04 The Processor Pt2
1 Introduction#
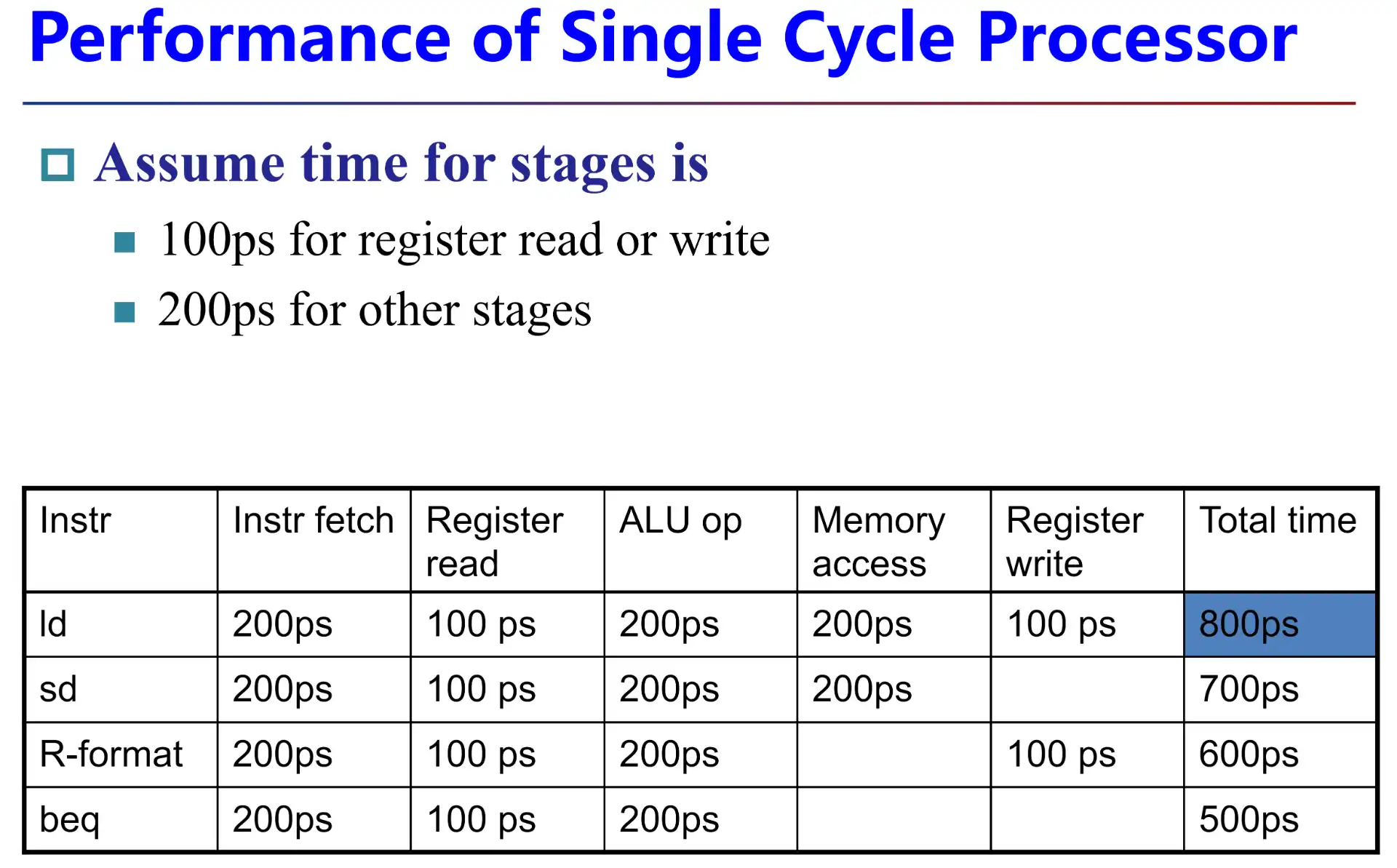
- 期中
ld指令使用了所有部分,其他指令都是从ld做减法,减去未使用的部分 - 设计主频的时候,需要按照最长周期来设计,才能符合单周期的定义
- longest delay determines clock period
- critical path: load instruction
- 变频不能在指令尺度完成
2 RISC-V Pipiline#
- IF: inst fetch from inst memory
- ID: inst decode & reg read 放一起是因为读寄存器很快
- EX: execute operation or calculate address
- MEM: access mem operand
- WB: write result back to reg
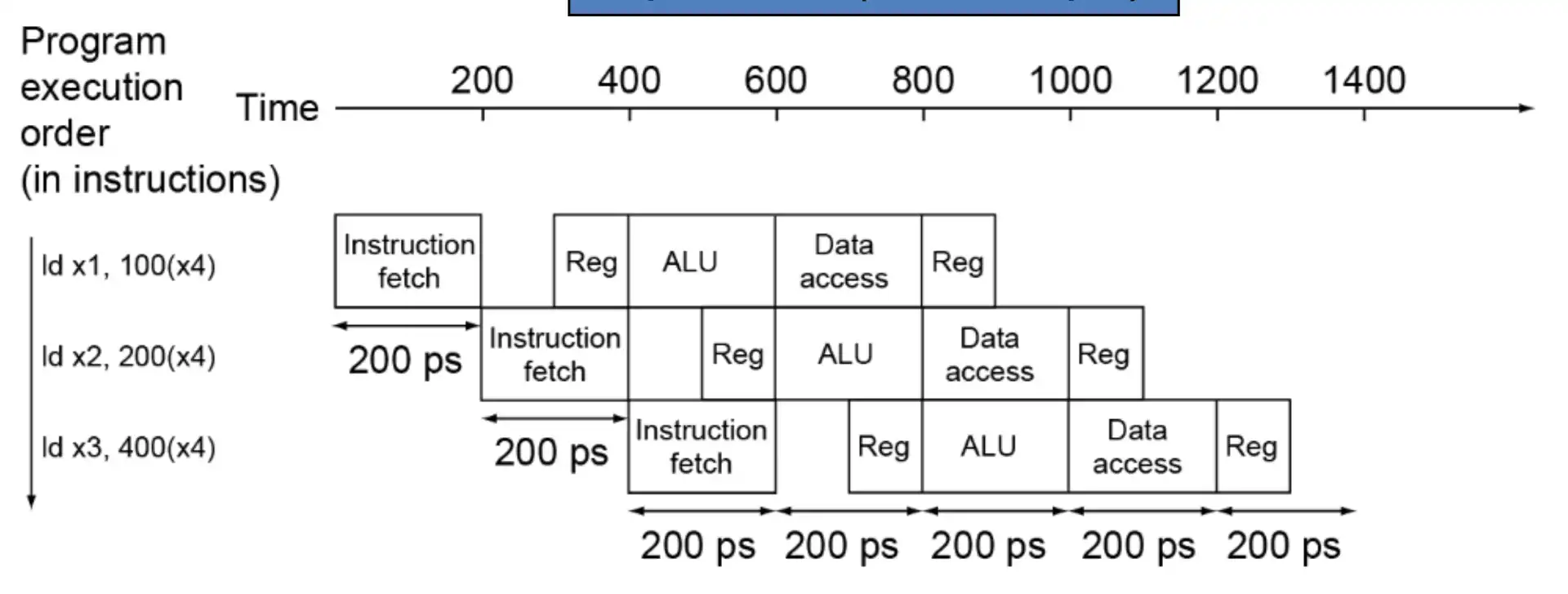
-
注意这里的 reg 设计,读在后写在前,思考有什么好处
- 一个周期内能够同时读写
- 如果出现上下指令数据依赖,由于先写后读,能够解决部分问题
- Speedup due to increased throughput 增加了吞吐量,未提升执行速度,但带来了提速
2.1 Piplining and ISA Design#
- 指令定长,inst fetch and decode 更简单
