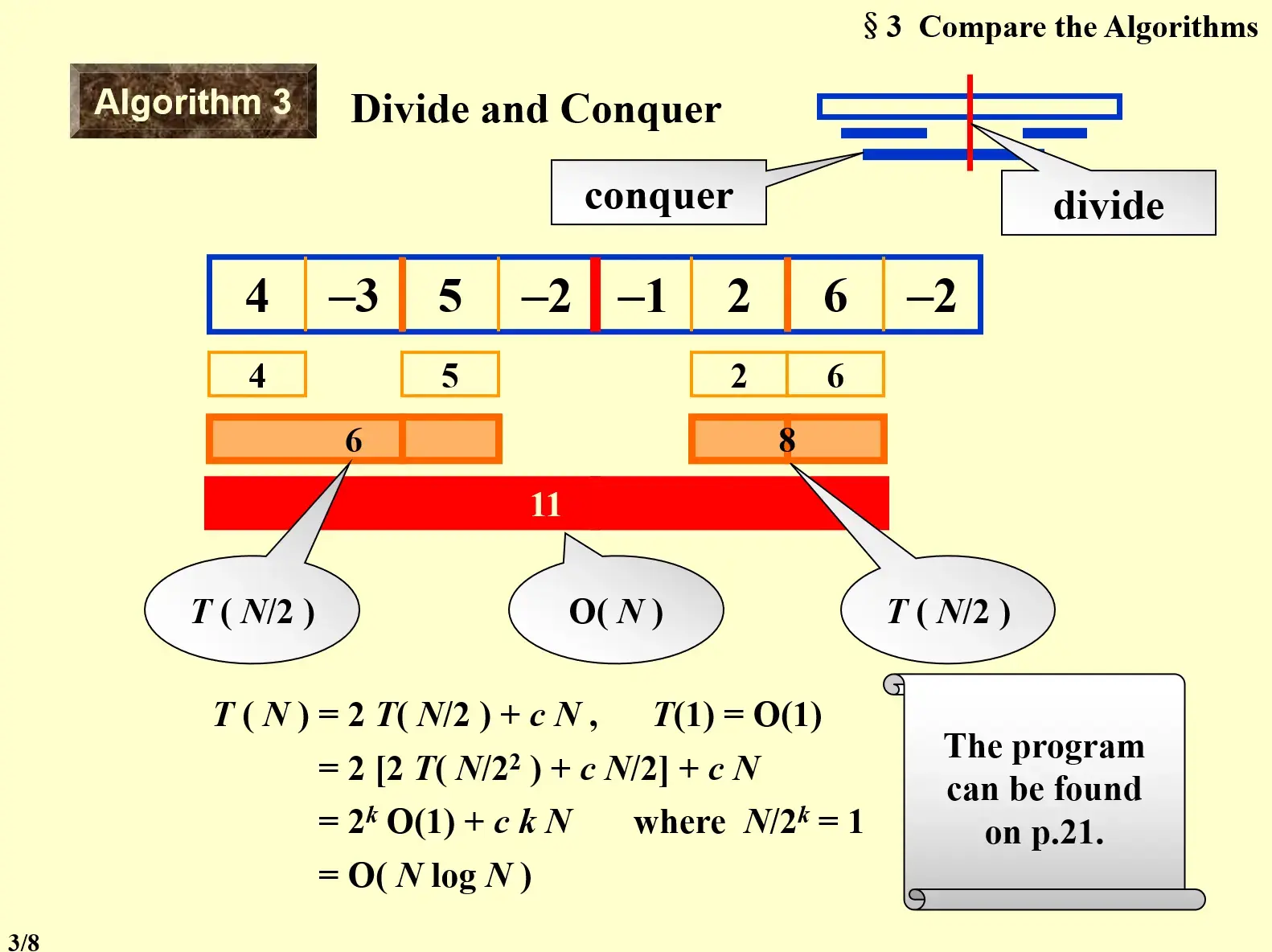
- 先 divide,找到每个最小单元(单个数)返回这个数
- 然后 conquer,需要进行判断
- 如果两个子序列连起来(加上中间部分)大于等于原来的两个子数列,则取这个大的
- 反之,取子序列中较大的‘
2.1.2 On-line Algotithm#
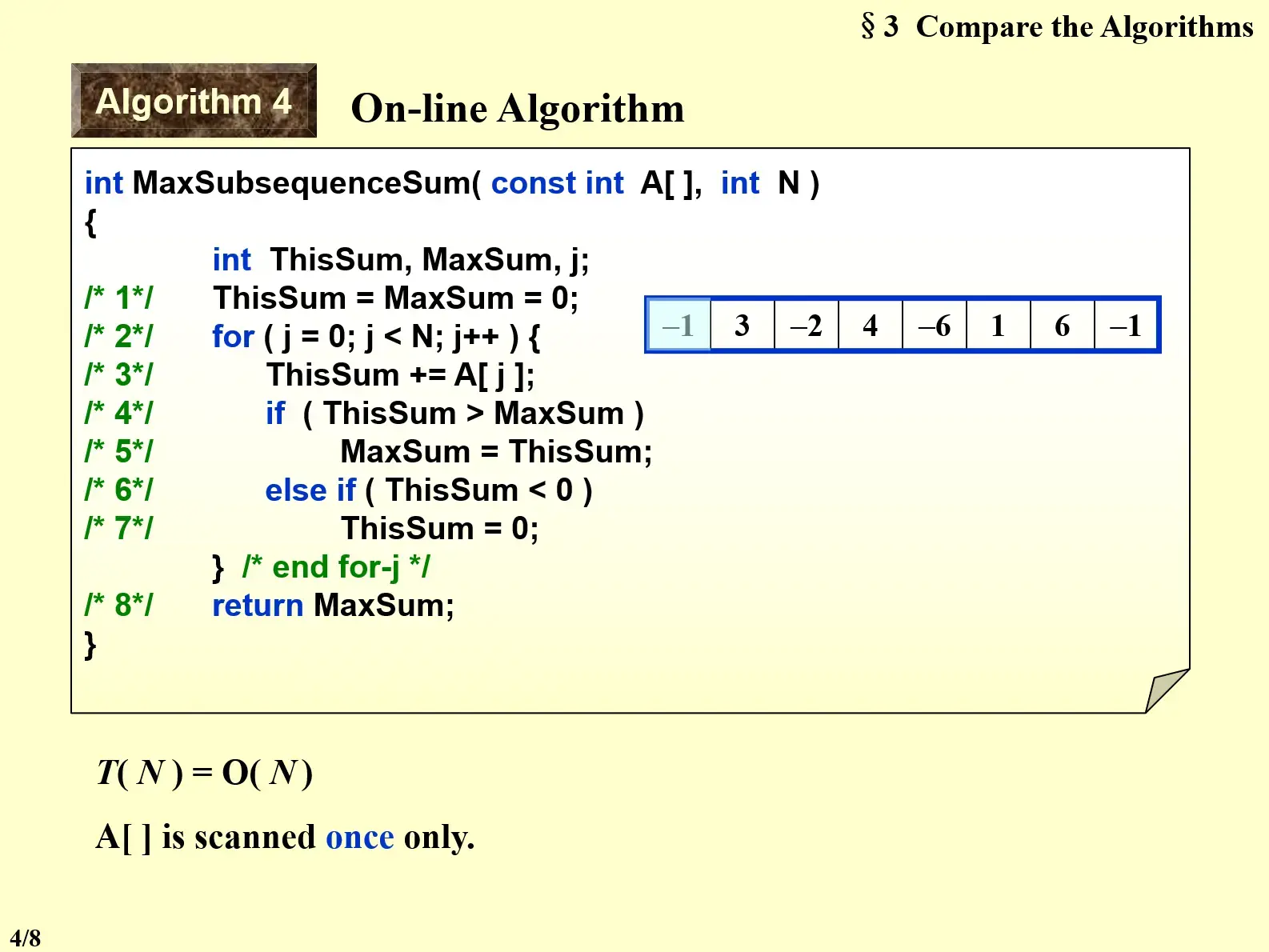
- 使用 ThisSum 记录这个子序列的和
- 如果 ThisSum 小于零,说明这个位置前面的子序列已经为负数,可以抛弃,重置 ThisSum 为 0
- 如果 ThisSum 大于 MaxSum,说明找到了新的最大和
3 Recursion Analysis#
