06 IO
1 Introduction#
- Three characters of I/O
- Behavior: input, output, storage
- Partner: human/machine
- Data rate: the peak rate at which data are transferred
- I/O 性能评价取决于应用场景
- Throughput 吞吐量 (e.g. data center)
- 数据传输速率
- I/O 操作处理速率
- Response time 响应时间 (e.g. PC)
- both (e.g. booking systems)
- Throughput 吞吐量 (e.g. data center)
-
I/O 设备的差异很大
1.1 Amdahl's Law#
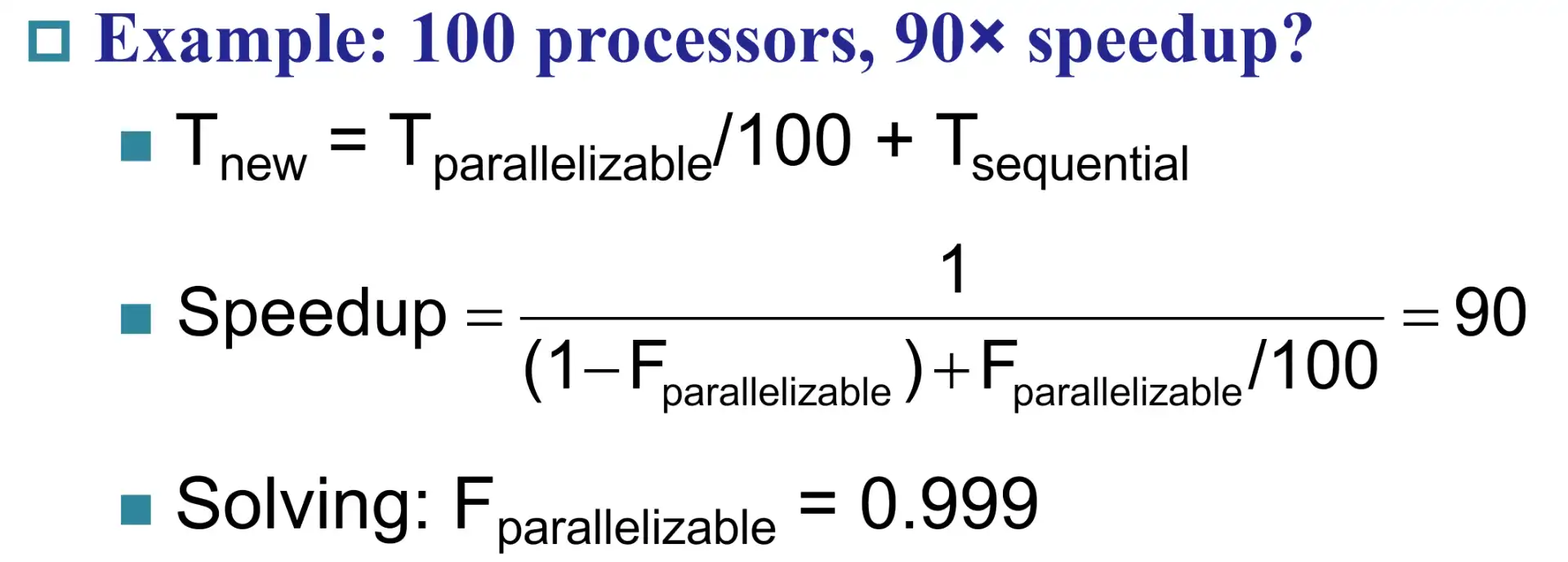
I/O 相比于 CPU 性能,更可能是瓶颈
2 Disks#
- SSD
- HDD
2.1 Access Time#
- Seek time: 磁头寻道时间,存在 min/maximum seek time
- Rotational latency: \(0.5\text{ rotation}/RPS\)
- Transfer time: 读取和传输一个 sector 的时间
- Disk controller: 控制器延迟
\[
\text{Access time}=\text{Seek time}+\text{Rotational Latency}+\text{Transfer time}+\text{Controller time}
\]
2.2 Dependability, Reliability, Availability#