- 指令格式固定,decode and read reg in one step
2.2 Hazards#
- Structure hazard:同一个模块同时被不同指令使用,是设计 ISA 的人需要考虑的
- Data hazard:数据依赖,第二条指令需要第一条指令的结果
- Control hazard:前面的指令对后面指令的 control action 产生影响,下一步的 fetch 取决于上一步是否
beq
2.2.1 Data Hazards#
- 操作称为 stall 停机
- 流水线中加入的称为 bubble
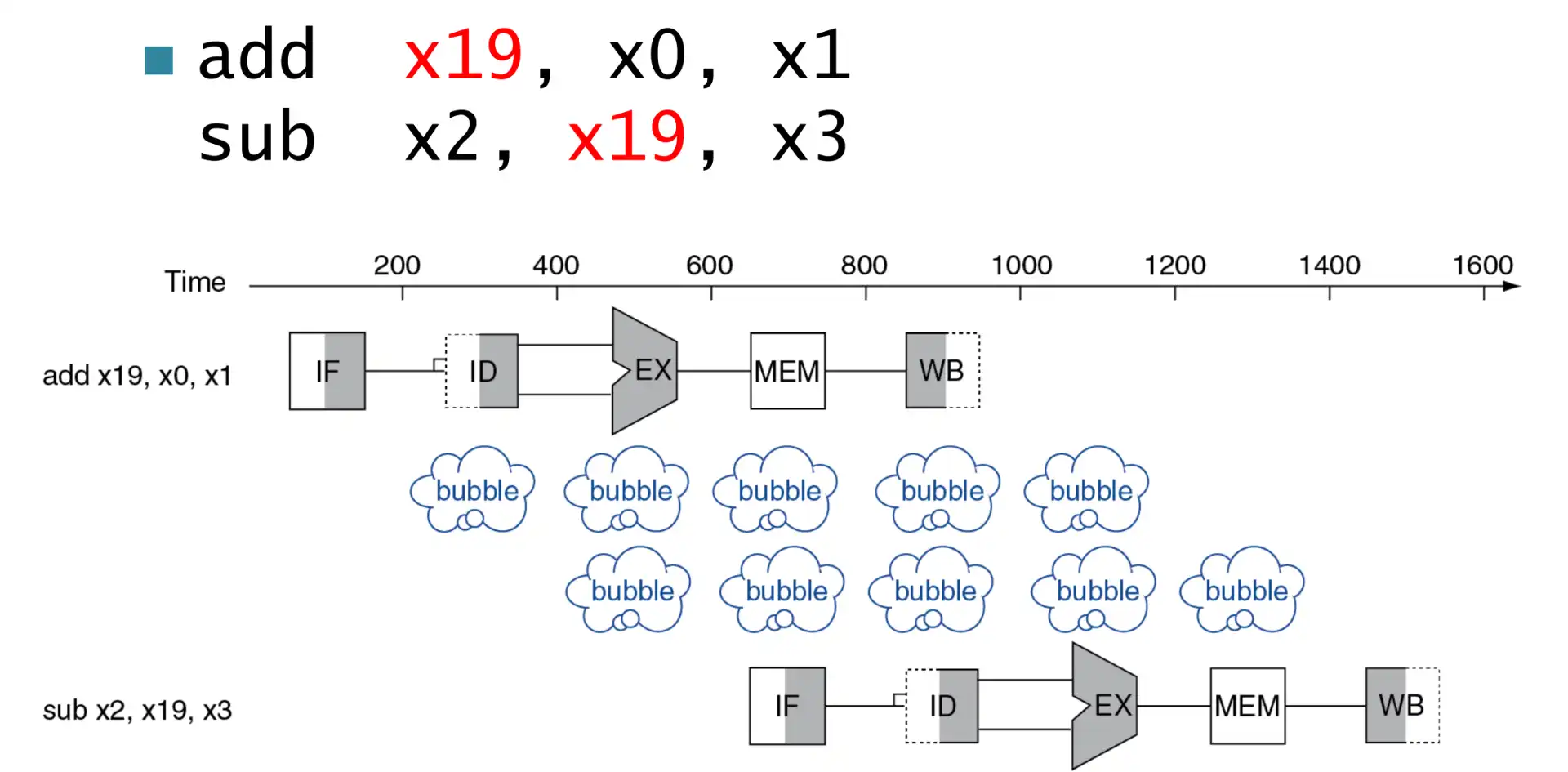
-
图中灰色的是真正在使用的部分
- 图中
WB, ID刚好对齐,于是能够解决 data hazard
2.2.1.1 Compute-Use 原本没有名字 可以不停#
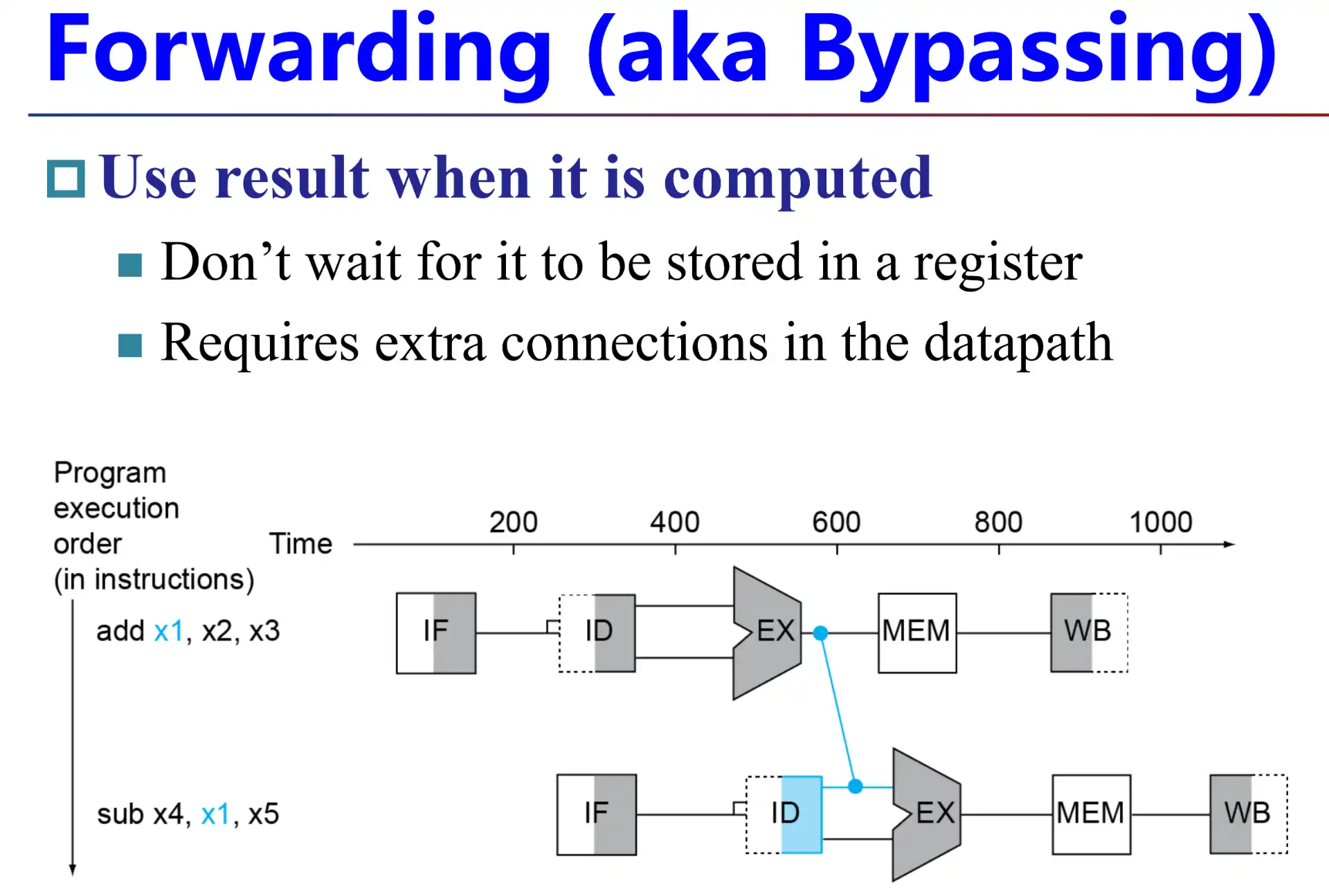
- 检测上下都是 R-type,产生依赖,而且第一条的
rd是第二条的rs,可以不进行 stall,但是需要修改 datapath
2.2.1.2 Load-Use Data Hazard 必停一次#
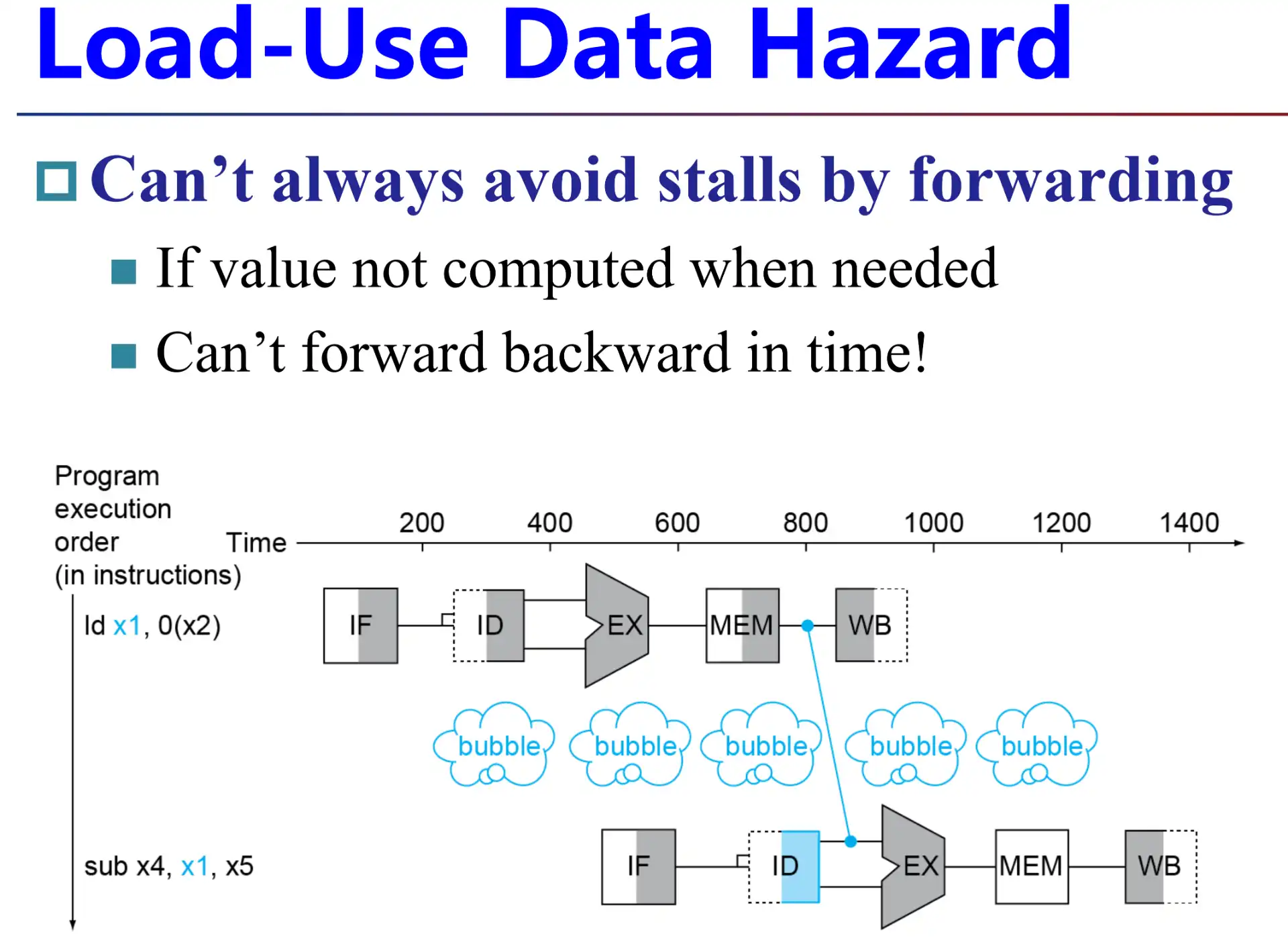
- 如果 load 之后马上使用,那么即使使用 forwarding 技术,也必然有一级 bubble
Code Scheduling