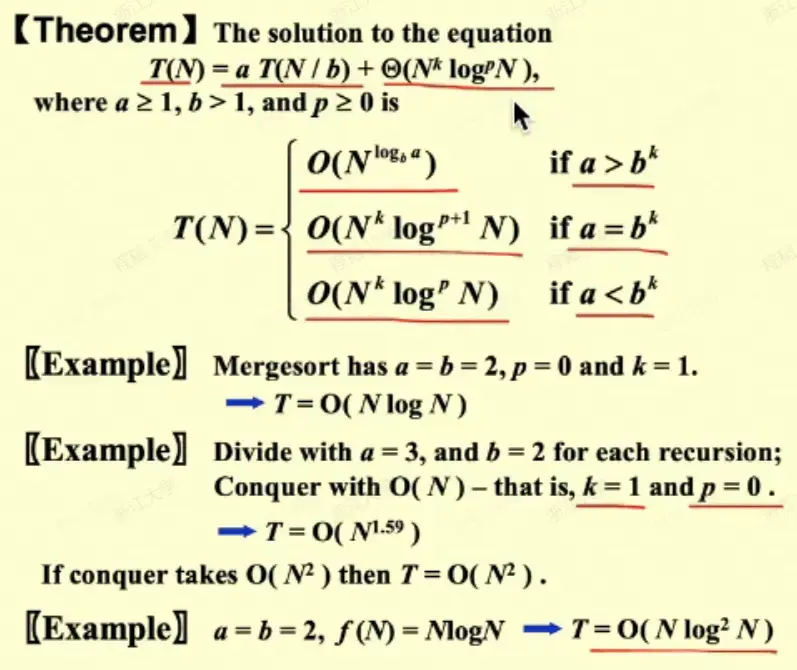
- 只需要记得前面的指数为 \(\log_ba\) 需要和后面的 \(k\) 进行比较
Example
- \(T(N)=2T(N/2)+N\) -> \(O(NlogN)\)
- \(T(N)=2T(N/2)+N\log N\) -> \(O(N\log^2 N)\)
4 HW#
4.1 Euclid's Algorithm 求 GCD 最大公约数#
- 辗转相除法 \(\mathrm{gcd}(a,b)=\mathrm{gcd}(b, a\,\mathrm{mod}\,b)\)
- 大除小
- 有余数,则计算小除余数
- 直到出现整除,输出最后那个除数就是答案
- 大除小
4.2 Exponentiation 快速幂#