- Dependability: reliability + availability
- Availability
- \(MTTF\) (mean time to failure) 发生错误的频率
- \(MTTR\) (mean time to repair) 修复时间
- \(MTBF\) (mean time between Failures) \(=MTTF+MTTR\)
- \(Availability=\frac{MTTF}{MTTF+MTTR}=\frac{MTTF}{MTBF}\)
2.3 Array Reliability#
- \(\text{Reliability of }N\text{ disks}=\text{Reliability of 1 Disk} / N\)
- \(\text{AFR (annual failure rate)}=\text{percentage of devices to fail per year}\)
- \(=8760 /\text{MTTF of 1 device}\)
- nines of availability
Three Ways to Improve MTTF
- Fault avoidance
- Fault tolerance
- Fault forecasting
2.4 RAID (Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks)#
- 提升 data availability
- 允许磁盘出错
- 数据冗余存储
- capacity penalty
- bandwidth penalty
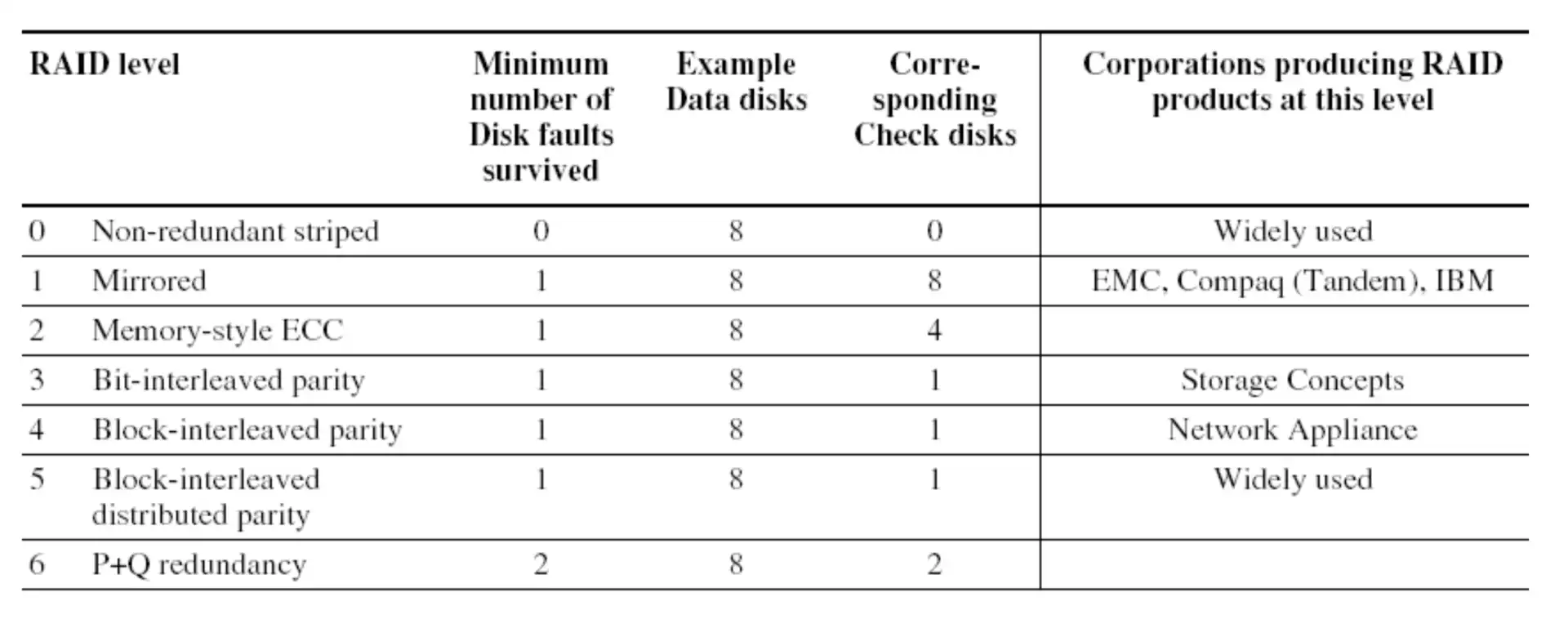
2.4.1 RAID 0: No Redundancy#
- 数据可以跨磁盘存储,但是没有冗余