可以在编译的时候让 ld 提前,于是可以从软件层面规避
2.2.1.2.1 example#
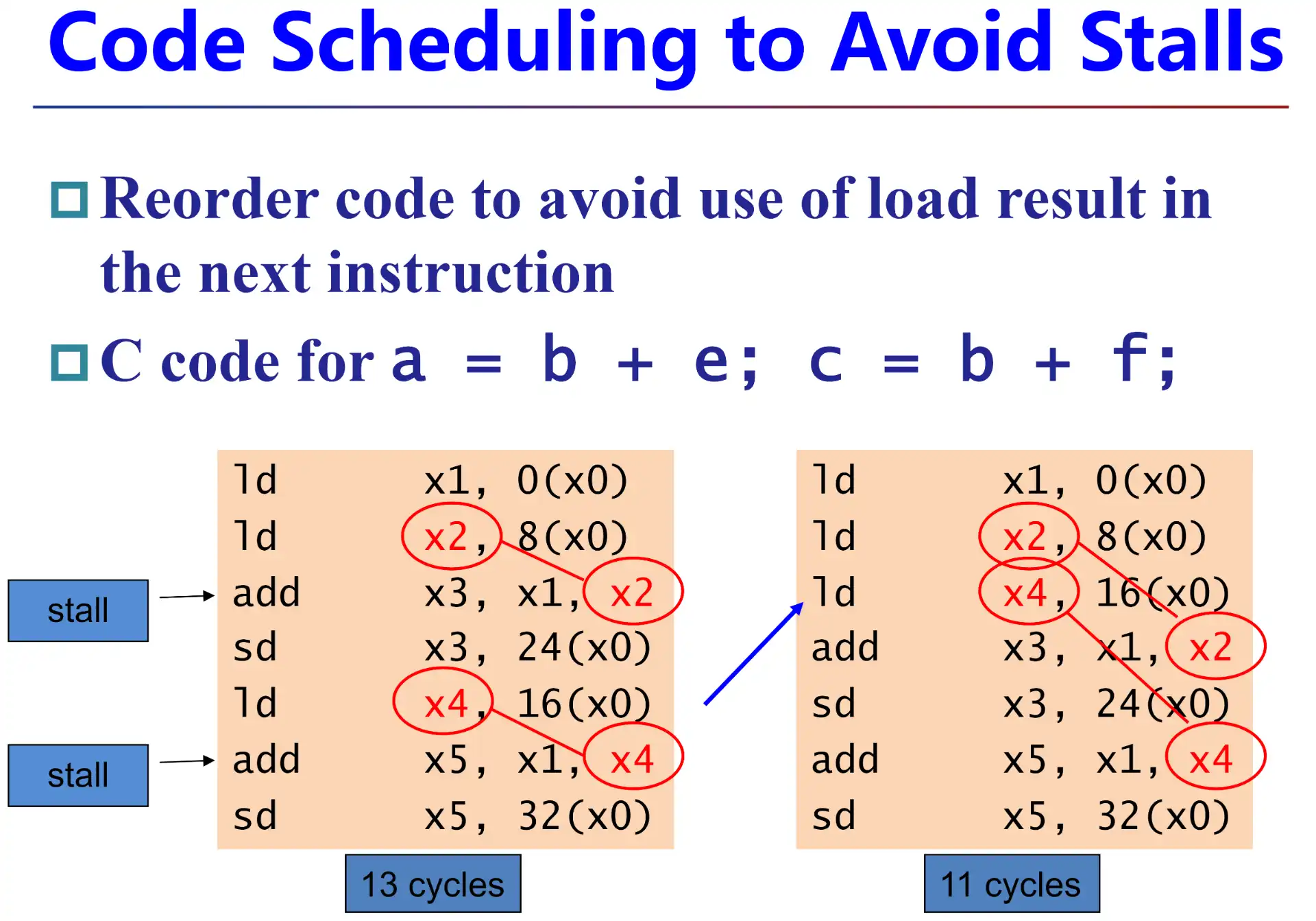
- 左侧:2 次 load-data,7 条指令,开头结尾 4,一共 13
- 右侧就没有 load-data 问题
2.2.2 Control Hazards#
- Branch 决定了控制流,下一个 IF 取决于 branch 的结果
- 可能的解法:在 ID 级放一个比较器
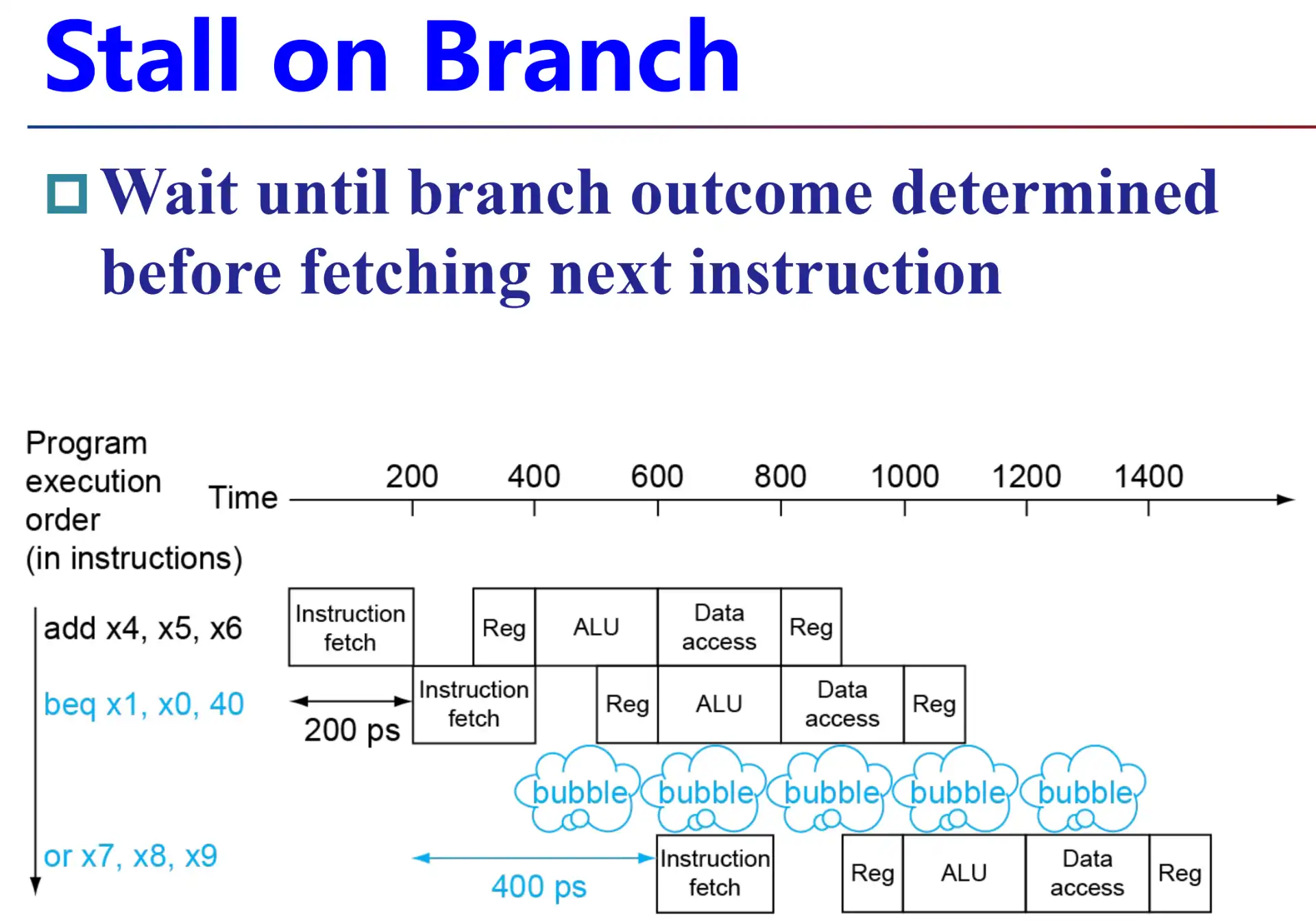
Warning
画流水线示意图的时候,stall 直接按照 NOP 一行来画最方便,每一条指令不同阶段之间不会有空,永远是 if id ex ma wb
-
为什么不能提前到 IF 级
- IF 级还没有进行 decode,无法判断是什么指令
- Prediction:直接执行 branch not taken?
- 有开销,如果最后 branch taken,那么需要擦除已经计算的内容,开销更大
2.2.2.1 Branch Prediction#
- Static: 编译的时候产生的预测
- 如 loop 应该按照 branch taken,taken 的频率比 untaken 更高
- Dynamic: 执行的时候进行预测
- e.g. record recent history of each branch
- when wrong, stall while re-fetching and update history