- 例如计算 \(7^{10}\) 可以看作 \(7^{(101010)_2}=7^{2^5}*7^{2^3}*7^{2^1}\)
- 根据公式 \(n^{2^{m-1}}*n^{2^{m-1}}=n^{2^m}\) 快速计算出所有的 \(7^{2^1}, 7^{2^2}, 7^{2^3}, 7^{2^4}, 7^{2^5}\) 然后选择其中用到的量算出结果即可
4.3 PTA#

- 可能需要自己算一下,也可以记住这个答案
- 这其实很简单,上面的显然是 log,下面的因为每次除三又乘三,所以是 O(N)
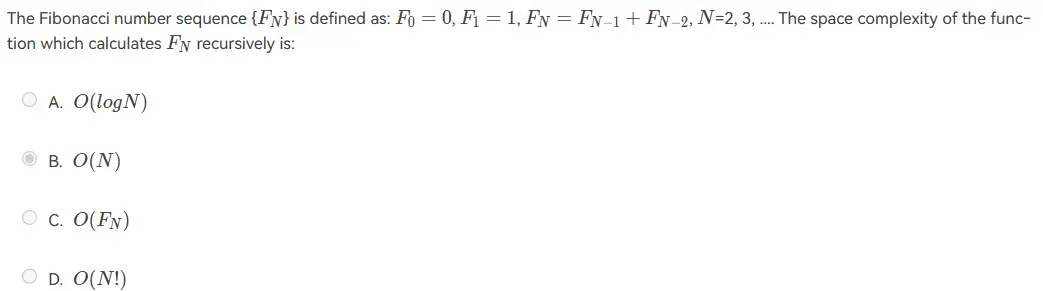
- 空间复杂度等于递归深度,而由于存在 \(F_{N-1}\),最大递归深度为 N