- 分布式访问,能够提升 performance
2.4.2 RAID 1: Mirroring/Shadowing#
- 写开销增加
- 读性能能够优化,e.g. 从闲置磁盘读取
- 效率低,需要 100% 冗余
2.4.3 RAID 3: Bit-Interleaved Parity Disk#
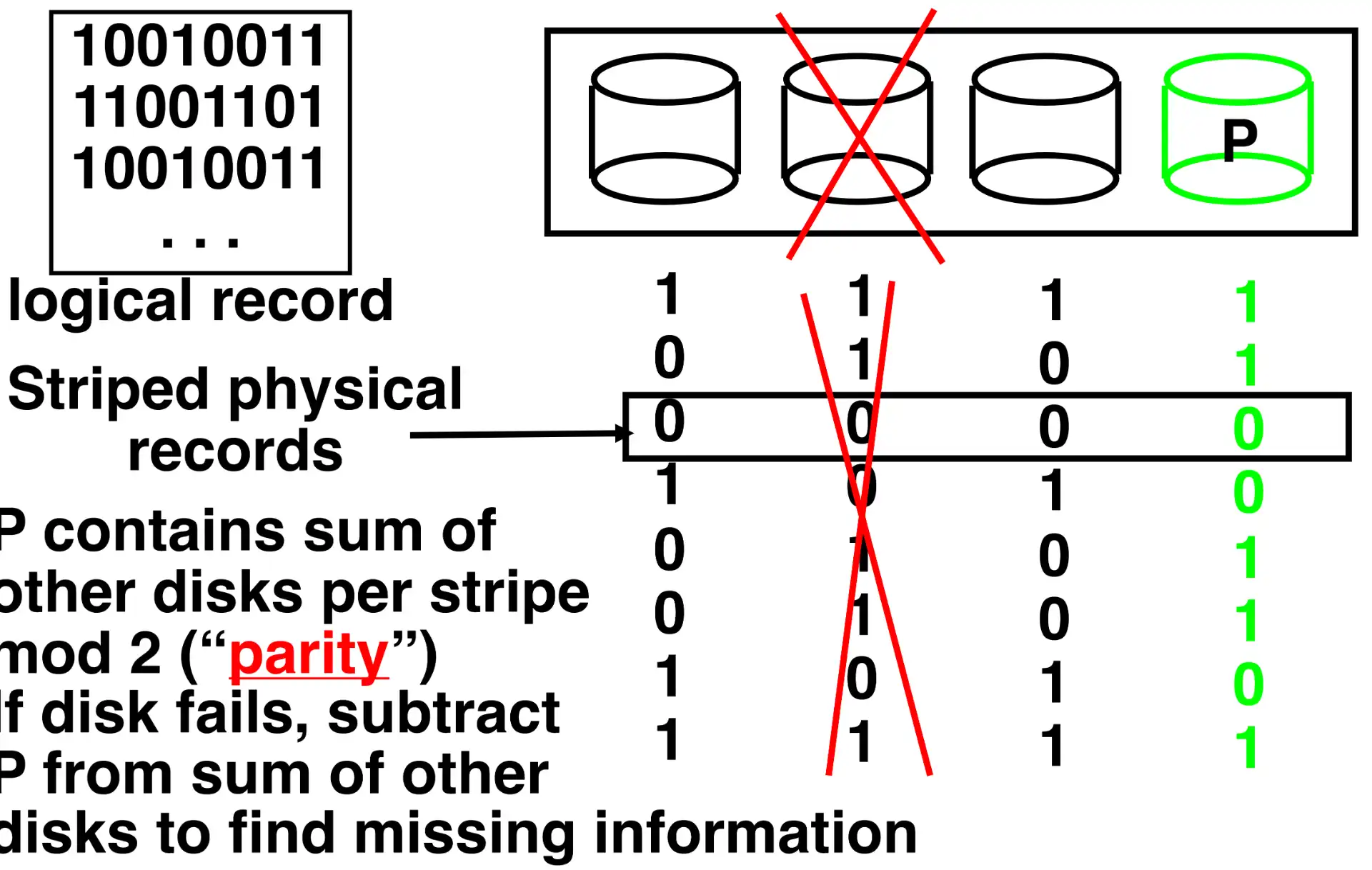
- 校验盘存储奇偶校验位
- 假设知道坏的盘,能通过其他盘恢复数据
-
能够实现热更换
-
如果出现错误,读取开销会很高需要读取所有其他磁盘
2.4.4 RAID 4: Block-Interleaved Parity#
沿用 RAID 3 思想,但是按照 block 打包 high I/O rate parity
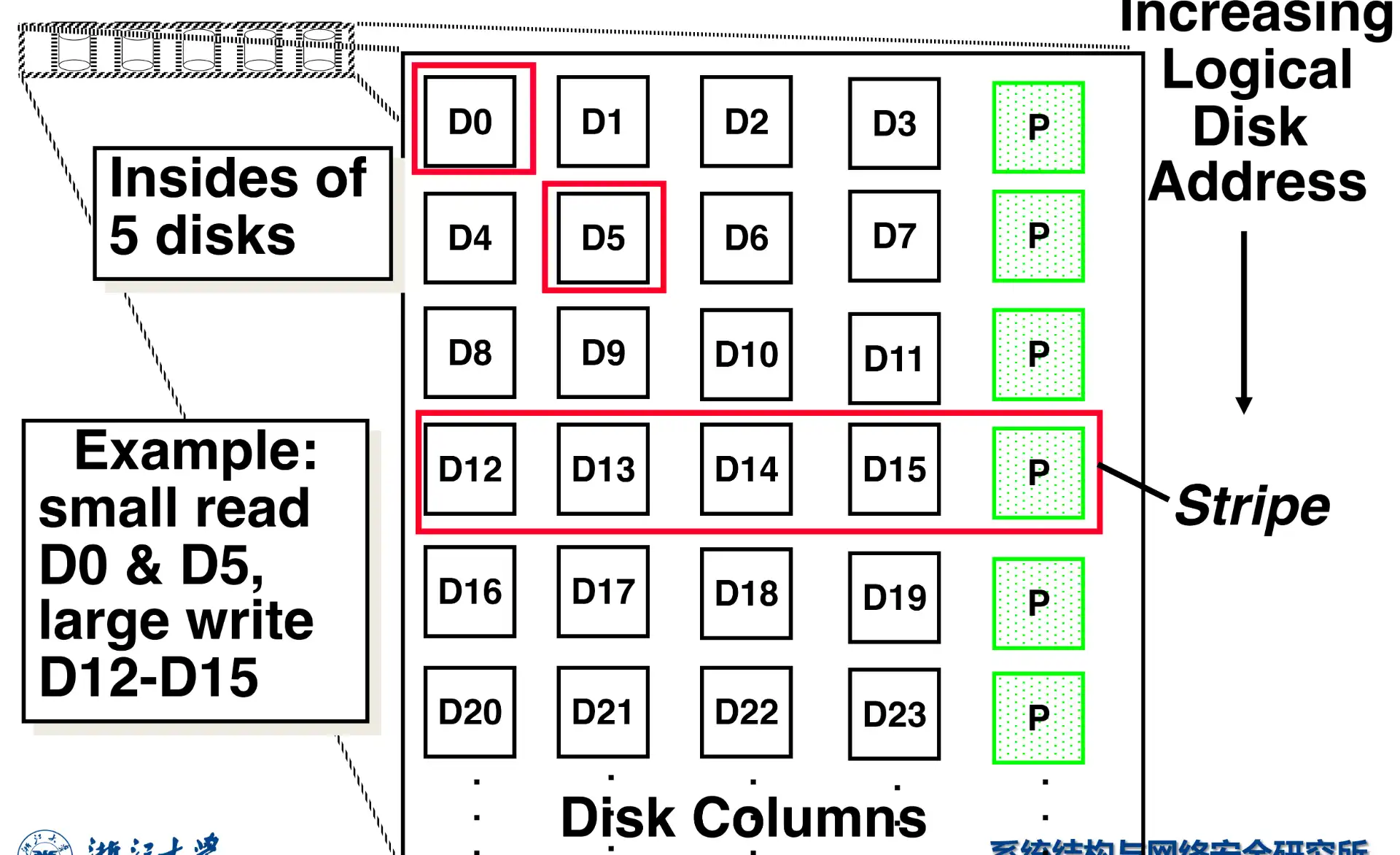
-
Problem: Small Writes
- 如果修改 D0,仍然需要重新读取所有盘来计算校验位
- Algorithm: \(P'=(D_{0}' \text{ XOR } D_{0})\text{ XOR }P\)
-
仍然存在问题,总是需要修改校验盘的数据
为什么 RAID 4 比 RAID 3 更好
- RAID 3 中,数据是按照 0 1 2 0 1 2 的顺序存储的,称为 striped physical records
- 如果访问较大的数据,需要同时读取所有数据盘
- 如果按照 block 分块,则更大概率只需要访问一个盘
2.4.5 RAID 5: High I/O Rate Interleaved Parity#
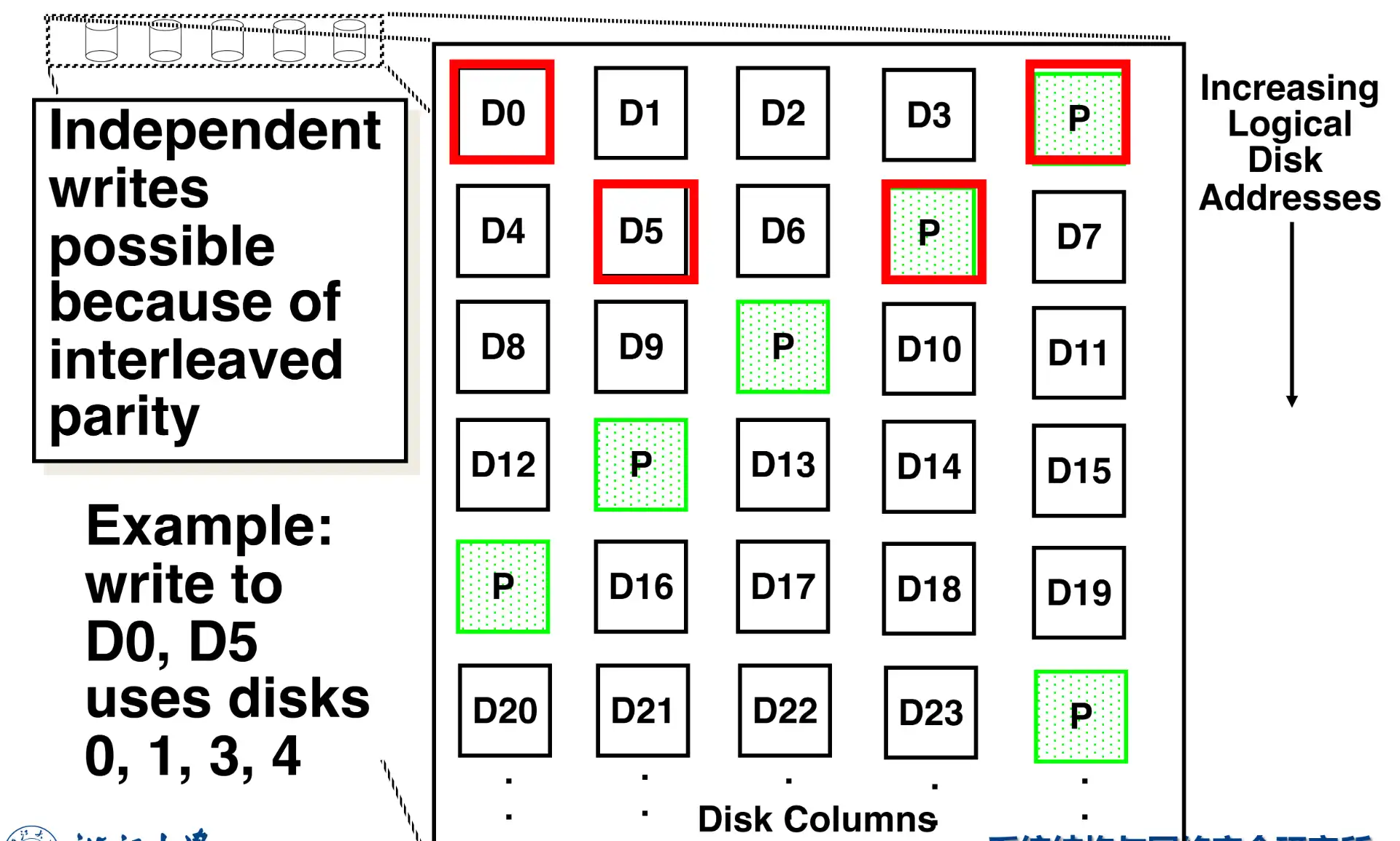
-
写时分散更新 parity
2.4.6 RAID 6: P+Q Redundancy#
允许两个磁盘同时出错