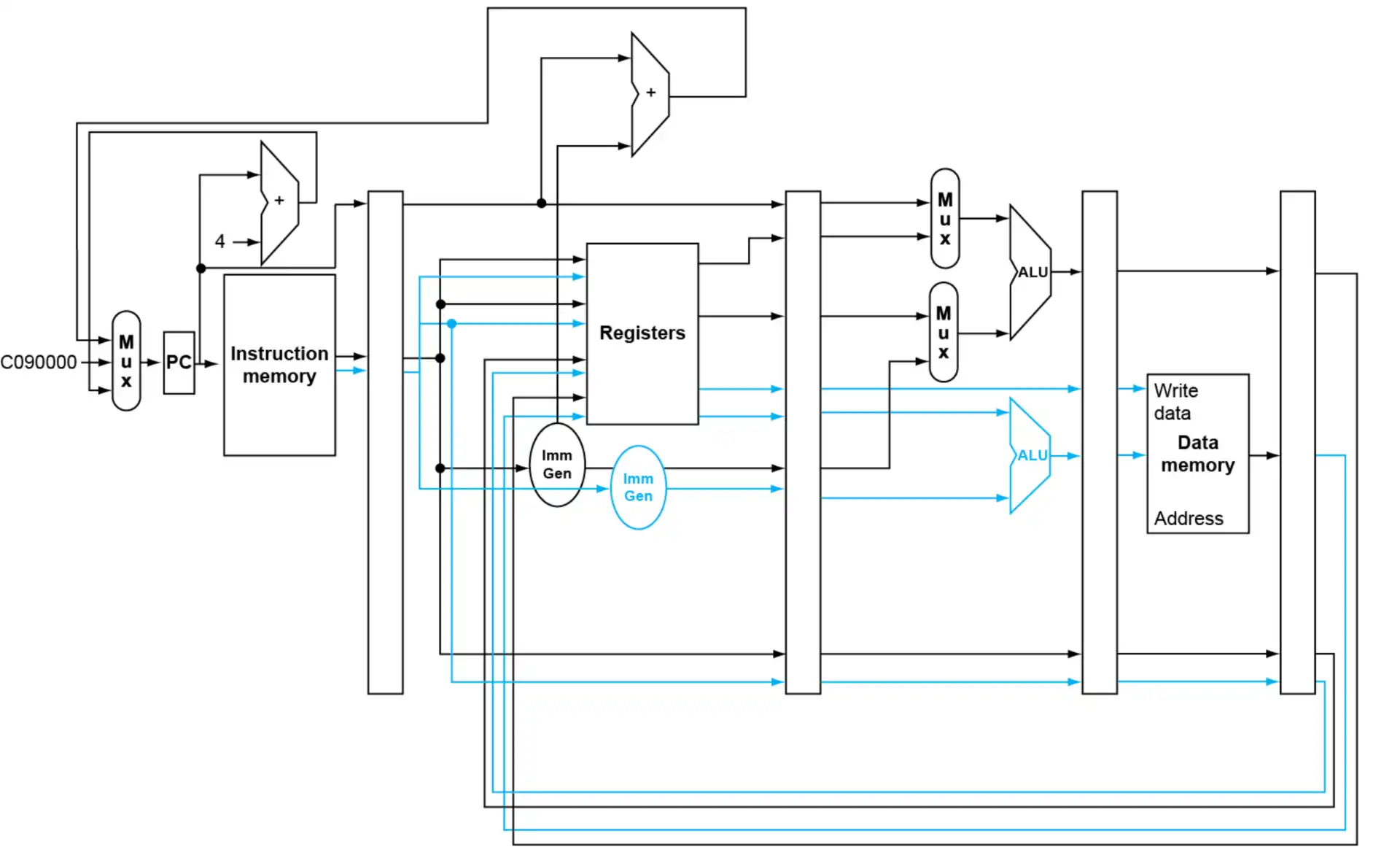
3 Pipeline Overview#
3.1 Datapath#
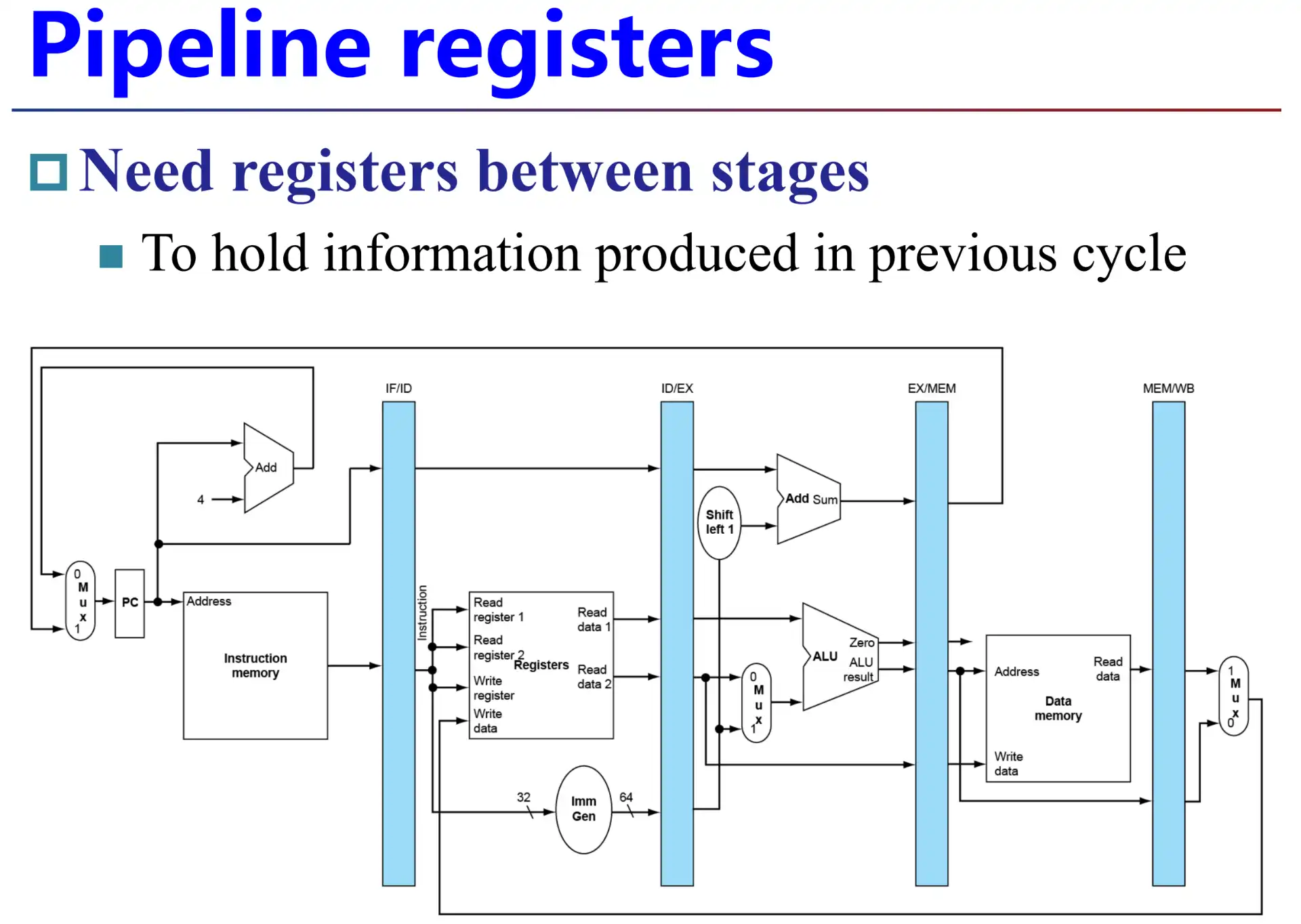
- 命名方式,上/下级简称
- 单周期流水线图/多周期流水线图
两种流水线表示方法
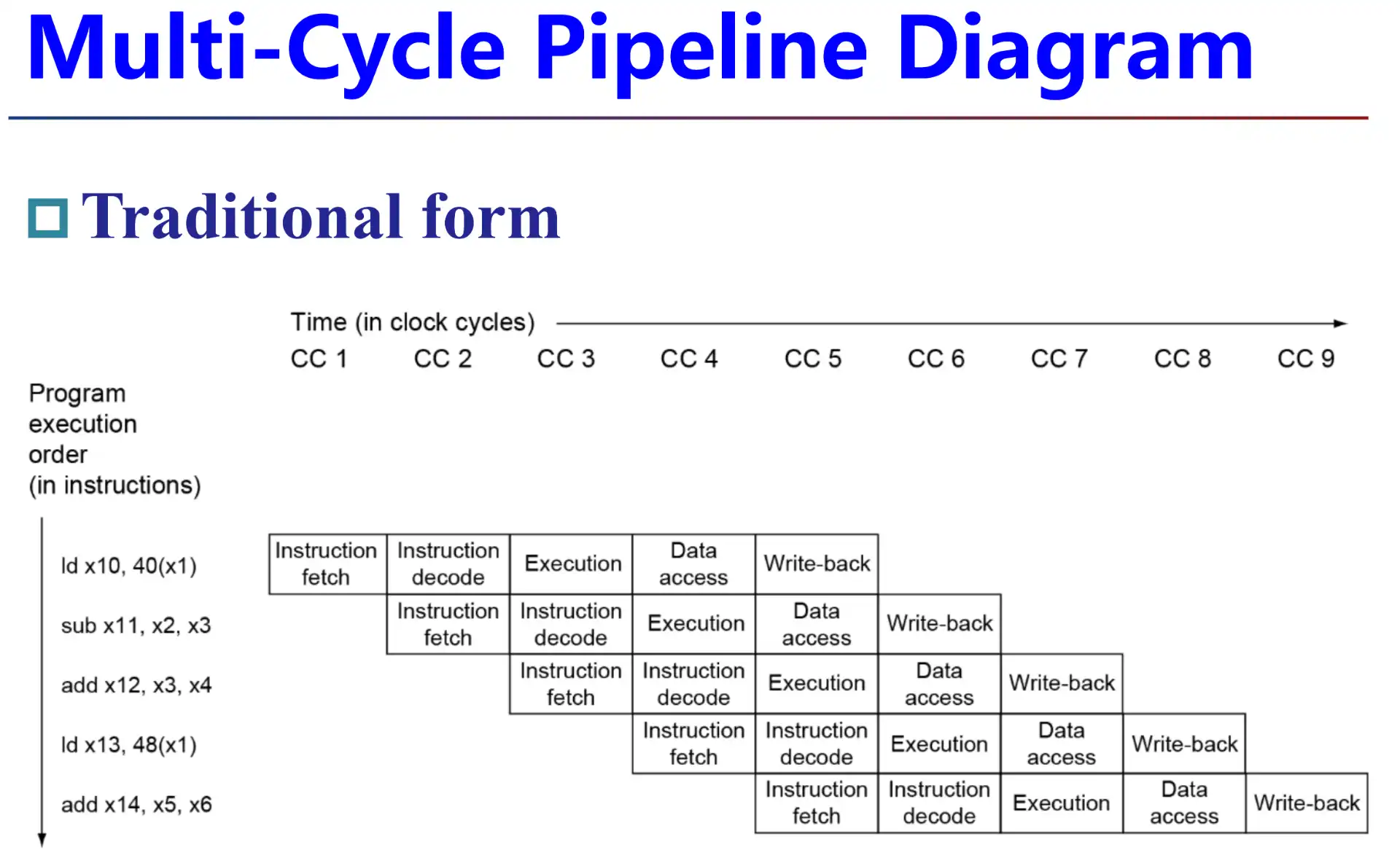
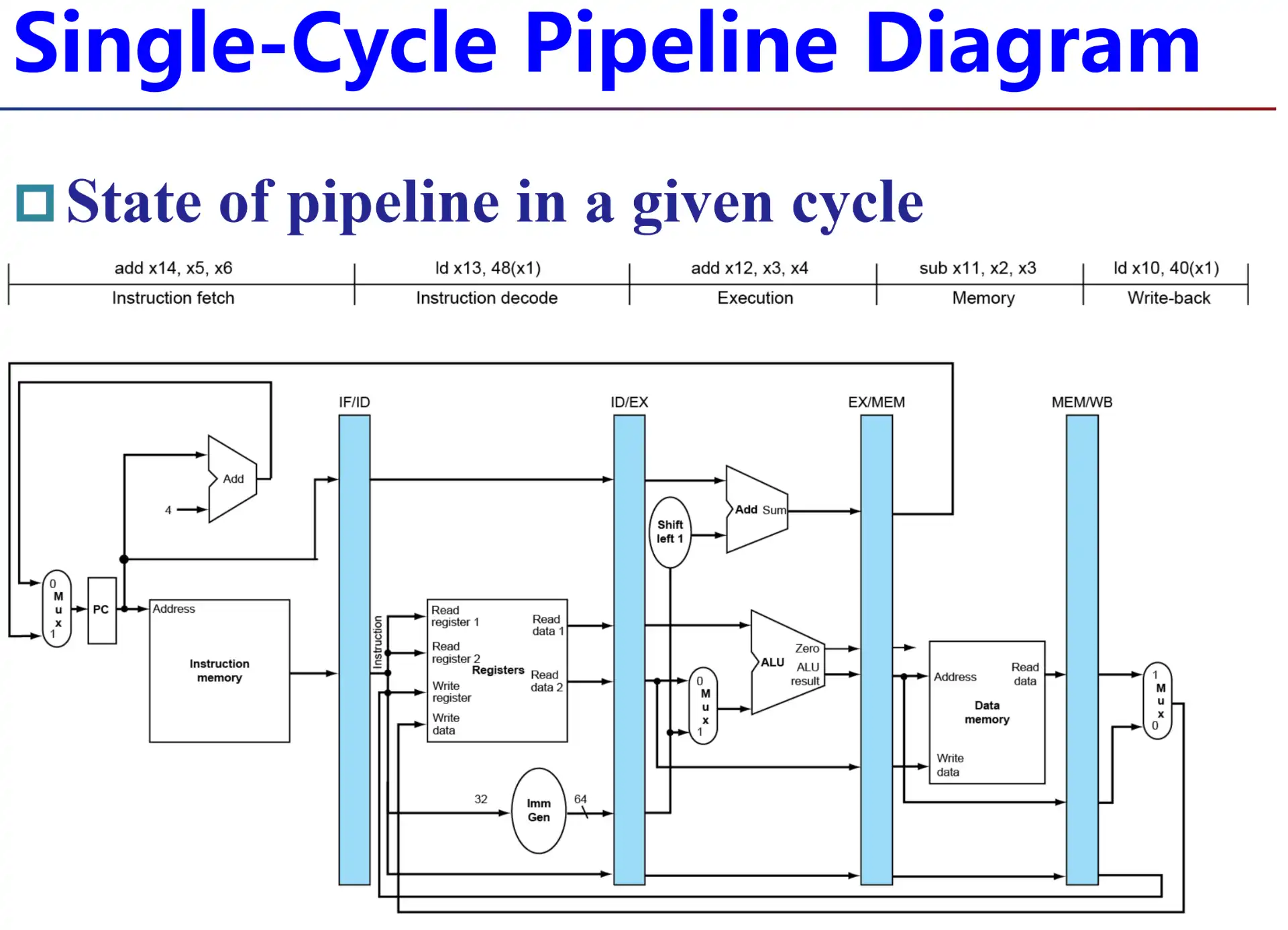
- 这里不需要将 branch 放到 MEM 级,其实直接放在 EX 级就好
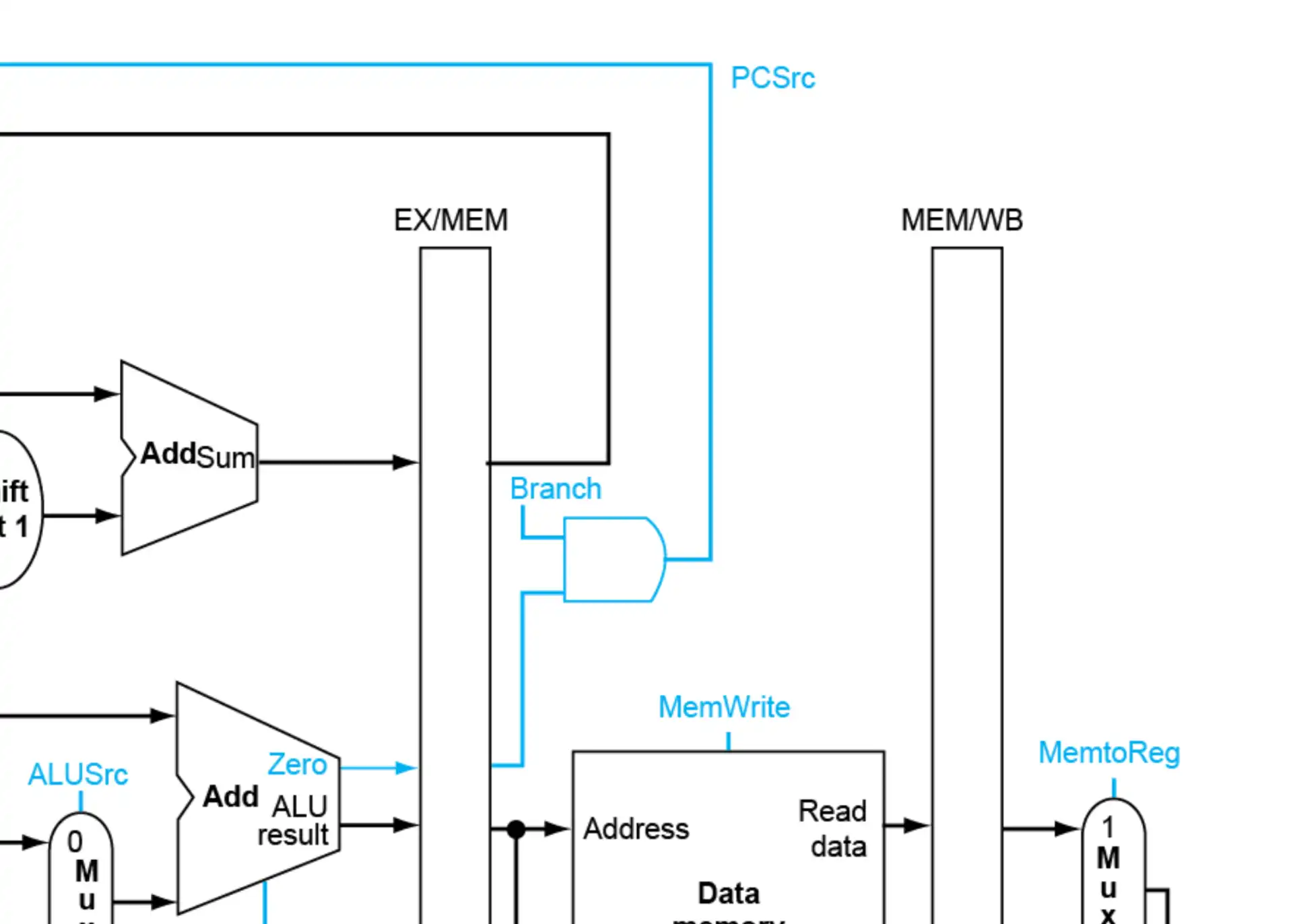
3.2 Control#
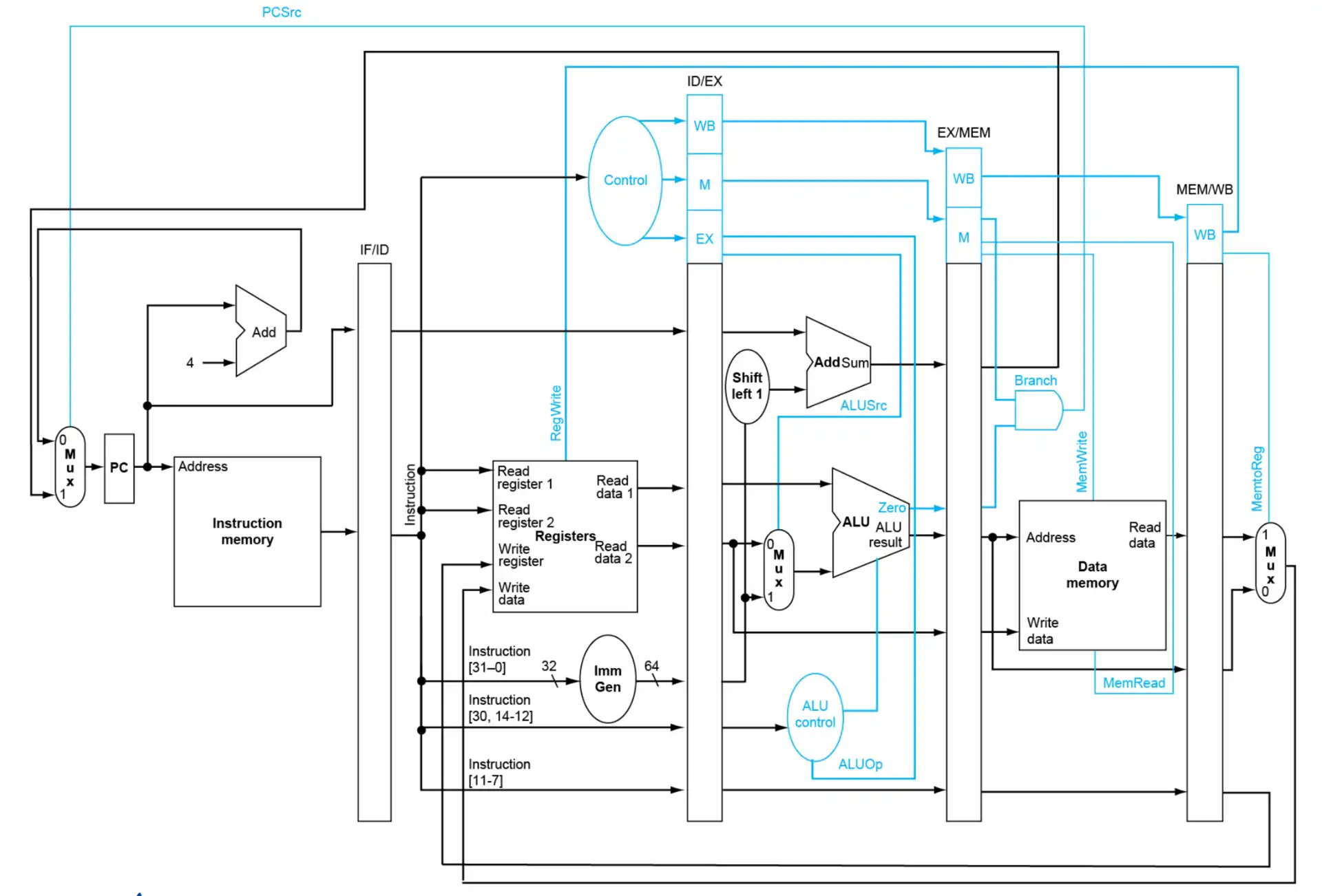
4 Data Hazards#
4.1 Forwarding 条件总结#
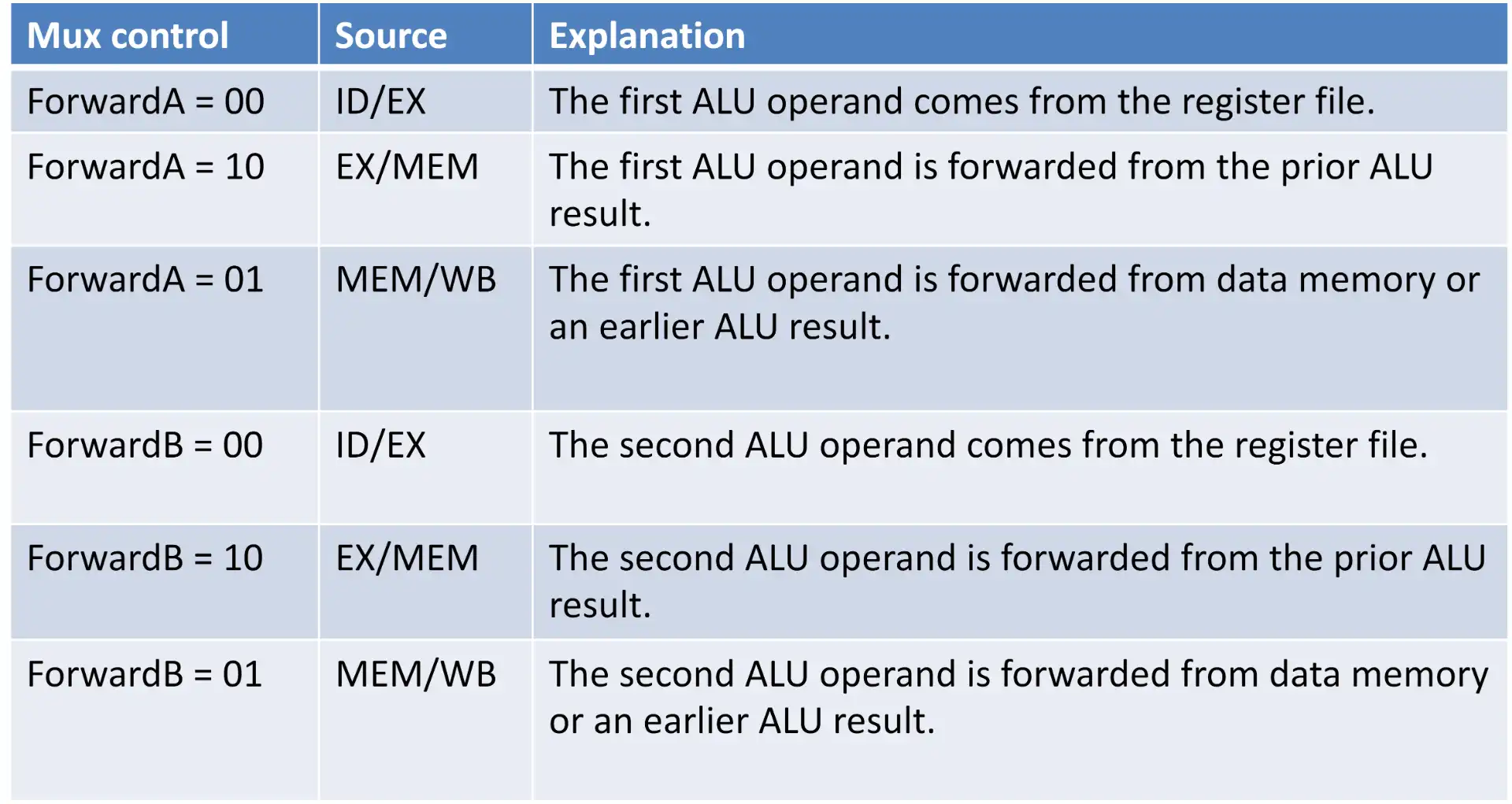
4.1.1 EX hazard#
4.1.2 Mem hazard load use#
4.1.3 Stall load use#
4.2 Forwarding#
4.2.1 从影响范围到 forwarding 设计#
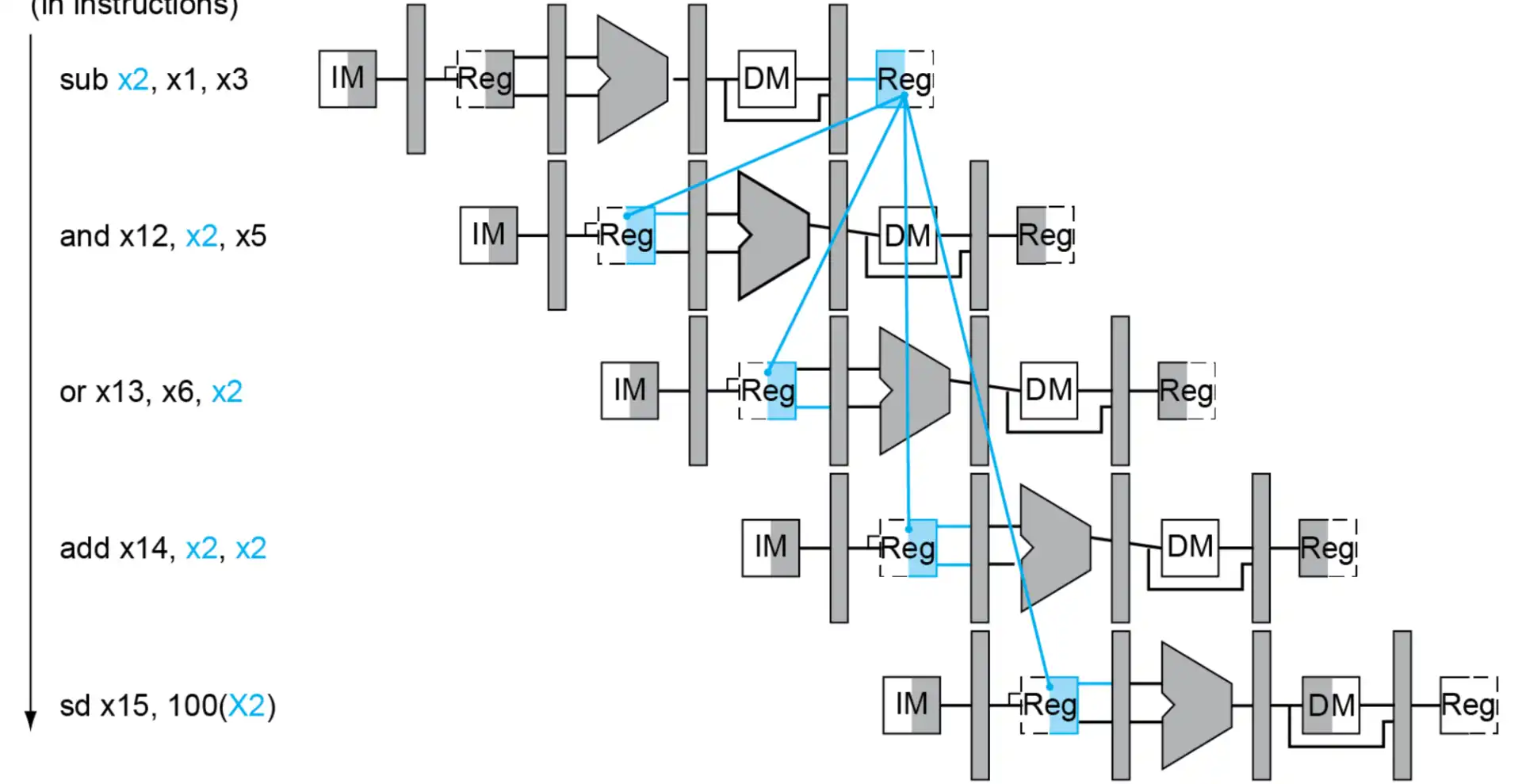
- 如果不进行 forwarding,会影响到接下来的两条指令
