05 Memory Hierarchy
1 Memory Intro#
- SRAM
- volatile
- DRAM
- volative
- Flash
- nonvolatile
- Magnetic Disk
- noevolatile
- cylinder, plate, track, sector, head
- plate 是双面的
磁盘计算
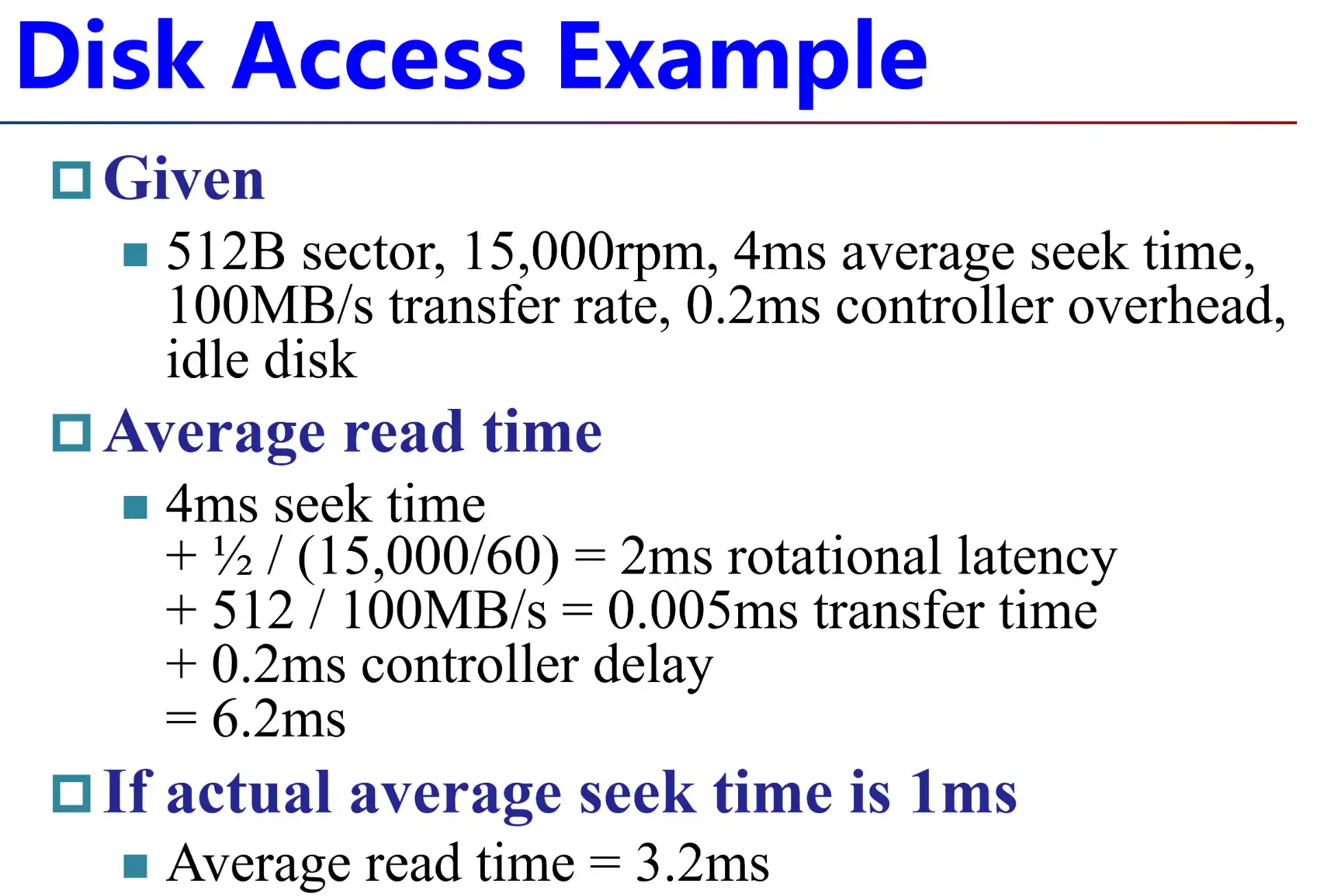 磁盘的主要瓶颈在于 rotation time
磁盘的主要瓶颈在于 rotation time
2 Memory Hierarchy Intro#
- Temporal locality 时间局部性
- 近期访问的数据会在短时间内再次访问
- e.g. 循环中的指令、计数器变量
- Spatial locality 空间局部性
- 近期访问的数据旁边的数据会马上被访问
- e.g. 数组遍历、sequential inst access
Taking Advantage of Locality
- 预测并从磁盘取到 DRAM
- 预测并从 DRAM 取到 SRAM
- Large and fast
2.1 Terms#
- Block(line): 在不同内存之间搬运的最小单元,一定是 word 的 \(2^N\),因为需要占用总线
- Hit: access the upper level and succeeds
- Miss: access the upper level and fails
- Hit Time: 访问命中的延时,包括了判断是否 hit 的时间
- Miss Penalty: miss 后,从 lower level 搬运数据到 upper level,以及到 CPU 的时间
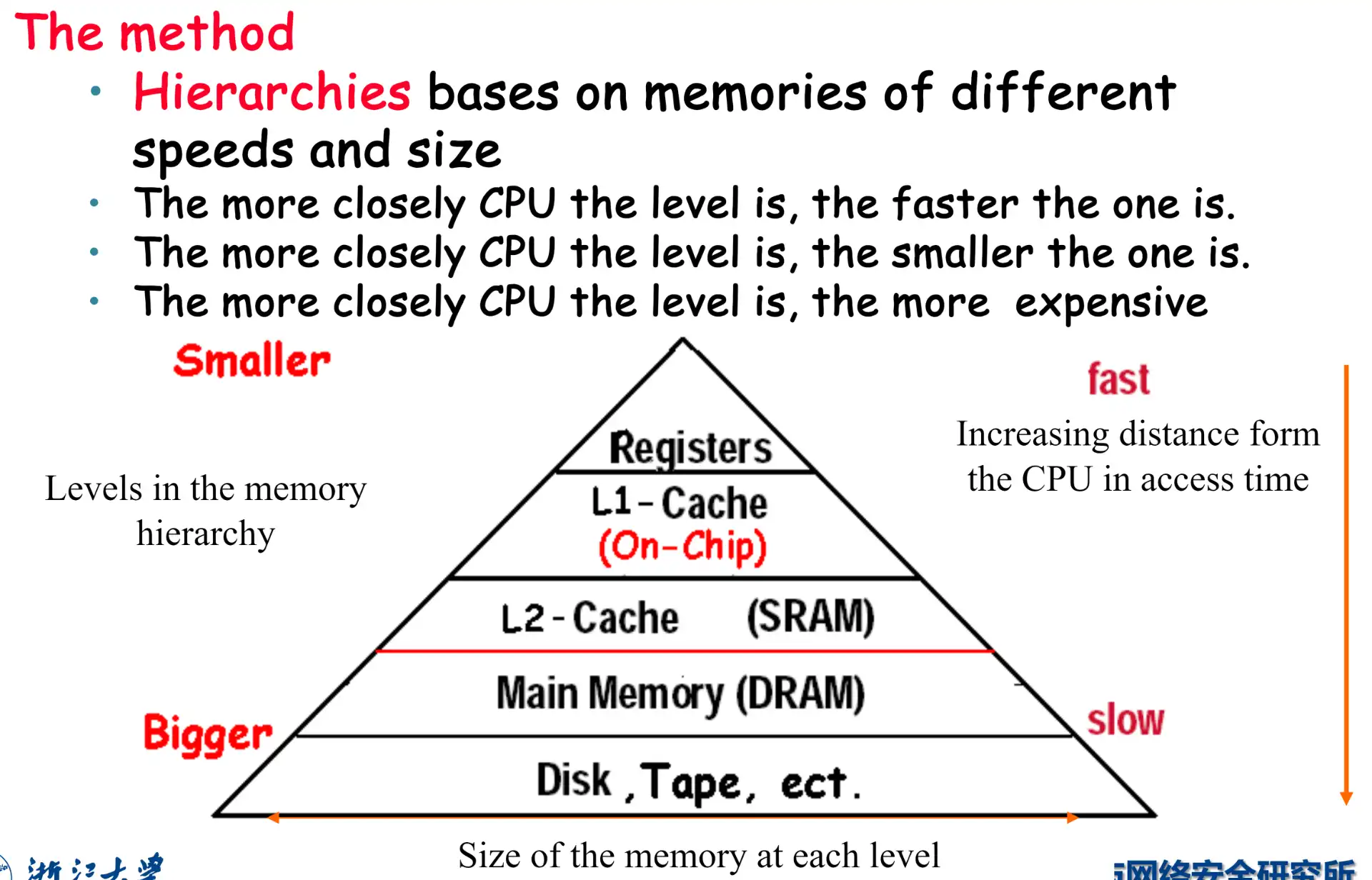
L1 Cache 和 L2 Cache 都是 SRAM,但是延迟有区别
- L1 Cache 主要目的是减少 hit time,容量较小,寻址更快