3 Buses and Other Connections#
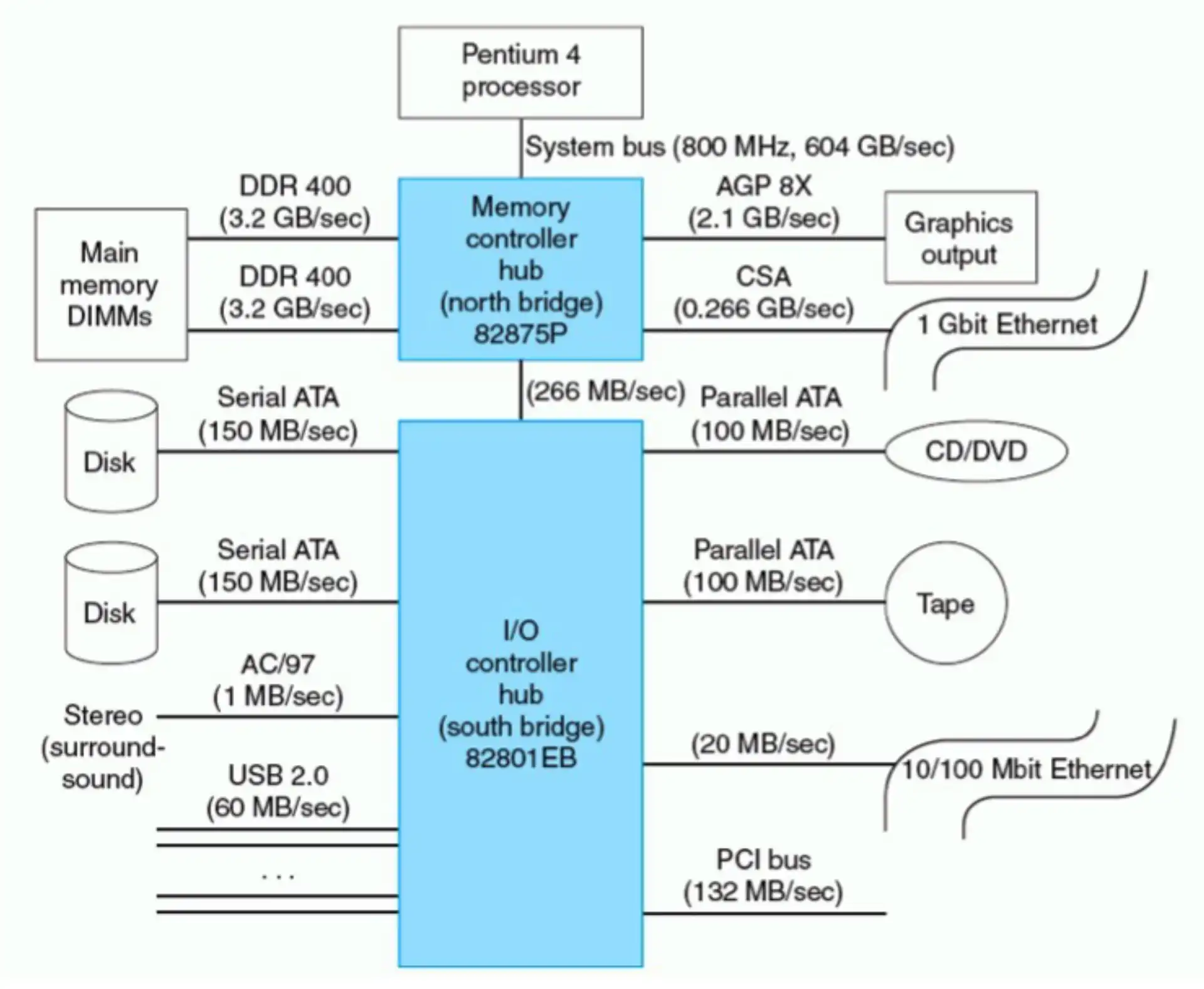
- North Bridge (Memory Controller) 速度更快
- Memory
- Graphic
- South Bridge (I/O Controller)
- Disk
- USB
3.1 Buses Basics#
- Shared communication link
- 2 types of lines
- Control lines
- Data lines
- 2 operations
- input: 数据从 device 到 memory
- output: 数据从 memory 到 device
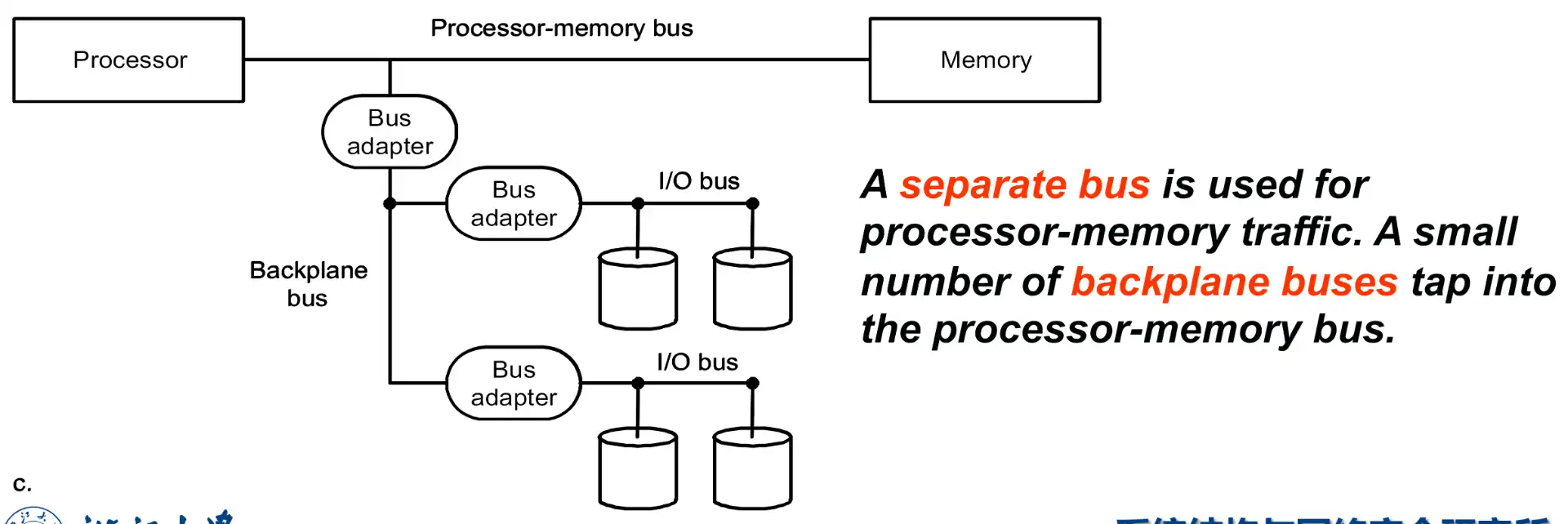
- 3 types of buses
- Processor-memory
- Backplane
- I/O
3.2 Synchronous vs. Asynchronous#
- sync
-
所有设备需要工作在同一频率
-
总线不能太长,否则 clock skew
-
fast and small
-
- async
- hand shaking
3.2.1 Handshaking Protocol#
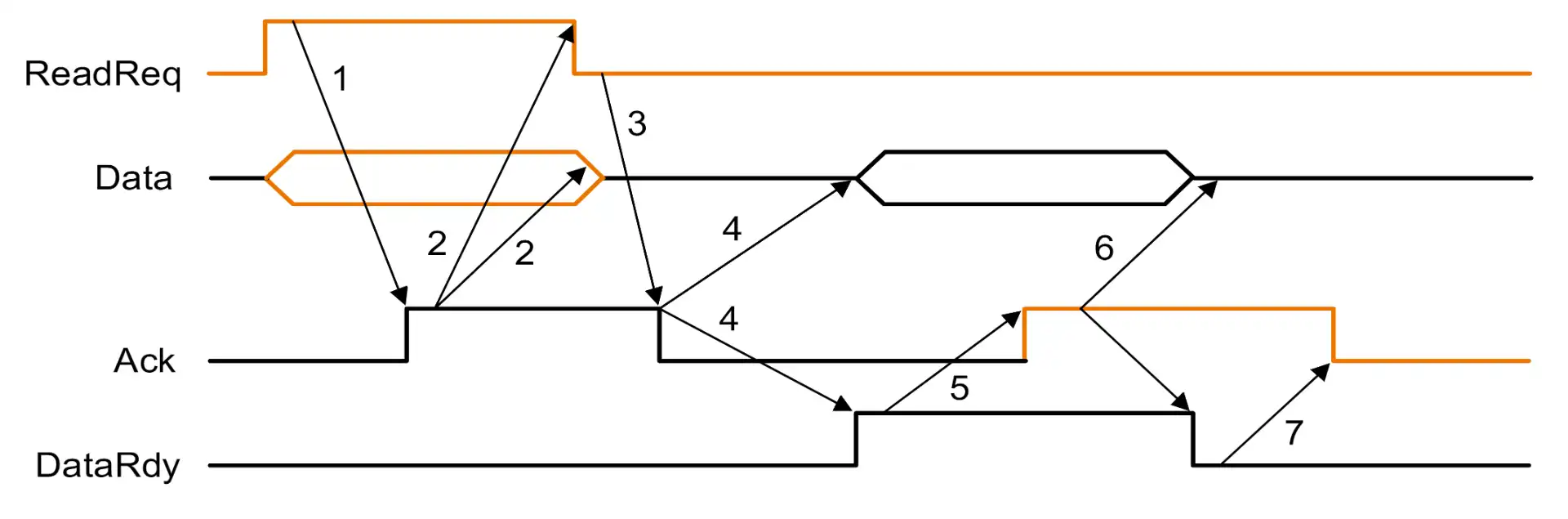
橙色信号是 I/O device 发出的,黑色信号是内存发出的 除了 4,其他箭头都表示 bus 延迟
- memory 得到
ReadReq信号,读入 bus 上的 addr,然后升起Ack信号 - I/O device 得到
Ack信号,降低ReadReq信号 - memory 得到
ReadReq下降,降低Ack,释放总线 - memory 准备好 data 之后,升起