- 上图的例子中是 and, or 受到 sub 影响
- Forwarding 条件
- EX/MEM.rd = ID/EX.rs1 or ID/EX.rs2 && EX/MEM.RegWrite
- MEM/WB.rd = ID/EX.rs1 or ID/EX.rs2 && MEM/WB.RegWrite
| Memory Hazard | |
|---|---|
Tip
感觉可以令 ID/EX 为当前周期指令,那么 EX/MEM 就是前一条指令,MEM/WB 就是前第二条指令,分别记为 f0, f1, f2
Double Data Hazard

- 永远 forward 最新的值,所以总是要优先取 EX/MEM 进行 forwarding,优先取上一条、靠左的,前面的策略已经能够满足这样的条件。
4.2.2 Datapath with Forwarding#
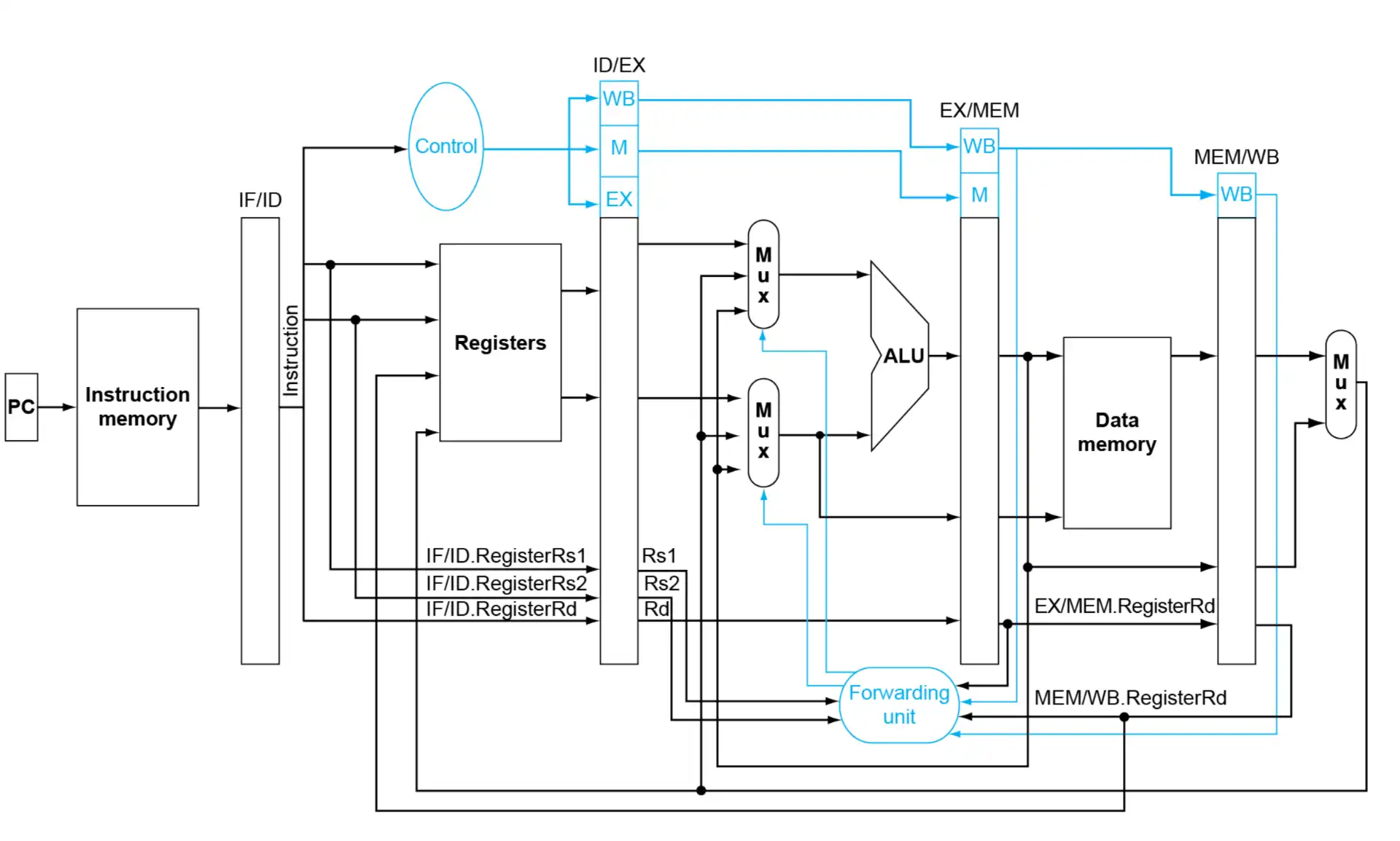
4.2.3 Load-Use Hazard#
4.2.3.1 Detection#
如果前一条指令要取内存,而且 rd 还是本条指令的 rs,那么必须停机一周期,插入 bubble
4.2.3.2 How to Stall#
- 保持 PC 寄存器不变
- 保持 IF/ID 寄存器不变
- nop (no operation)
- ID/EX 的所有控制信号都置零,寄存器地址置零
5 Branch Hazards#
5.1 Example: branch taken#