- L2 Chche 主要目的是增加 hit rate (避免读内存导致 CPU stall),容量较大,寻址更慢
3 The basics of Cache#
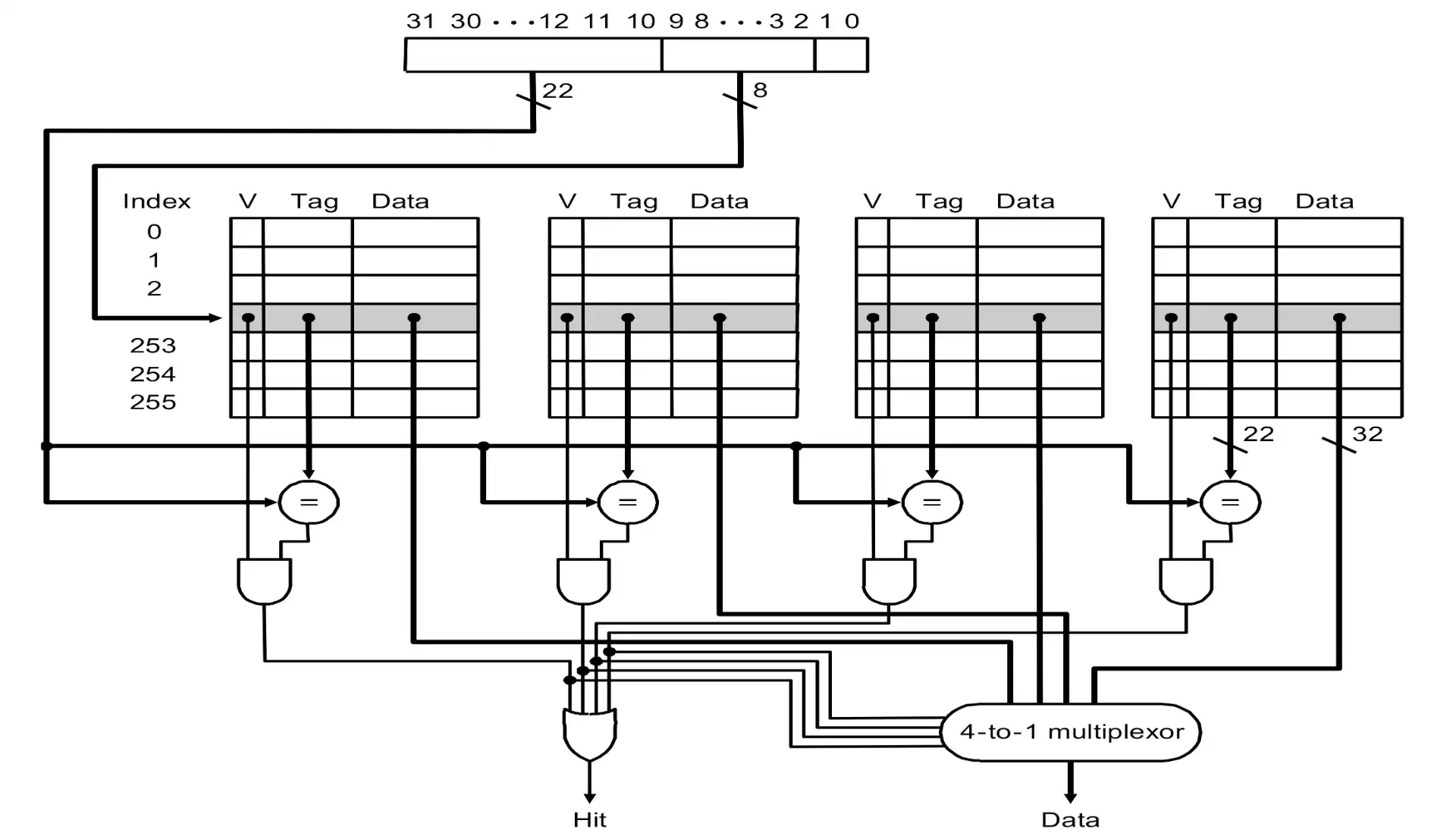
3.1 Direct Mapped Cache#
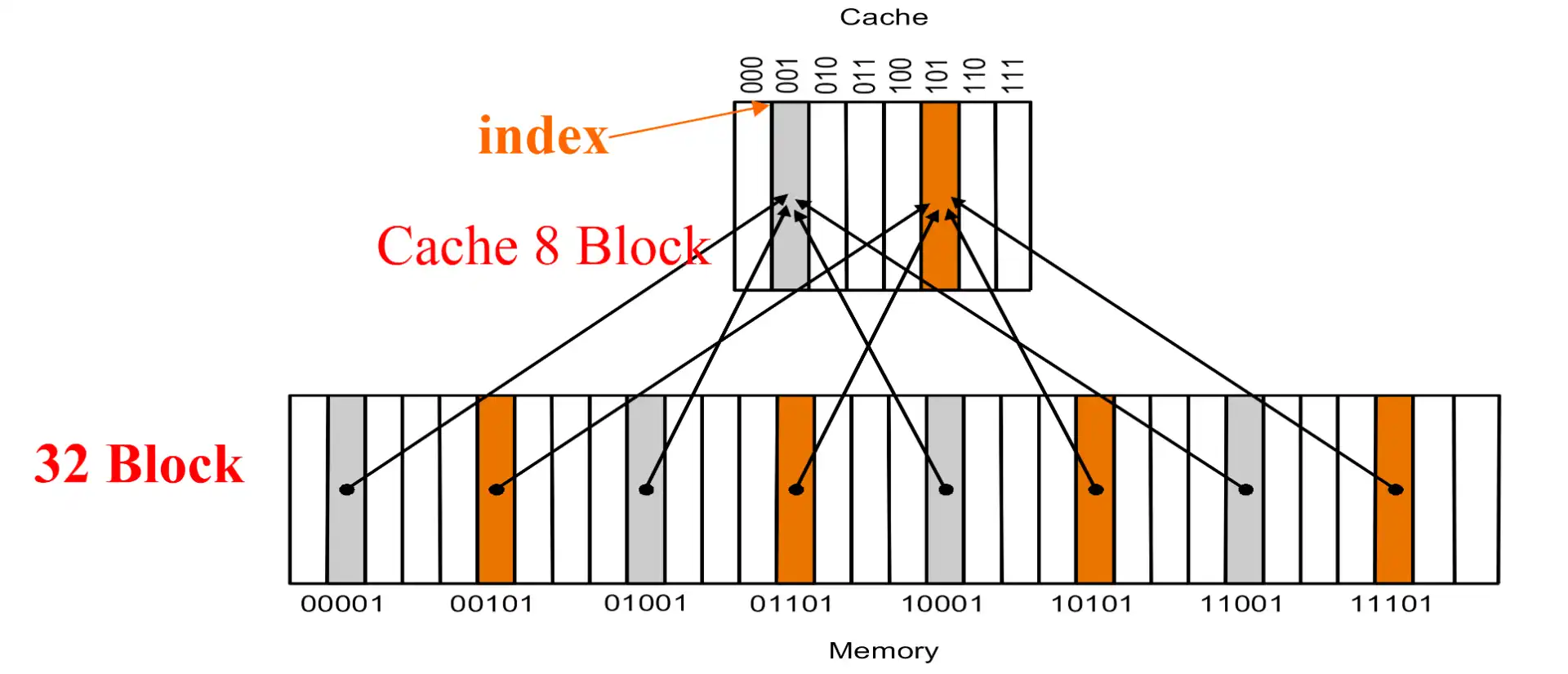
- 在 cache 中的地址是 (block address) mod (#blocks in cache),实际上就是取最低的几位
- \(\text{mem addr}=\text{block addr}\times\text{block size}+\text{block offset}\)
- tag: block addr 除掉 cache index 的高几位
- \(\text{\#tag bits}=32-\)
- valid bits: 标记 cache block 是否有效,避免未初始化访问
- pros and cons
- pro: 寻址快
- con: 可能造成竞争,e.g. 对同在一个 cache index 的两个数据的连续修改,每一次都会 miss
3.1.1 相关计算#
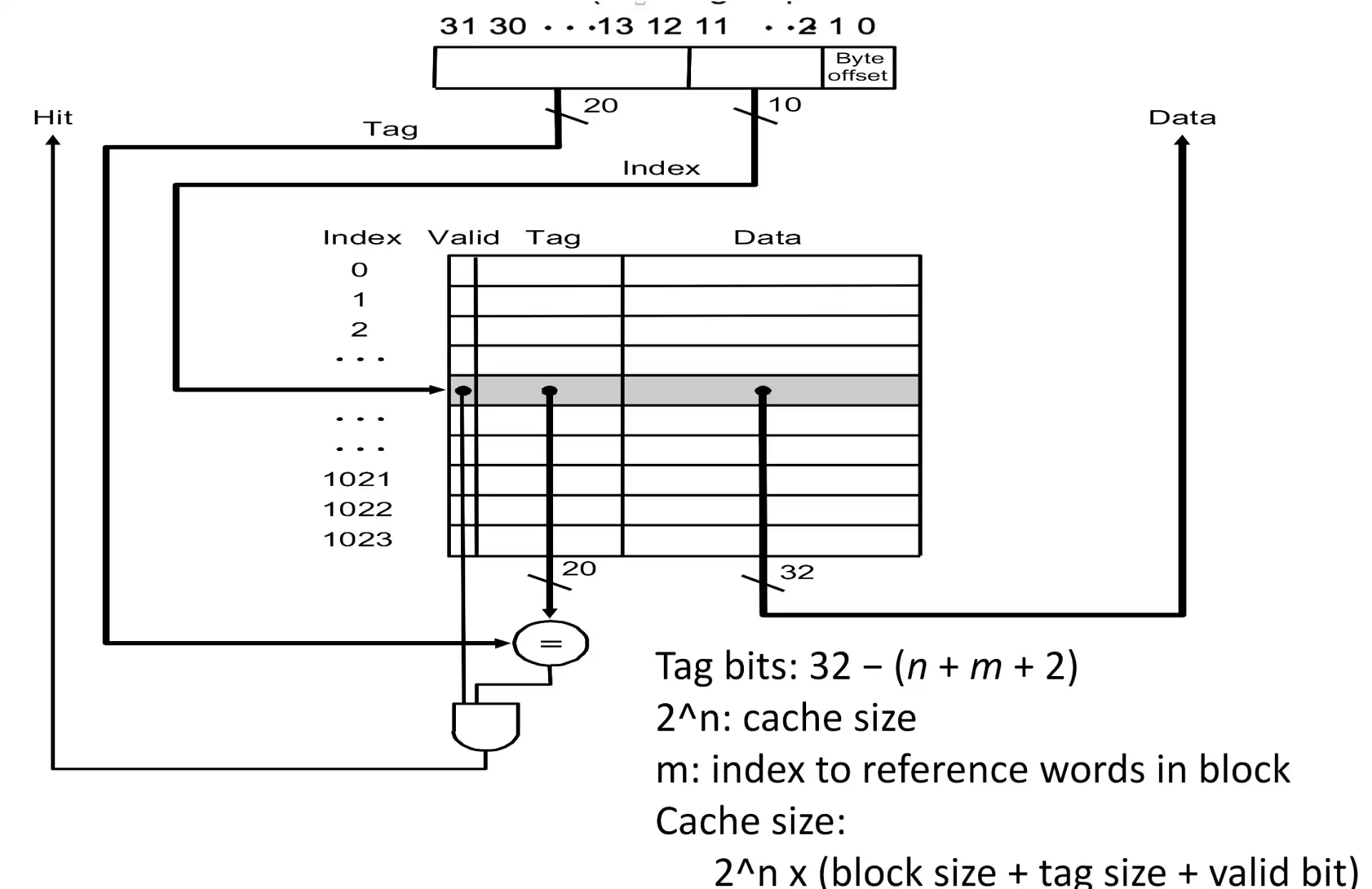

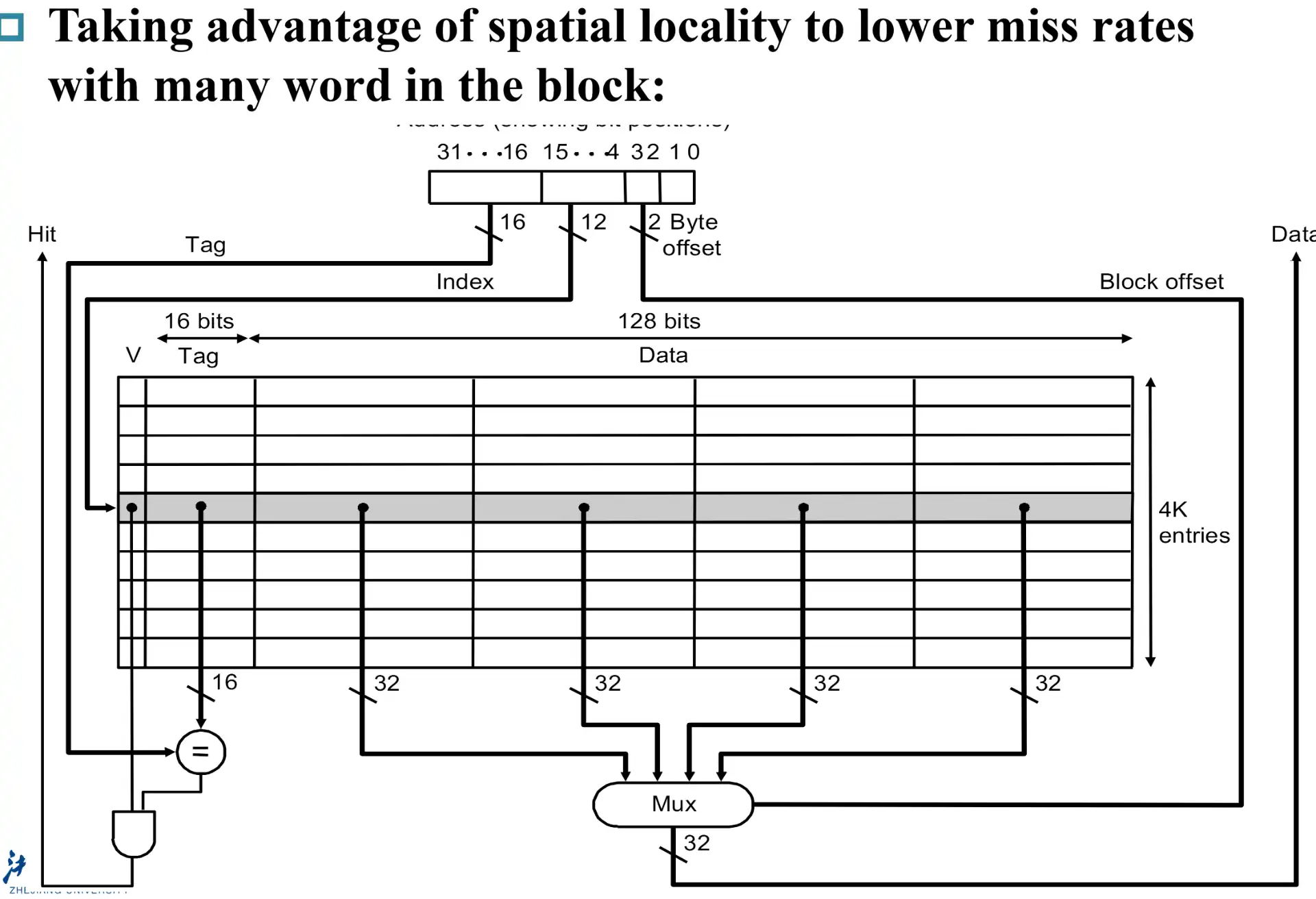
- address: | tag bits | cache block index | cache block word offset | word byte offset (2 bits) |
- cache entry: | valid bit | tag bits | block data |
Example

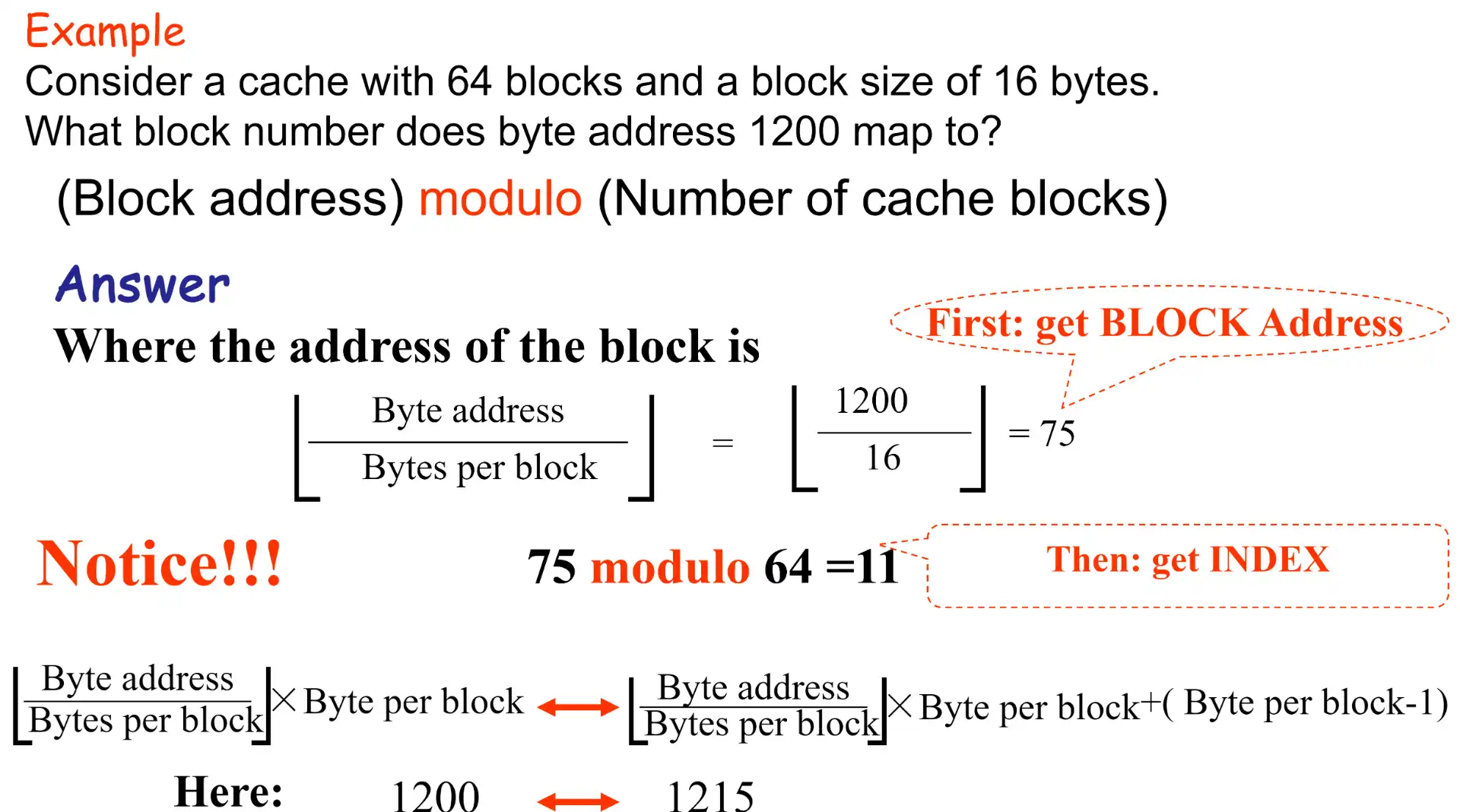
3.2 Miss Rate vs Block Size#
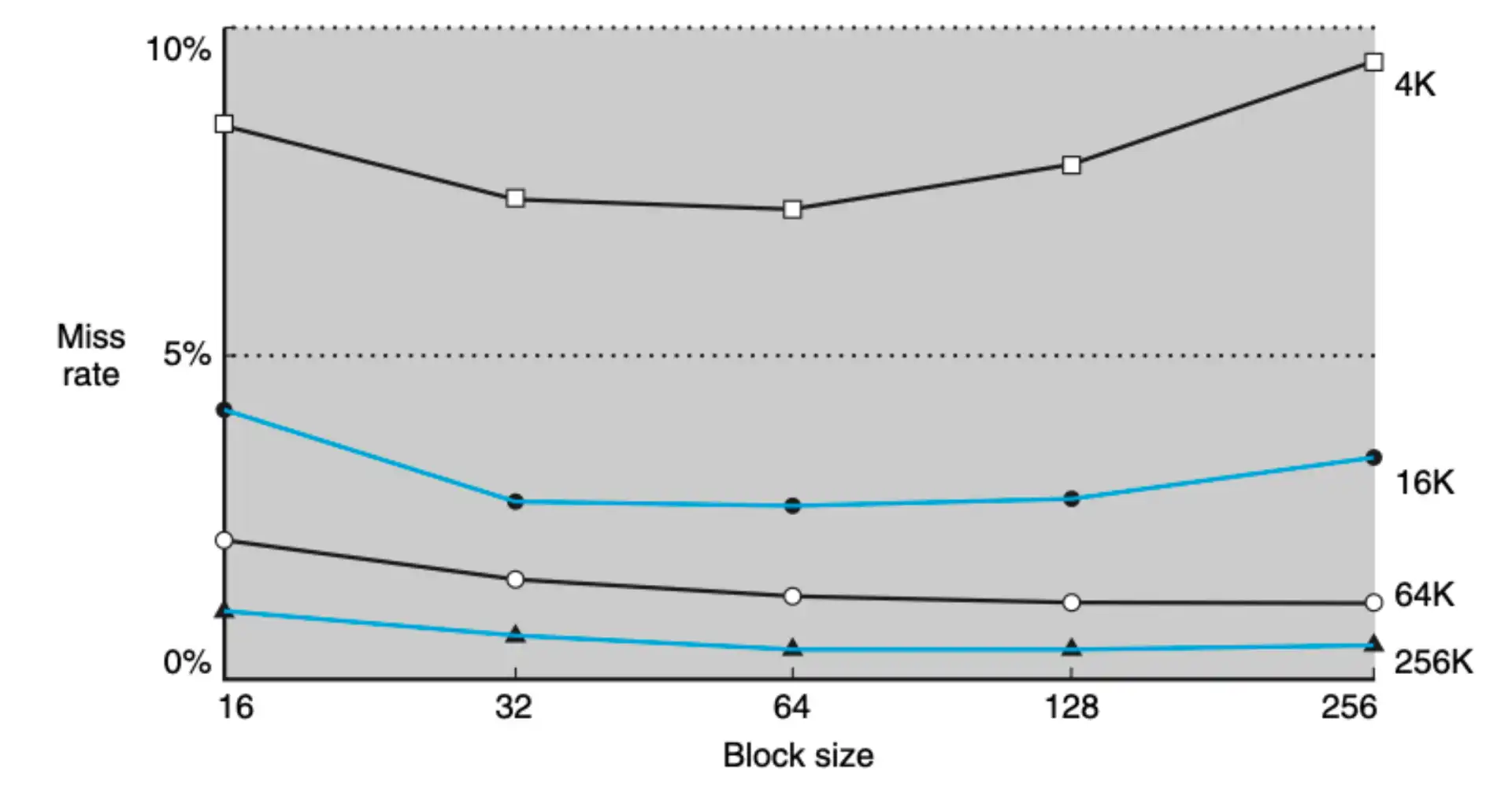