DataRdy,将 data 放到 bus 上 - I/O device 得到
DataRdy信号,读入 data,升起Ack - memory 得到
Ack,降低DataRdy - I/O device 得到
DataRdy下降,降低Ack,释放总线
3.2.2 Arbitration 仲裁#
设置 bus master (CPU is always a bus master),管理请求
- I/O device 向 CPU 发出请求
- CPU 响应并给 memory 访存的 bus control signal
- I/O device 开始访存,CPU 进行监控
仲裁的两个考虑因素
- bus priority 设备优先级
- fairness 总线长度问题
3.2.3 计算题#

- sync
- 传输 addr 50ns
- 访存 200ns
- 传输 data 50ns
- 300ns, \(\text{bandwidth}=4\text{B}/300\text{ns}=13.3\text{MB/s}\)
- async
- step 1: 40ns
- step 2, 3, 4: \(\max(2 \times 40\text{ns}, 200\text{ns})=200\text{ns}\)
- step 5, 6, 7: \(3\times 40\text{ns}=120\text{ns}\)
- 360ns, \(\text{bandwidth}=4\text{B}/360\text{ns}=11.1\text{MB/s}\)
3.2.4 Increase bandwidth#
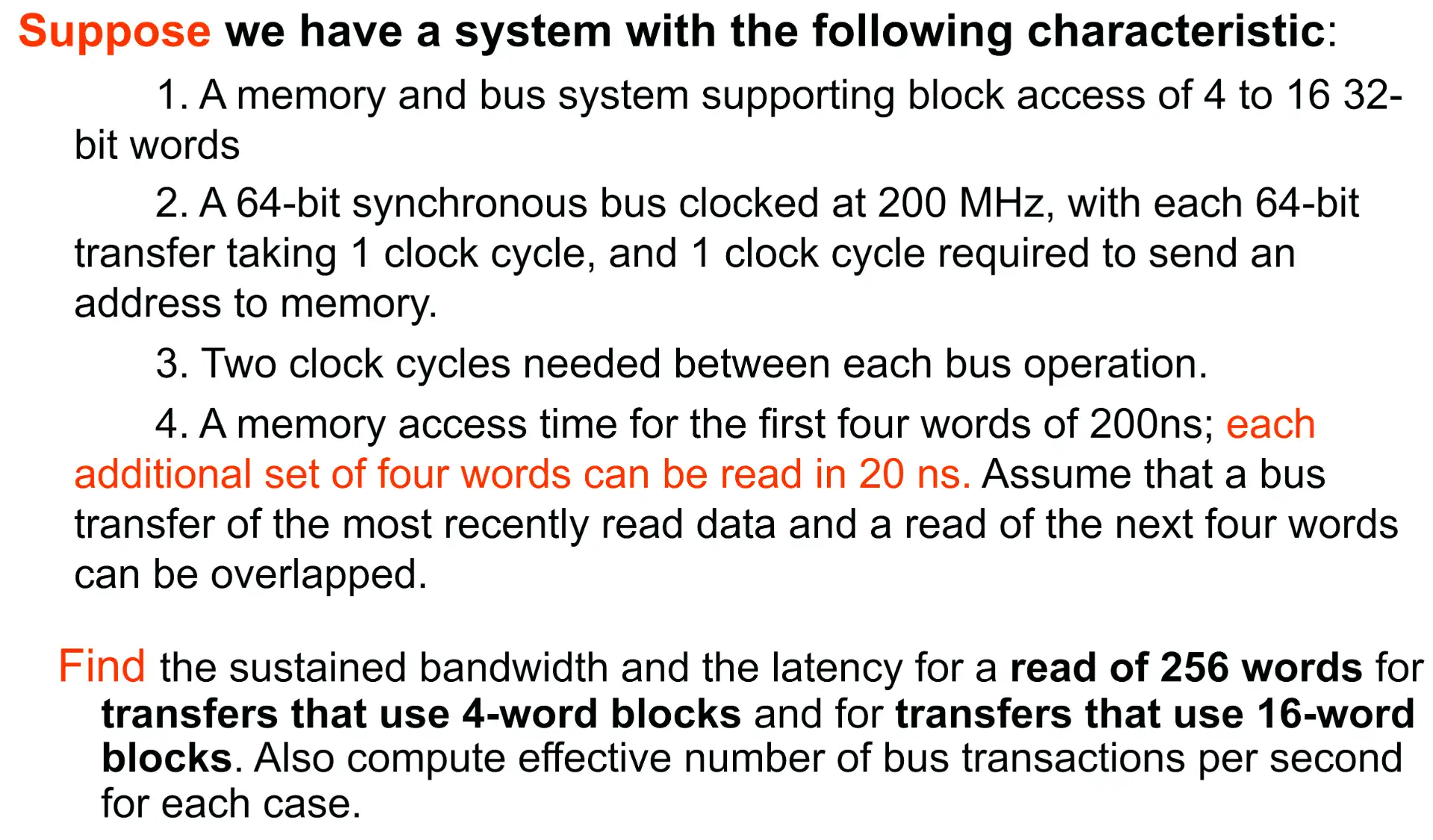
- 4 word
- send addr to memory: 1 cycle