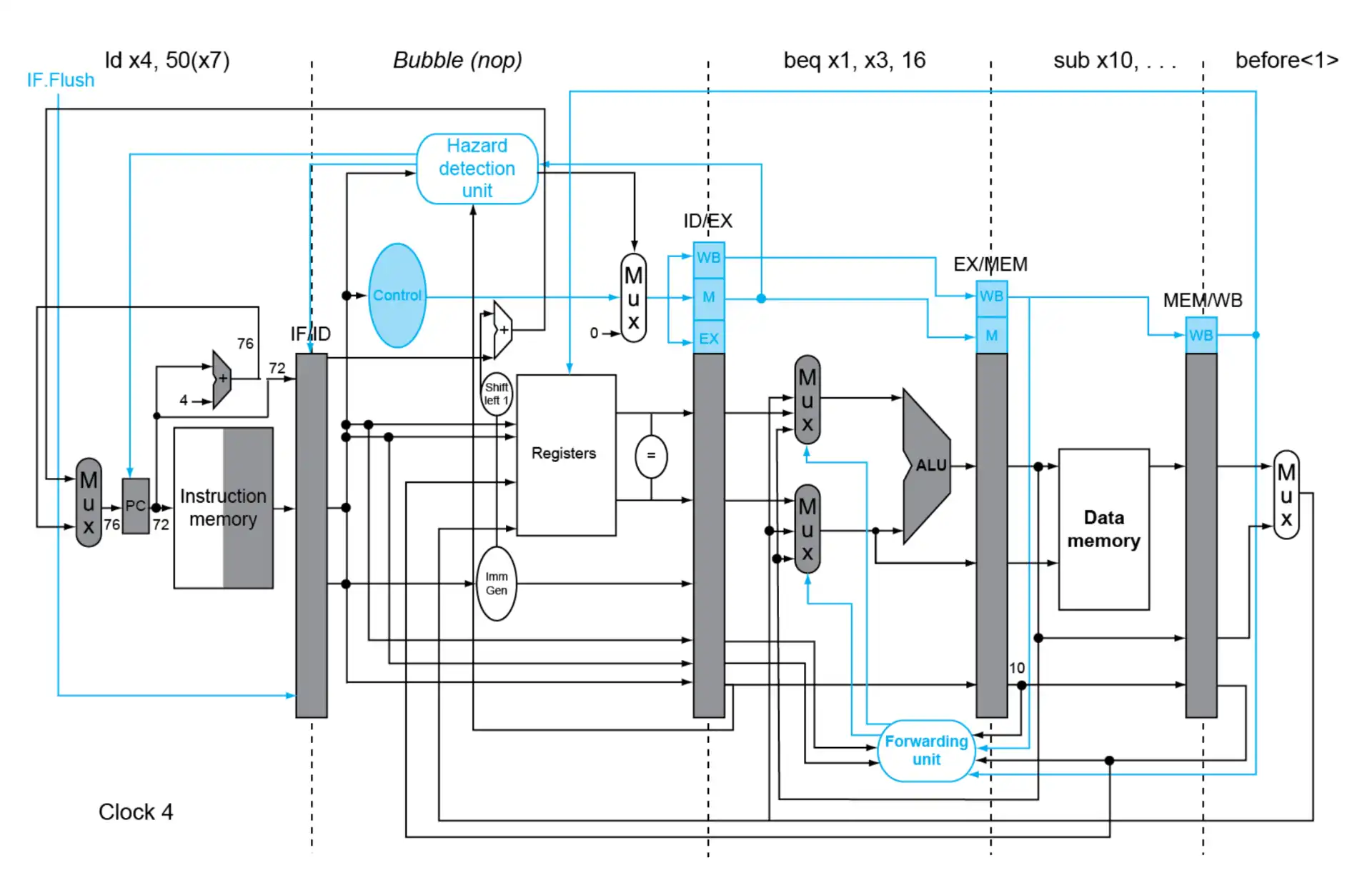
- 即使将 branch 提前到 ID 级,也可能产生至少一个 bubble
5.2 Dynamic Prediction#
- 1-bit 预测器,预测错误一次就改变预测
问题
对于嵌套循环,在两个外层循环之间,对内层循环的结尾跳转会产生两次连续错误的预测
- 第一次:预测 taken,但是实际上内层循环结束,于是预测改为 untaken
- 第二次,预测 untaken,但是实际上刚进入内层循环,于是预测改为 taken
5.2.1 2-bit Preidctor#
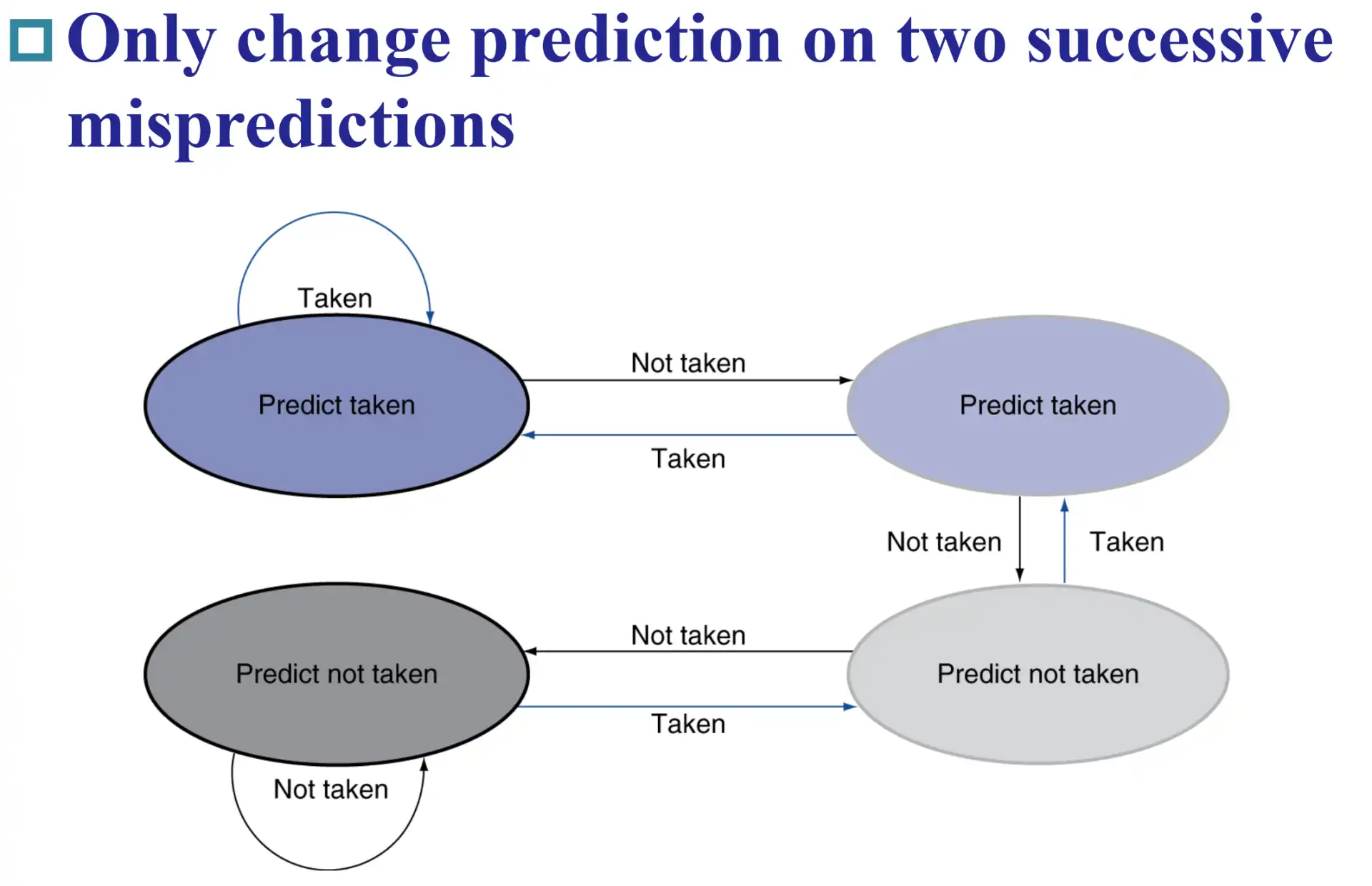
Check
连续两次预测失败才会改变预测 2-bit 状态机,这样在嵌套循环中只会出错一次
5.3 Calculating the Branch Target#
Question
即使有预测器,而且预测正确,仍然需要计算跳转的目标地址
- 将 PC 跳转映射关系做成 Table 存起来称为 Branch target buffer,执行到 branch 就直接执行对应跳转地址的指令
- If hit and inst is branch predicted taken, can fetch target immediately
5.4 Handling Exceptions#
- 保存 PC 到 Supervisor Exception Program Counter 寄存器,方便操作系统定位