- 总容量越大,miss rate 越低
- 容量一定
- 若 size 太小,无法利用空间局部性,e.g. 一个数组遍历,要分成更多段来读取到 cache
- 若 size 太大,无法兼顾分散访问
Attention
- 设计的目标不只是降低 miss rate,而是关注总的 penalty
- 如果 block 较大,可能会 miss rate 比较低,但是读取搬运的开销更大
3.3 Hit and Misses#
3.3.1 Read miss#
- miss 的 penalty 近似
- inst cache miss
- data cache miss
- 处理 miss
- 保留原始的 PC
- main memory read (in multiple cycles)
- write to cache, update tag/valid
- 从原始的 PC 重新执行,这次一定会 hit
3.3.2 Write#
- write hits: different strategies
- write-back: 只更新 cache,不更新低级存储
- pros: 速度更快
- cons: inconsistent,数据不一致
- write-through: 写穿透,同步更新低级存储
- cons: 慢
- write-back: 只更新 cache,不更新低级存储
- write miss: 读取到缓存,再进行 write hit 操作
为什么一定要将整个 block 读取到 cache 再写入?
因为与 main memory 的通信一定是以 block 为单位的,cpu 只能在 cache 中执行 word 级别操作,所以一定要保证整个 block 都在 cache 中,否则 main memory 可能会被覆盖
4 Set associative#
Reducing cache misses by more flexible placement of blocks
Intro: Fully associative