- read memory, 200ns, 40 cycles
- send data: 2 cycles,因为需要传输 2 次,一次 64 bit
- between operation: 2 cycles
- total: \(45\text{cycles}\times 64\text{blocks}=2880\text{cycles}\)
- 16 word
- 单次 bus operation
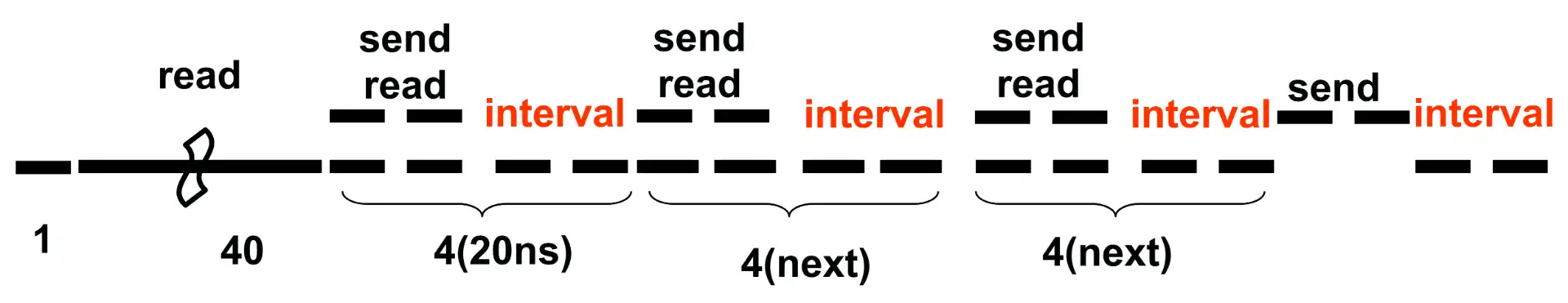
- 内存访存一次得到 4 个 word
- 总线宽度是 64 bit,同时传输 2 word,一次访存需要两个 cycle 来传输
- 一个 operation 读取 16 个 32 word,需要读取 4 次数据,其中第一次需要 40 cycle,其他只用 4 cycle,每次取数据的间隙就能够完成上一轮 4 个 word 的传输,所以存在 interval
- 前三个 interval 是访存时间决定的
- 最后一个 interval 是因为总线存在 2 个周期的延迟
- 256 word 一共需要 16 次 operation: \(57\text{cycles}\times 16\text{blocks}=912\text{cycles}\)
- 单次 bus operation
Tip
使用更大的 block 能够提升总线带宽
4 Interfacing I/O Devices#
4.1 I/O 指令的种类#
- memory-mapped I/O: 将设备映射到内存地址,使用访存指令就可以进行 I/O 设备控制
- special I/O inst:
in a1, port - command port, data port: status reg, data reg...