- 将错误码保存到 Supervisor Exception Cause Register (SCAUSE),方便操作系统检查
- 64 bits,大多数没用
- 2 undefined opcode; 12 hardware malfunction
- 跳转到 handler
- read cause, transfer to relevant handler
- determin action required
- if restartable: 修正并用 SPEC 返回
- pipeline 需要 flush 错误的指令
- else: 终止,上报错误
Vector Interrupts
硬件决定要选择哪种 handler 并跳转,处理起来更快,但是硬件会更加复杂 RISC-V 不使用
Example

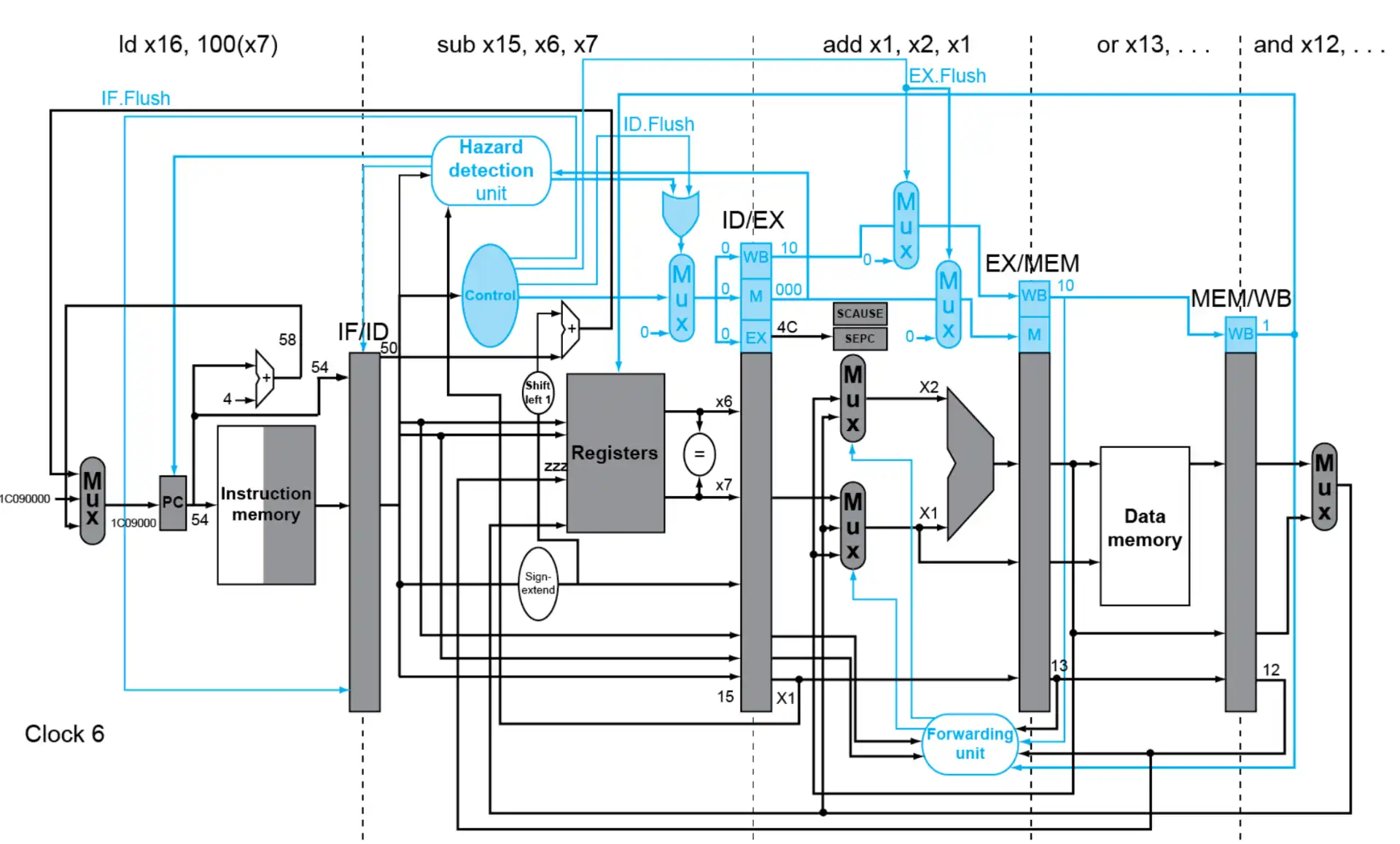
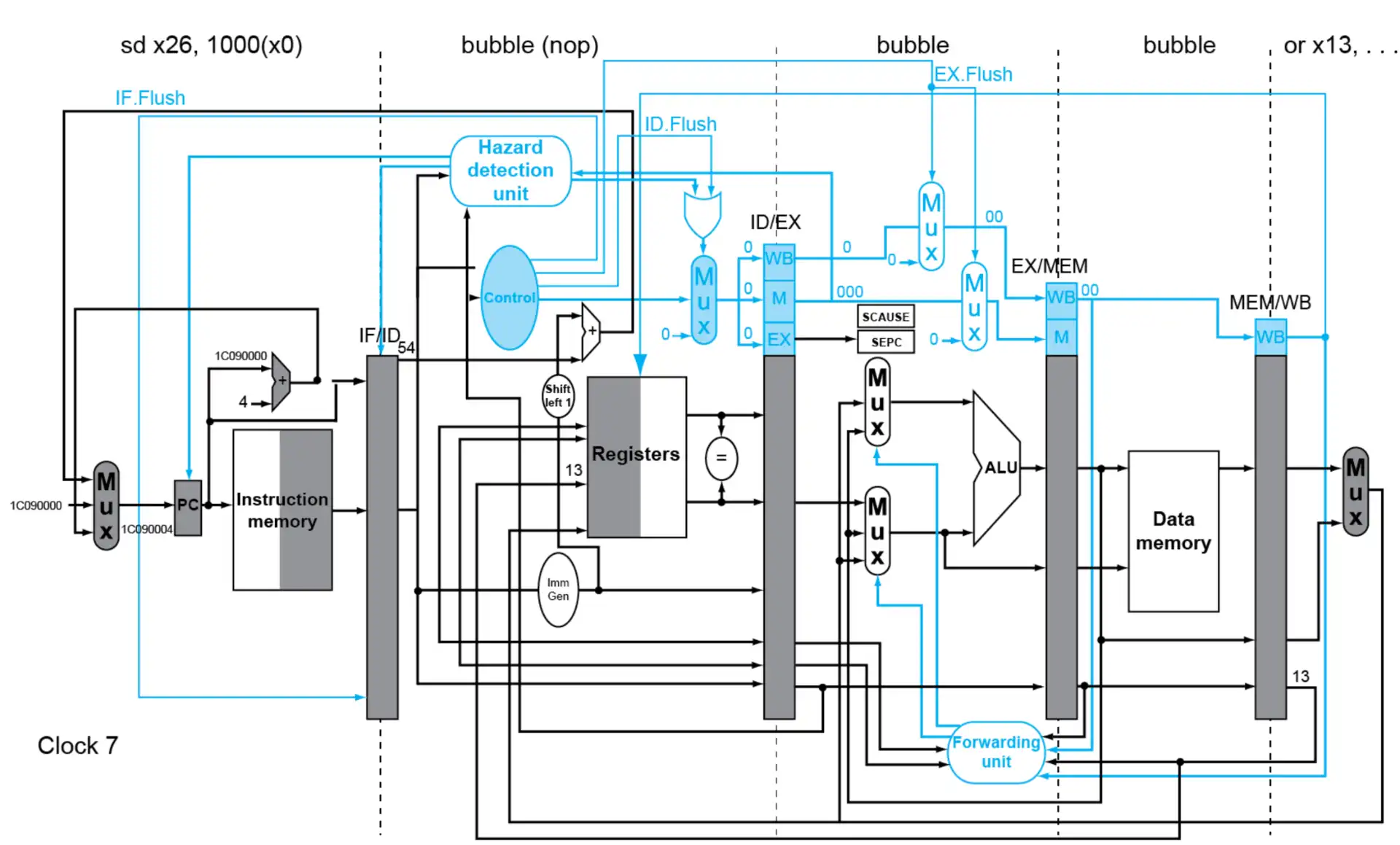
这里的
sd x26, 1000(x0)是 handler 内部的指令了
- Multiple Exceptions: 如果同时产生了多个错误,处理最早产生的错误
- Imprecise Exceptions: 直接停止流水线并保存状态,让 handler 来修正,硬件更加简单
5.5 Instruction-Level Parallelism %% fold %%#