- direct mapped: 可能导致竞争,利用率不高
- fully associative: block can go anywhere in cache
- cons: 查找非常慢
- block can go anywhere within its set
- \(n\)-way set associative 指的是一个 set 的 block 容量为 \(n\)
- direct mapped = 1-way set associative
- fully associative = n-way set
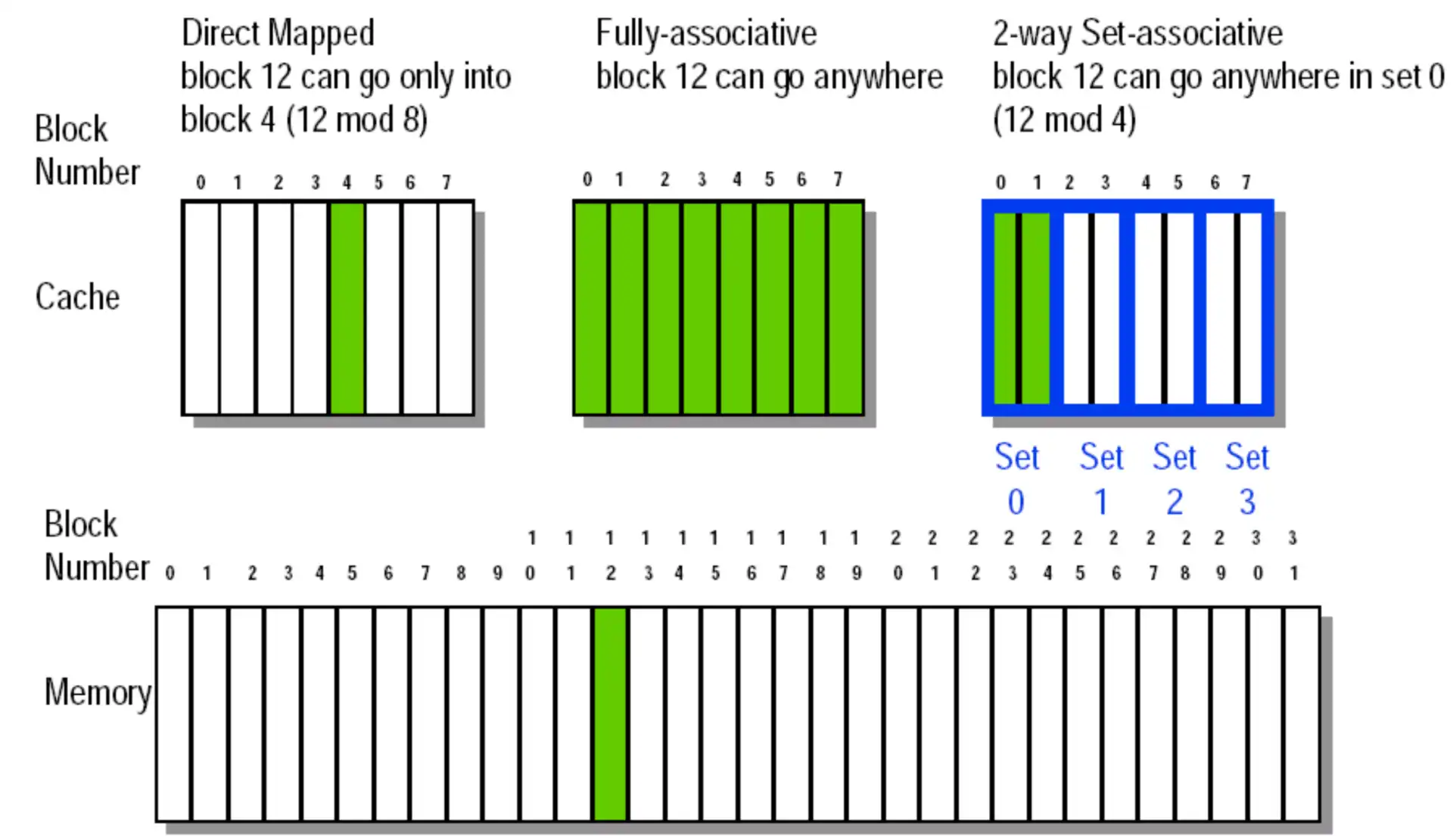
4.1 Block Identification#
- | Tag | Index | Offset |
- offset: block 内部的 byte offset
- index: select sets
- tag: 剩余的物理地址
- tag + index = block address
fully-associative
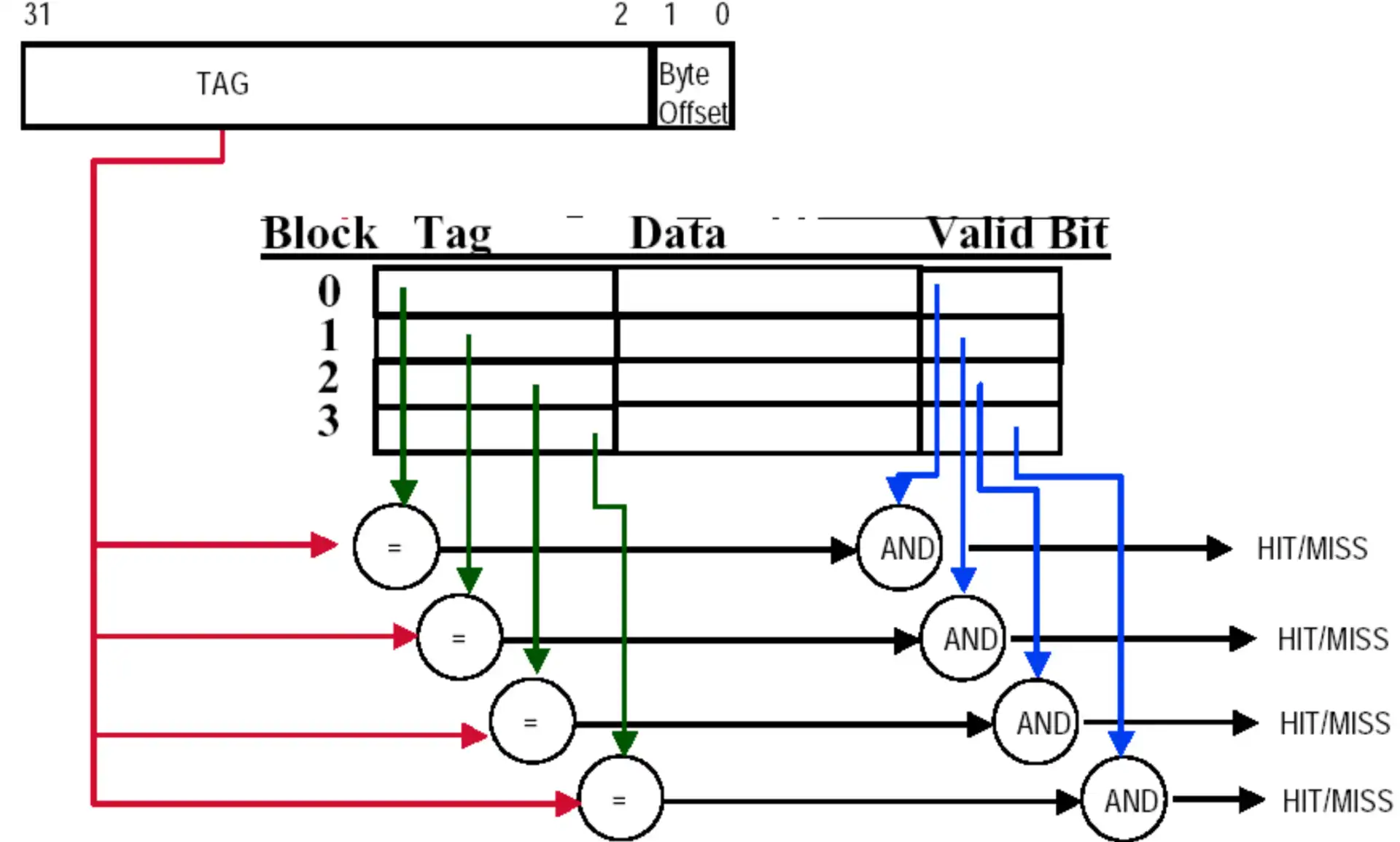
Note
- associative identification 可以用电路并行实现,但是电路规模太大也不行
4.2 Block Replacement#
- random
- LRU(Least-recently used)
- 使用表或增加 cache block unit 宽度来记录
- FIFO(First in, first out)
4.2.1 LRU#
- 使用 1-bit,每 \(T\) 个周期都清零,能够表示至少 \(T\) 个周期内没有用过
-
事实上,会使用类似二叉树的方法,每个 internal node 会保存一个 bit,表示最新访问路径,并不总是能找到最优解
- e.g. leaf[0:3],按照 12304 的顺序访问,访问 4 的时候会替换 2
5 Write Strategy#
also written to main memory?