4.2 I/O to processor#
- polling: 每隔多少周期检查一次 I/O
- interrupt: I/O 中断
- DMA (direct memory access): device controller 在 I/O 和 memory 中传输数据
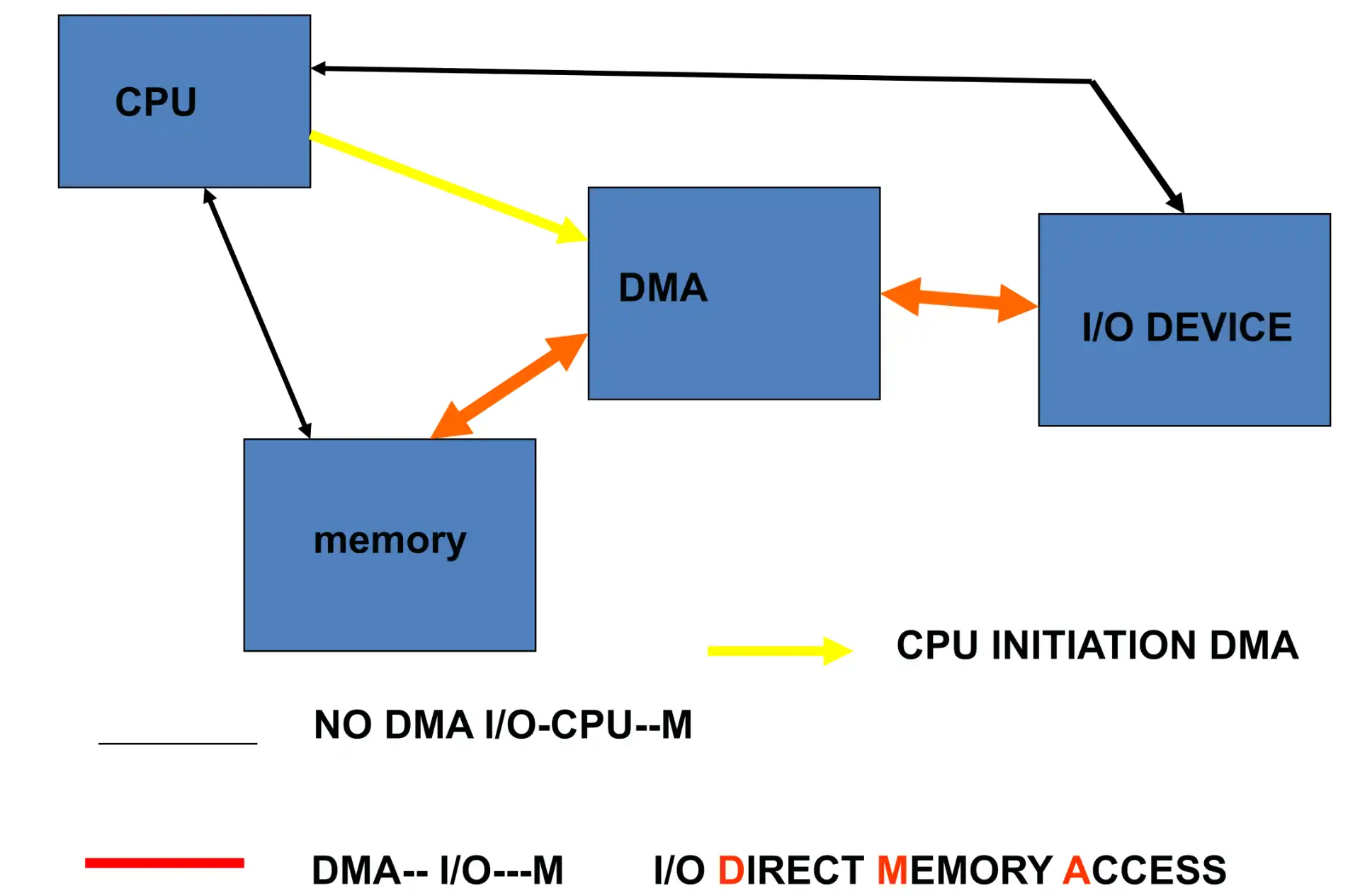
-
在传输大量数据时,CPU 只用指示 DMA 进行传输,减少了 CPU 占用
-
- DMA (direct memory access): device controller 在 I/O 和 memory 中传输数据
计算题