5.5.1 Multiple Issue 多发#
- Static
- 编译的时候将指令打包放入 issue slots 发射槽
- 编译器需要检测和避免 hazards
- Dynamic
- CPU 检测指令流,每个周期选择一些指令发送
- 编译器负责指令重排
- 将硬件单元作为资源,有空闲就能跑指令 理论上可以有更好的性能
- 乱序执行 out-of-order execute
- 顺序保存 in-order commit
- 可以多加几个缓存队列,增大硬件利用率
5.5.2 Speculation 前瞻运行#
- 静态动态都能用
- compiler 做 reorder
- 硬件去 look ahead
- 可能预测出错,但是可以修正
5.5.3 ILP in RISC-V#
- Static Dual Issue: compiler must remove some/all hazards
- 一条 ALU/branch inst
- 一条 load/store inst
- 64bit 对齐
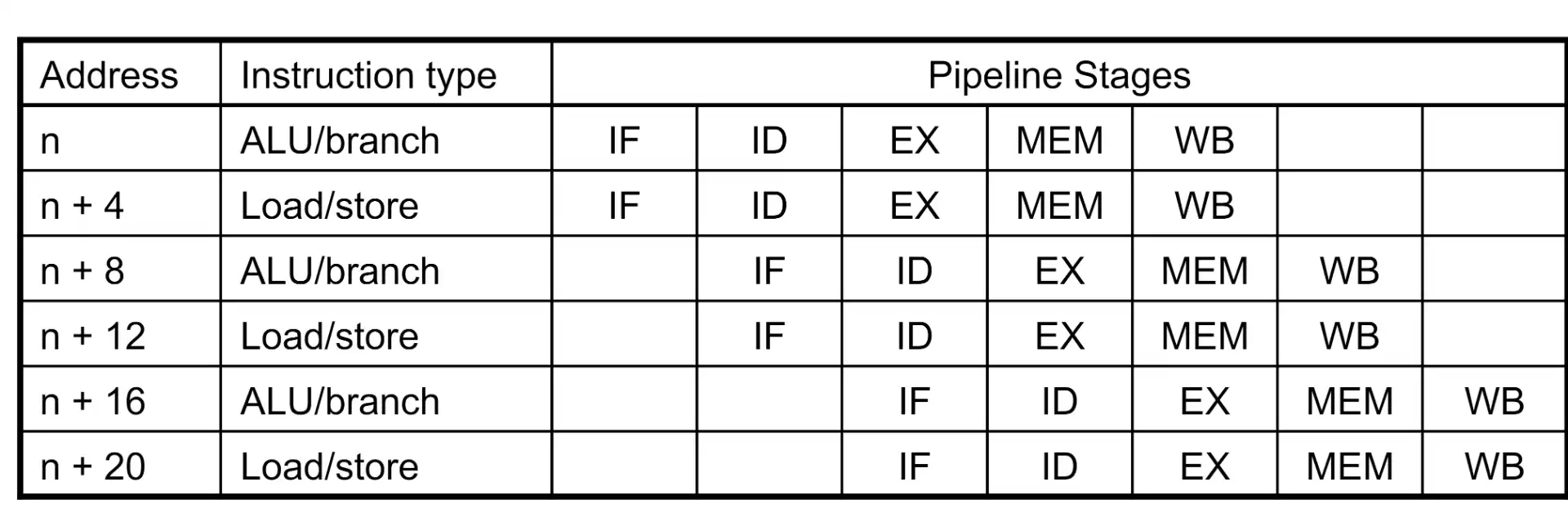
Bug
会导致 hazard 的检查范围更大
5.5.3.1 Scheduling#

5.5.3.2 Loop Unrolling#
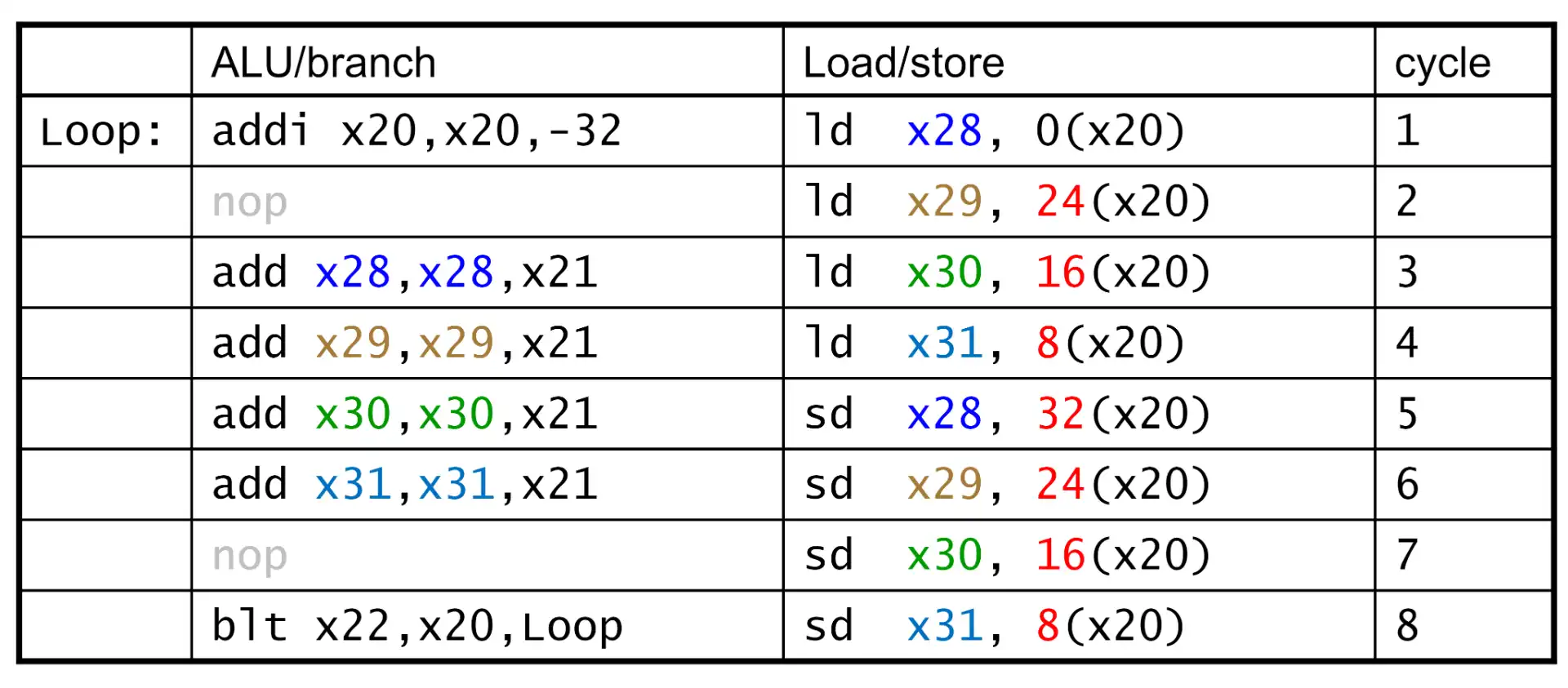
- 涉及 register rename,原本的寄存器用的是同一个,但是 unroll 后为了避免 hazard 需要用多个