- write-through cache
- 总是写入到 main memory
- 可以随意丢弃 block
- write-back cache
- 需要额外的 dirty bit,标记 block 是否有修改;如果有,覆盖前需要写回
-
lower bandwidth: cache block 可能会多次访问、修改since data often overwritten multiple times
5.1 Write Stall#
- write stall: 执行 write through 时 CPU 等待时间
- Write buffers: 写入 main memory 的数据缓存区
- write-through 开销能够减小
-
buffer 有极小可能被写满
5.2 Write Misses#
- Write allocate: 先把 block 加载到 cache
-
如果只需要修改 block 中的部分内容,但内存只能以 block 为单位读写,所以需要 write allocate
-
- Write around: 直接写入 main memory
- e.g. 变量在 init 的时候置零,且不立即使用,那么采用两种策略的开销是一样的,因为都加载到 cache 一次
Note
 m+2 实际上也可以合并,直接进行 block 内的 byte 寻址
m+2 实际上也可以合并,直接进行 block 内的 byte 寻址
6 Memory System#
6.1 Memory Addressing#
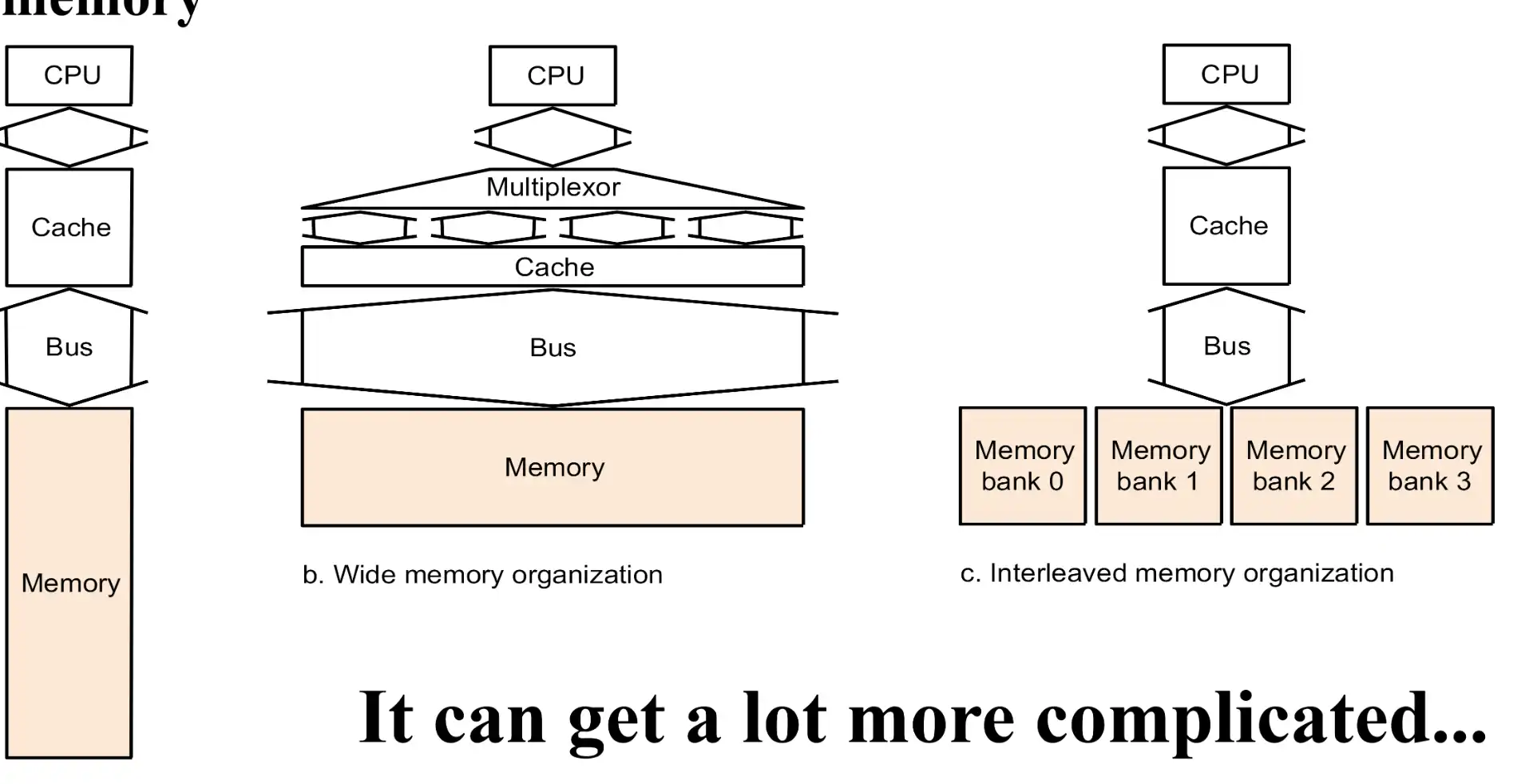
- Interleaved memory 的效果最好
6.2 Multi-level caches#
Target
- 提升 high-level 的寻址速度
- 降低 SRAM 的 miss rate
Example
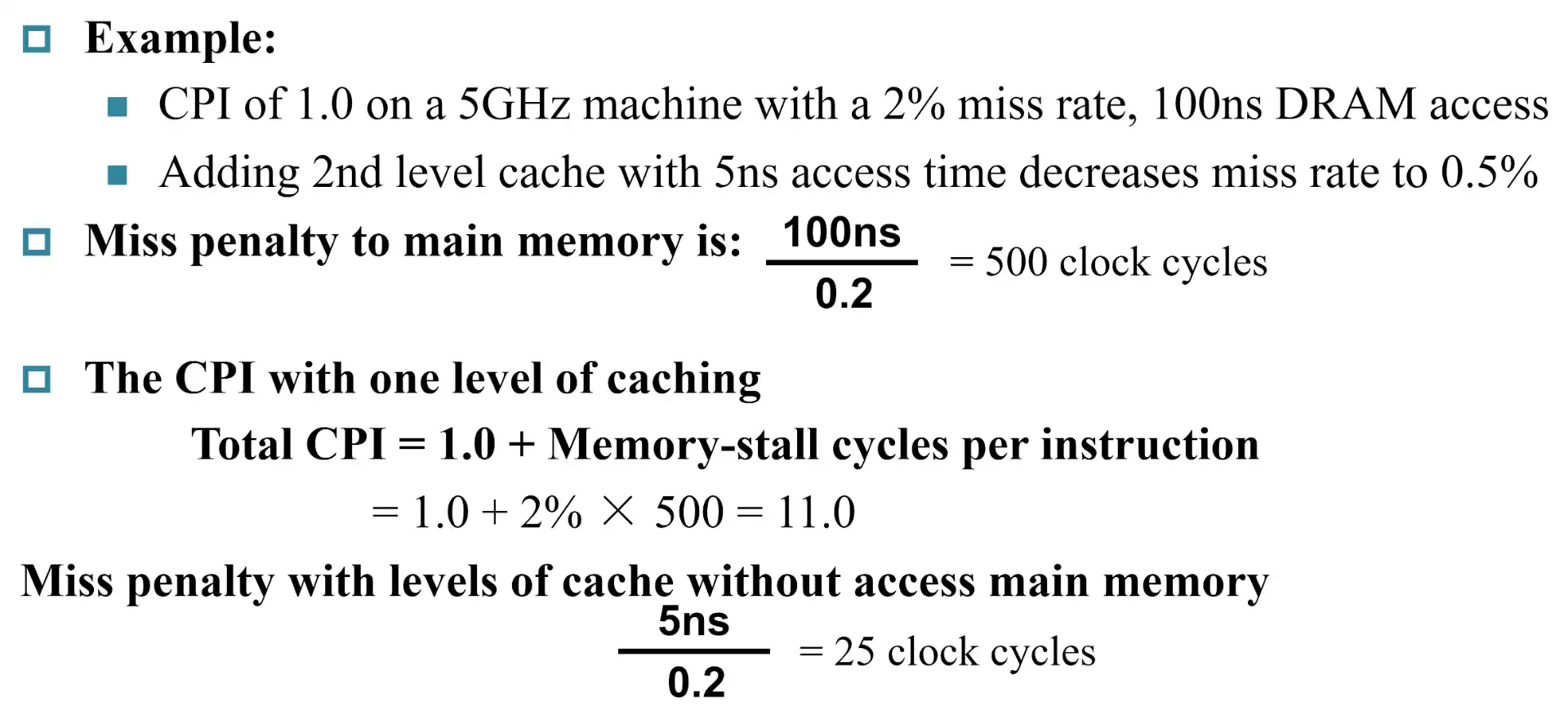
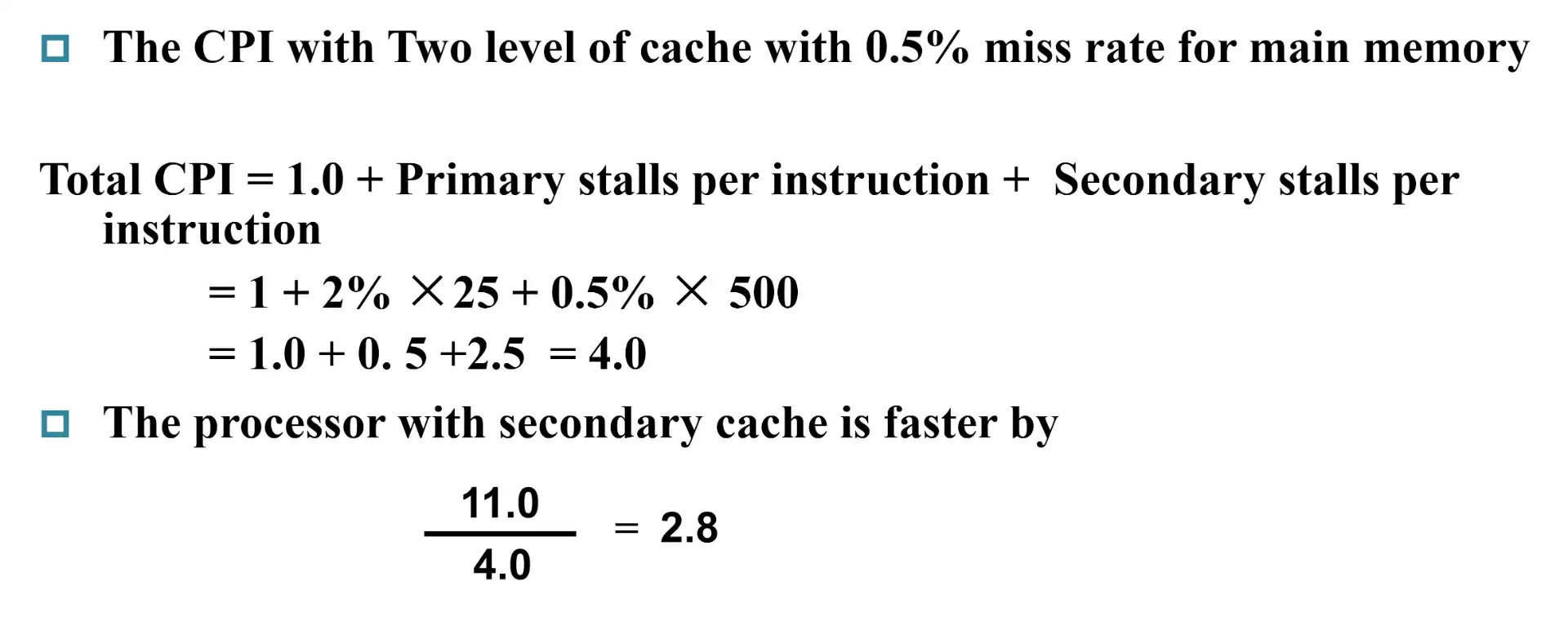
7 Measuring and imporving cache performance#