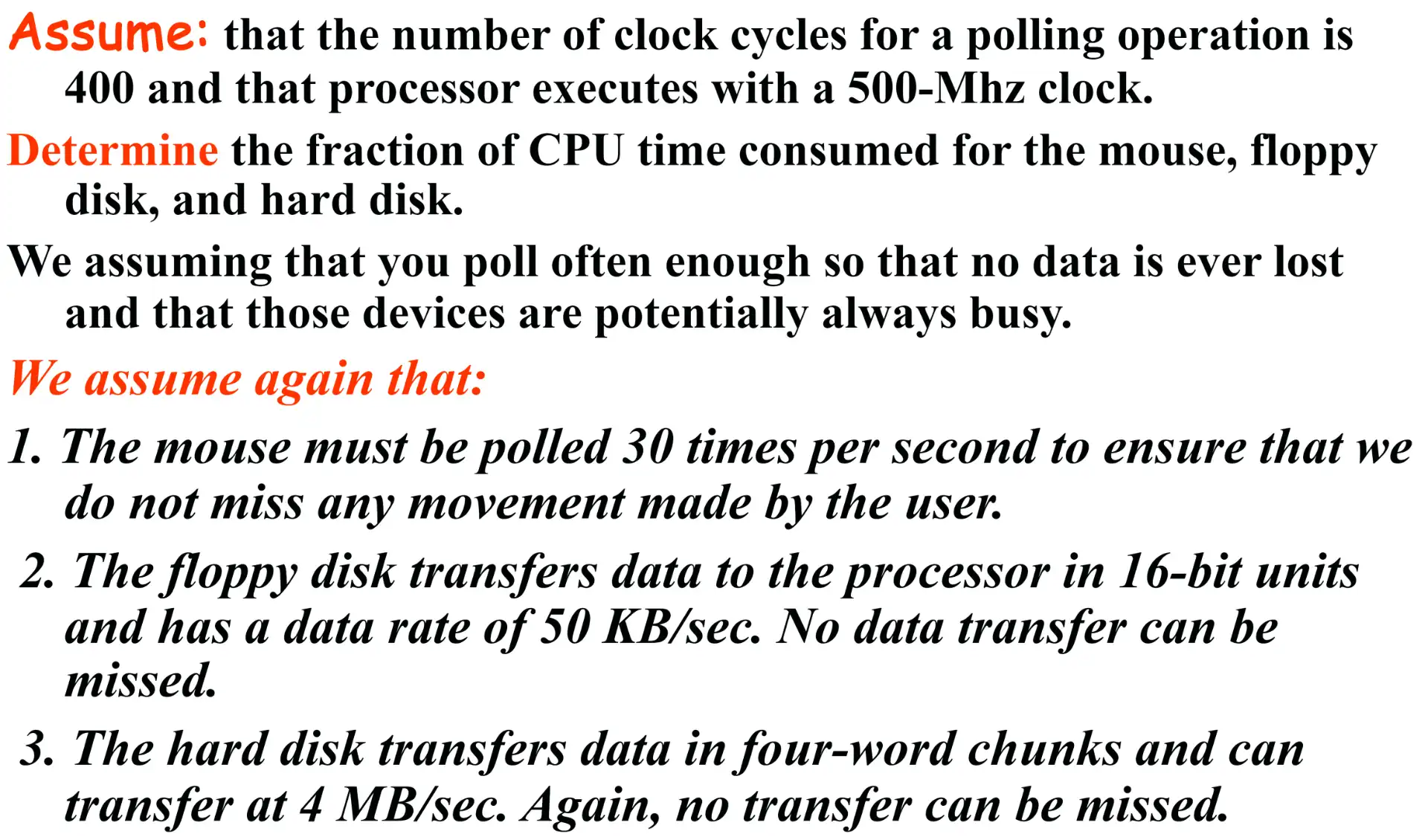

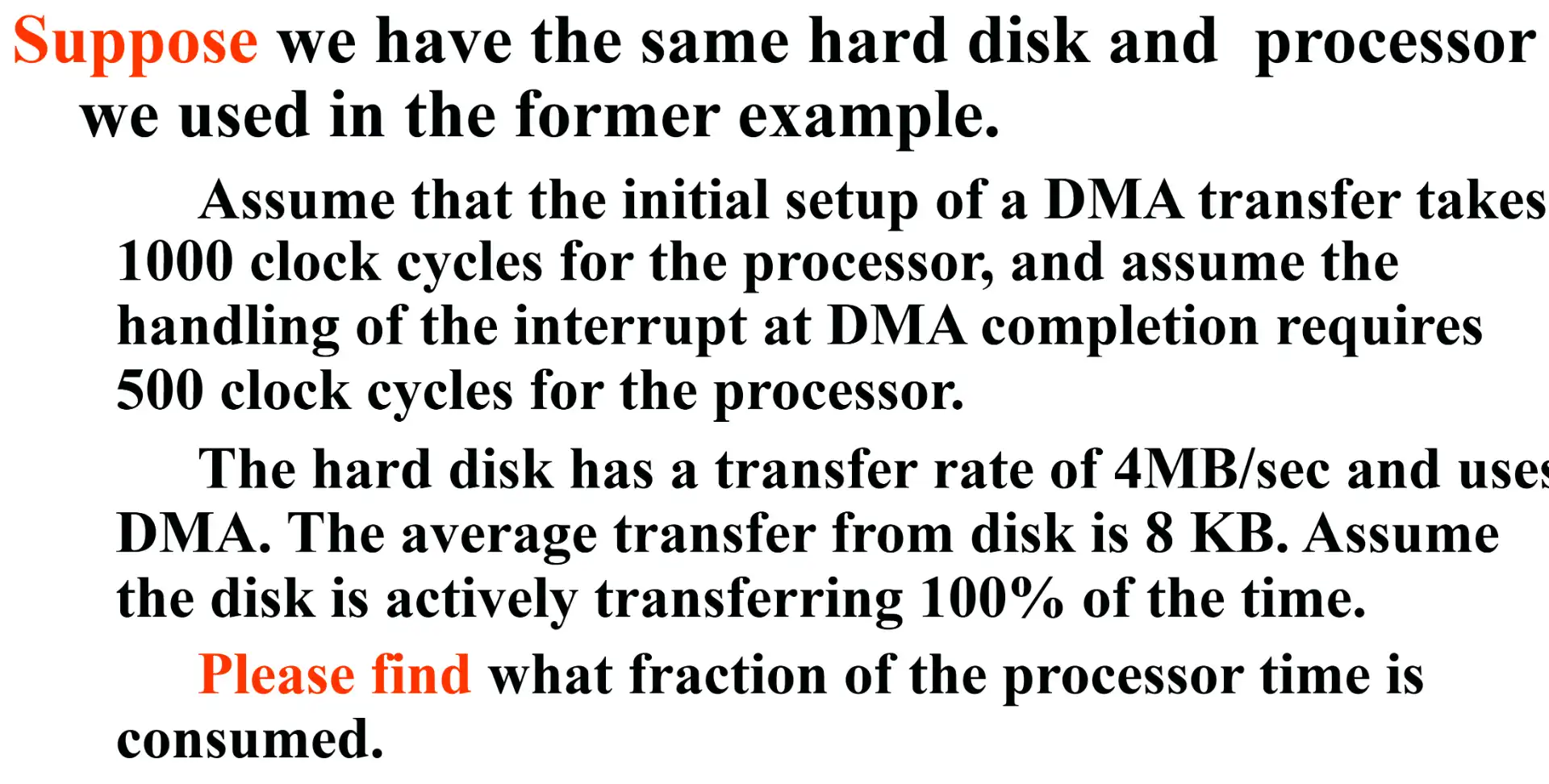
这几道题是为了证明,interrupt with DMA > interrupt > polling 虽然题目中疑似 polling 进行连续数据传输会更快,这是因为 interrupt 会有 overhead;但是在数据访问频率很低或访问数据很少的时候,interrupt 效率会更高,这是因为 polling 为了不丢失数据总是需要高频问询
5 I/O System#
找到 I/O 瓶颈
Question