- \(\text{Average Memory Access Time(AMAT)}=\text{hit time}+\text{miss time}=\text{hit time}+\text{miss rate} \times\text{miss penalty}\)
- \(\text{CPU Time}=\text{CPU exe. clock cycles}+\text{Mem-stall clock cycles}\)
7.1 Mem-stall cycles#
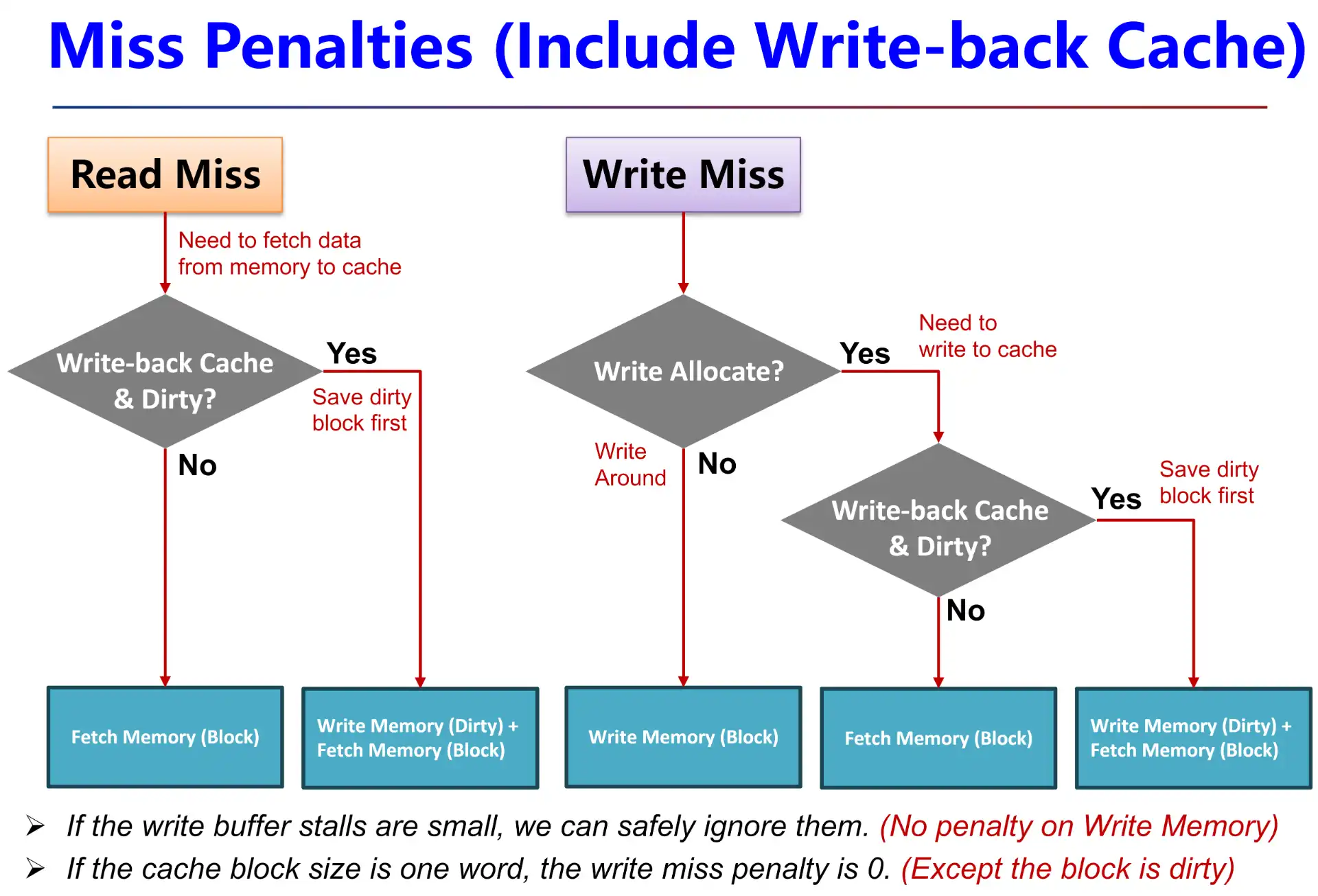
- \(\text{Mem-stall cycles}=\text{\#mem inst.}\times\text{miss ratio}\times\text{miss penalty}=\text{Read-stall cycles}+\text{Write-stall cycles}\)
- \(\text{Read-stall cycles}=\text{\#Read inst.}\times\text{Read miss rate}\times\text{Read miss penalty}\)
- \(\text{Write-stall cycles}=(\text{\#Write inst.}\times\text{Write miss rate}\times\text{Write miss penalty})+\text{Write buffer stalls}\)
-
Read miss penalty = Write miss penalty,都多了个从 low level fetch 的过程
- If write buffer stalls are small, we can safely ignore them
-
If thecache block size is one word, the write miss penalty is 0
- 因为不需要再从 low-level 写到 high-level
7.2 Combine reads and writes#
忽略 write buffer stalls,可以得到
\[
\text{Mem-stall clock cycles}=\text{\#Mem access}\times\text{Miss rate}\times\text{Miss penalty}
\]
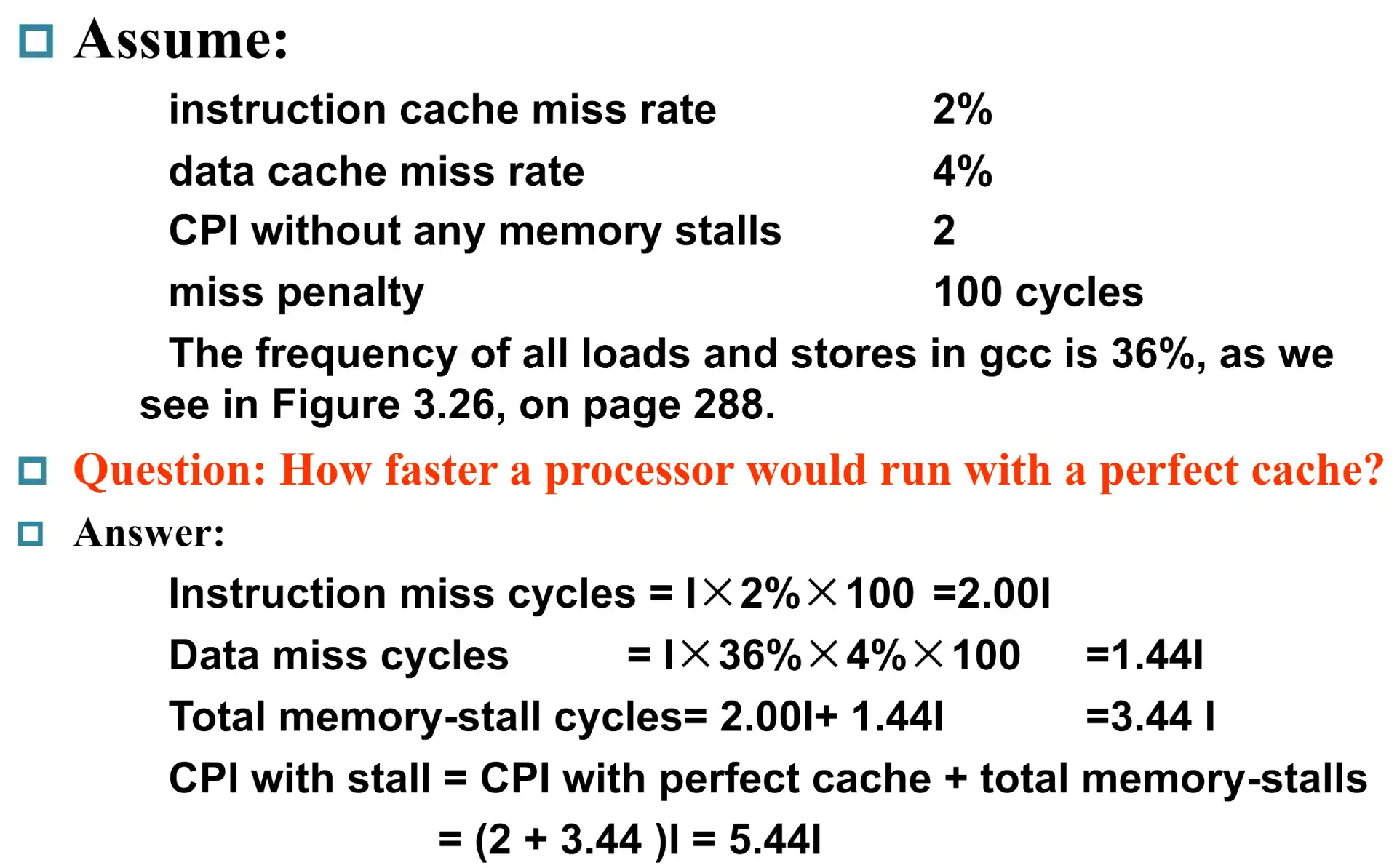
7.3 计算题#
Warning
如果 clock rate 变快一倍,miss penalty 也会翻倍
8 Virtual Memory#
Target
- 多线程内存共享
- 内存安全,每个程序的虚拟地址可能有不同的映射,无法篡改
- 将磁盘映射成内存,扩大可用内存
Pages: virtual memory blocks#
-
#virtual pages > #physical pages, not really now
- page faults: 数据不在内存中,需要从 disk 读取
- 由于 miss penalty 很大,所以 page 要设计的比较大 (e.g. 4KB)
- 使用 LRU 来降低 miss rate
- page fault 让软件来处理,因为 stall 的开销本身就很大
- write-through 开销太大,write buffer 没有用处,只用 write back
- | virtual(physical) page number | page offset |
Page tables#
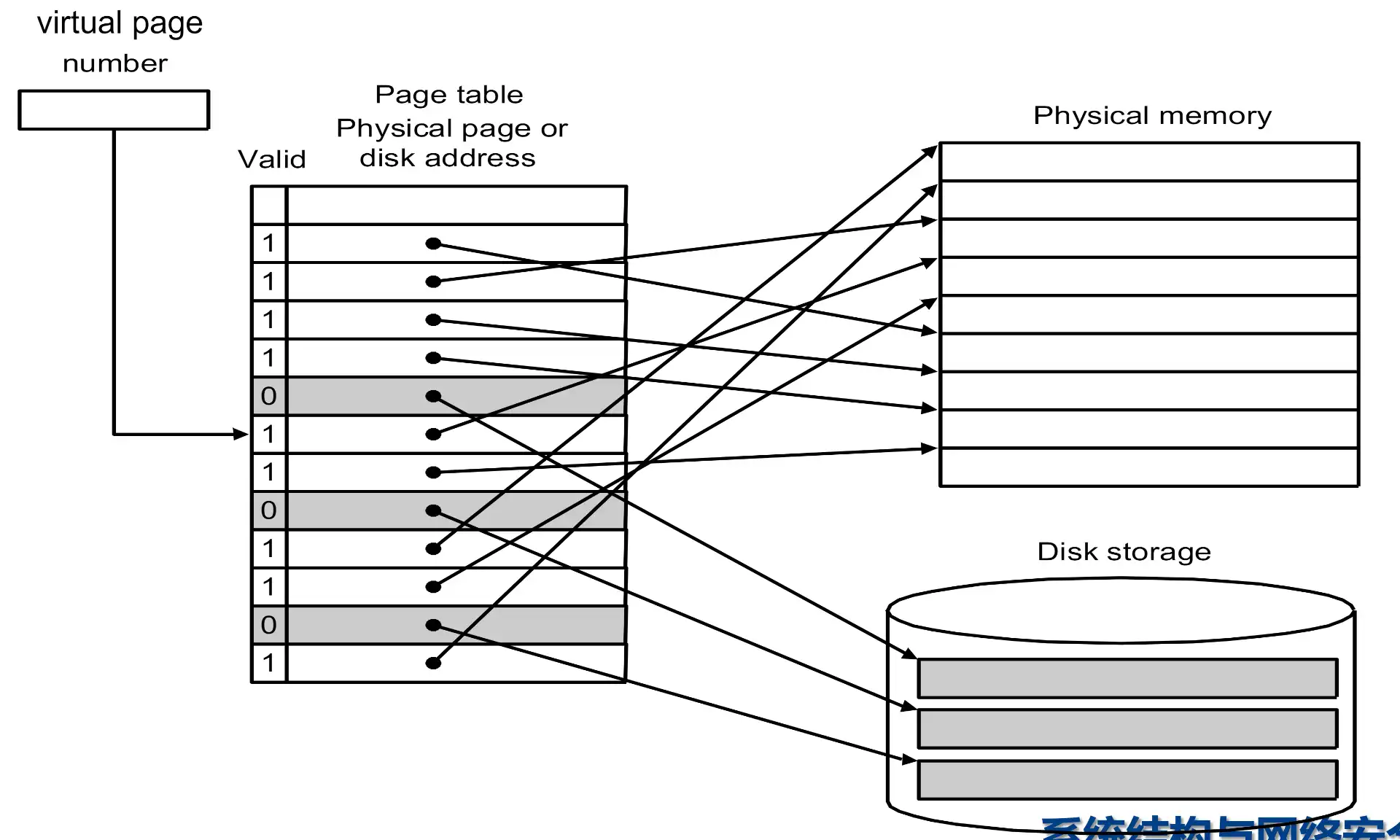
- 使用 virutal page address 查表,得到 physical address
- 保存在内存中特殊的位置
- 一个 page table register 保存了对应程序的 page table 的基地址,不同的程序有各自的 page table,可以实现隔离
- valid bit 表示对应的数据是否在内存中
计算#

Page faults#
- When the OS creates a process, it usually creates the space on idsk for all the pages of a process.
- page fault 发生时,OS 会根据 page table 找到对应的 disk 上的 page,并搬运到主存
- OS 也会实现 LRU
TLB(Translation-lookaside Buffer)#
a cache on the page table
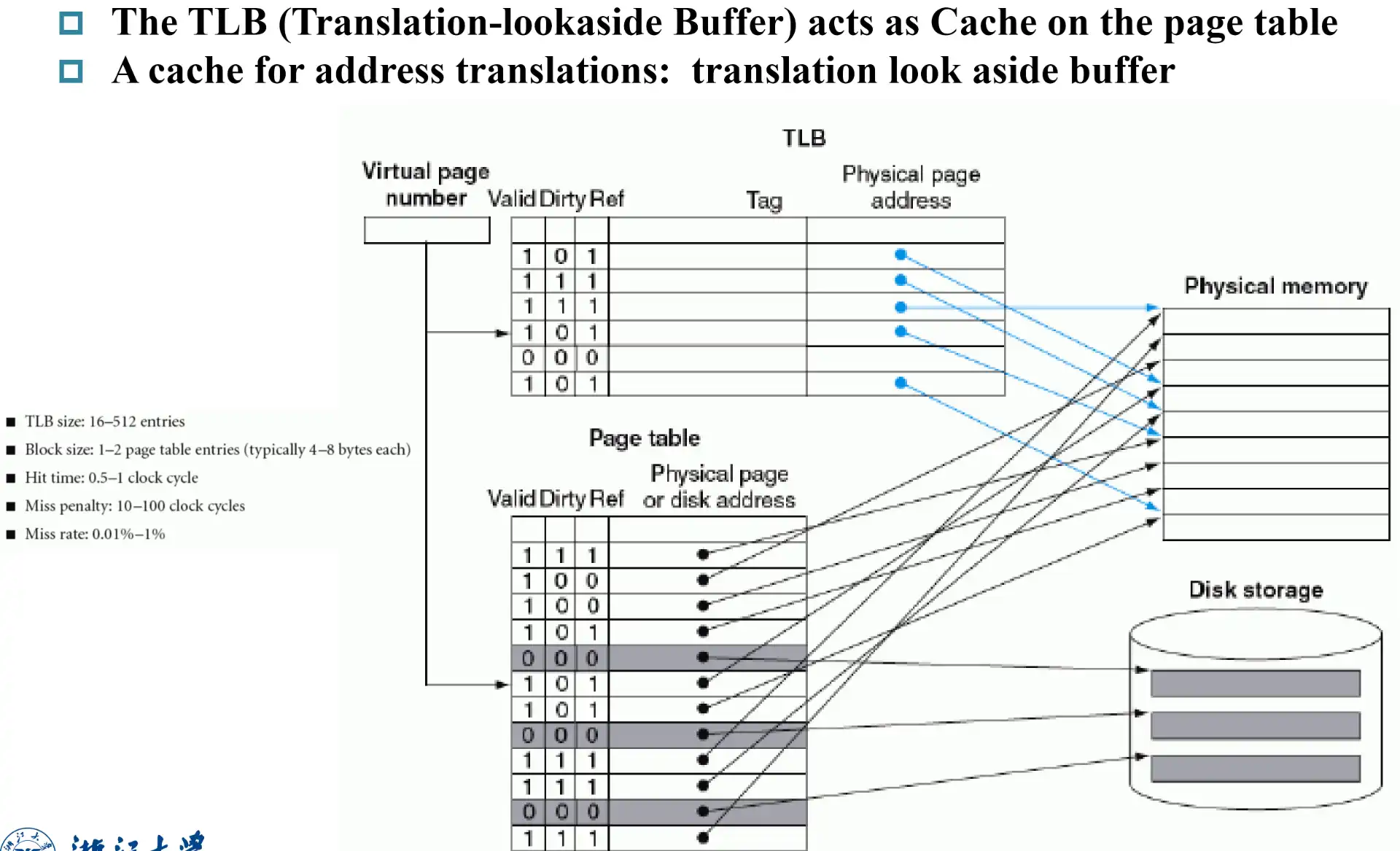
- 使用 tag 实现 associative
- reference bit 定期清零,实现简单的 LRU
Virtual address 访问 data 流程#
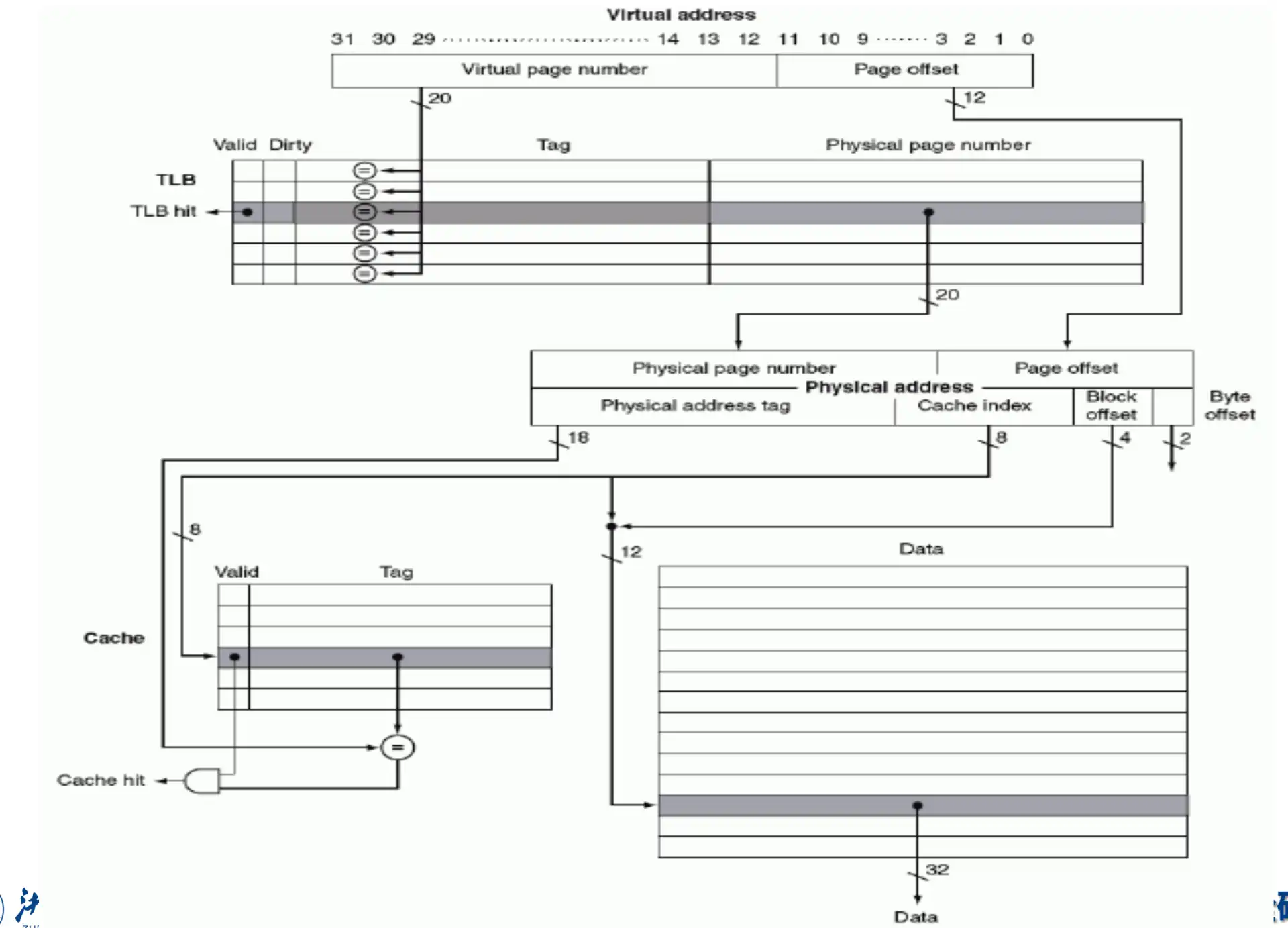
- Translation 过程:
virtual mem addr -> physical mem addr- 在 TLB 中查找 virtual page number
- 若 hit,得到 physical page number
- 若 miss,需要查找 Page Table
- 若 hit,得到 physical page number,更新 TLB
- 若 miss(invalid),page fault 操作,retry 时 hit,得到 physical page number,更新 TLB
- 在 TLB 中查找 virtual page number
- Physical Memory Access:
physical mem addr -> data- 查找是否在 cache 中
- hit,返回数据
- miss,查找更低级缓存或主存,并向上更新
- 查找是否在 cache 中
Note
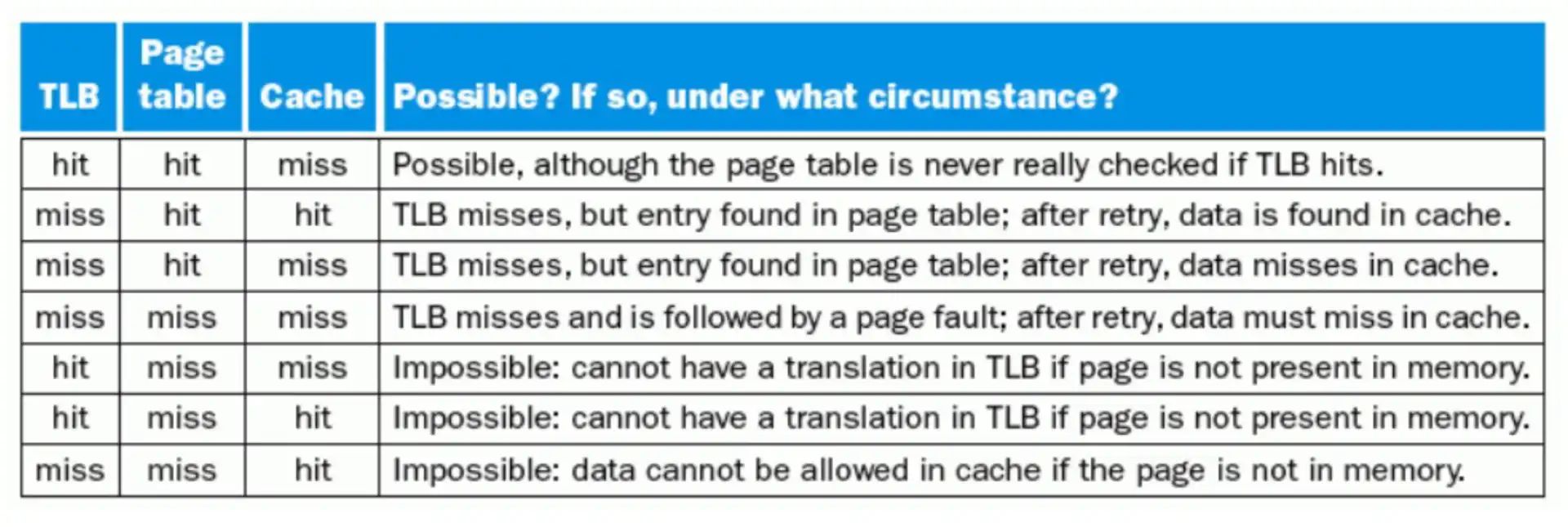
- 如果数据不在 main memory 里,不可能 TLB hit 和 cache hit
- 有可能 TLB miss 但是 cache hit