01 Computer Abstraction and Technology
1 Introduction#
1.1 Some Key Words#
- inst set
- datapath
- pipelines
- virtual memory
- cache
1.2 Structure of a Computer#
- Computer/System
- Software
- Hardware
- CPU
- Control unit
- Datapath
- Path (MUX)
- ALU: adder, multiplier
- Registers
- ...
- Memory
- I/O Interface
- CPU
1.3 von Neumann Architecture#
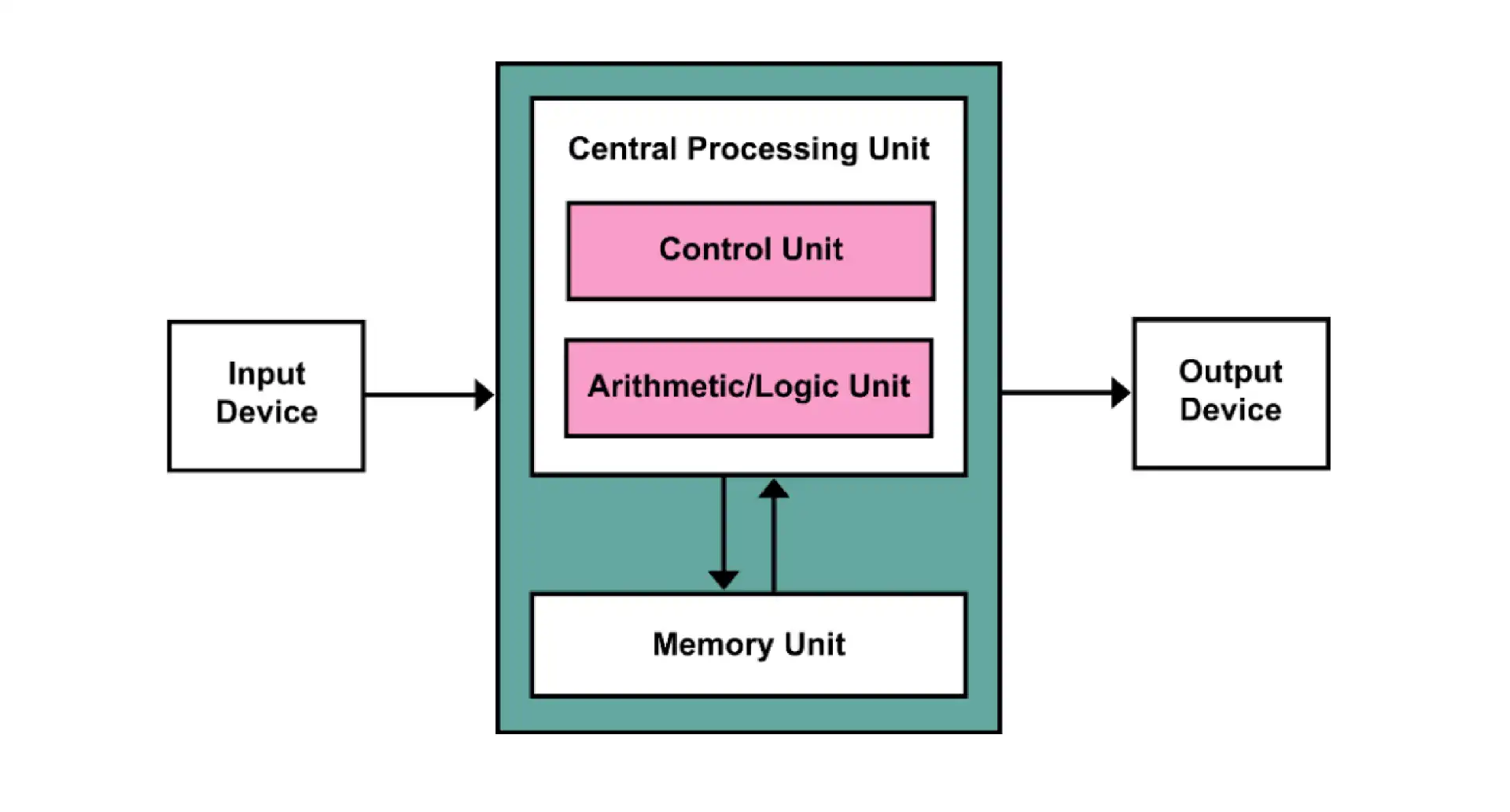
- 计算和存储分离
- 数据与指令保存在同一个存储器
- I/O 设备
- 指令集架构
2 Computer Organization#
2.1 Memory#
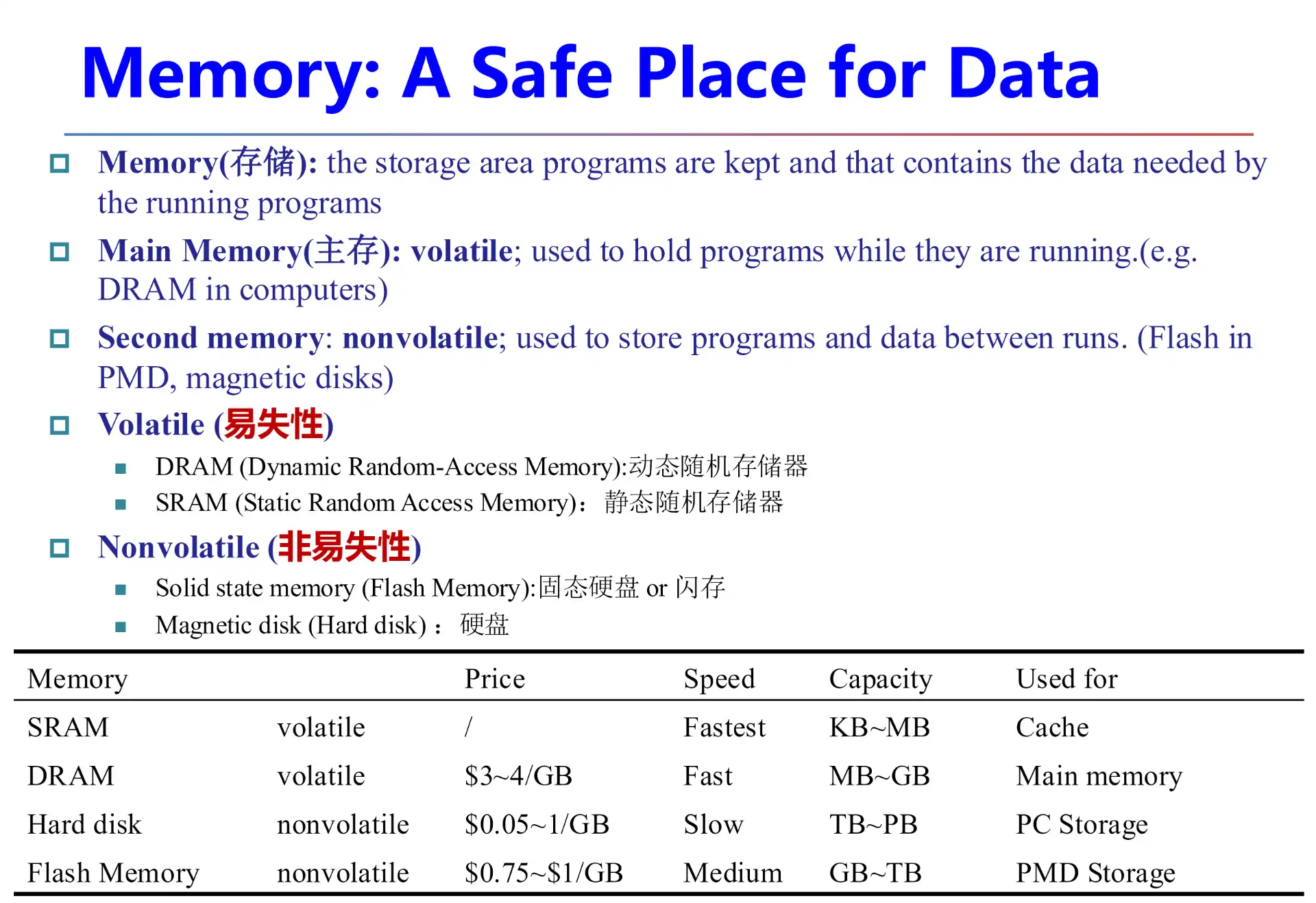
2.2 ISA#
- 从高级硬件语言到底层硬件
- 只要支持同一套 ISA,硬件和软件就能配合
3 How to build processors?#
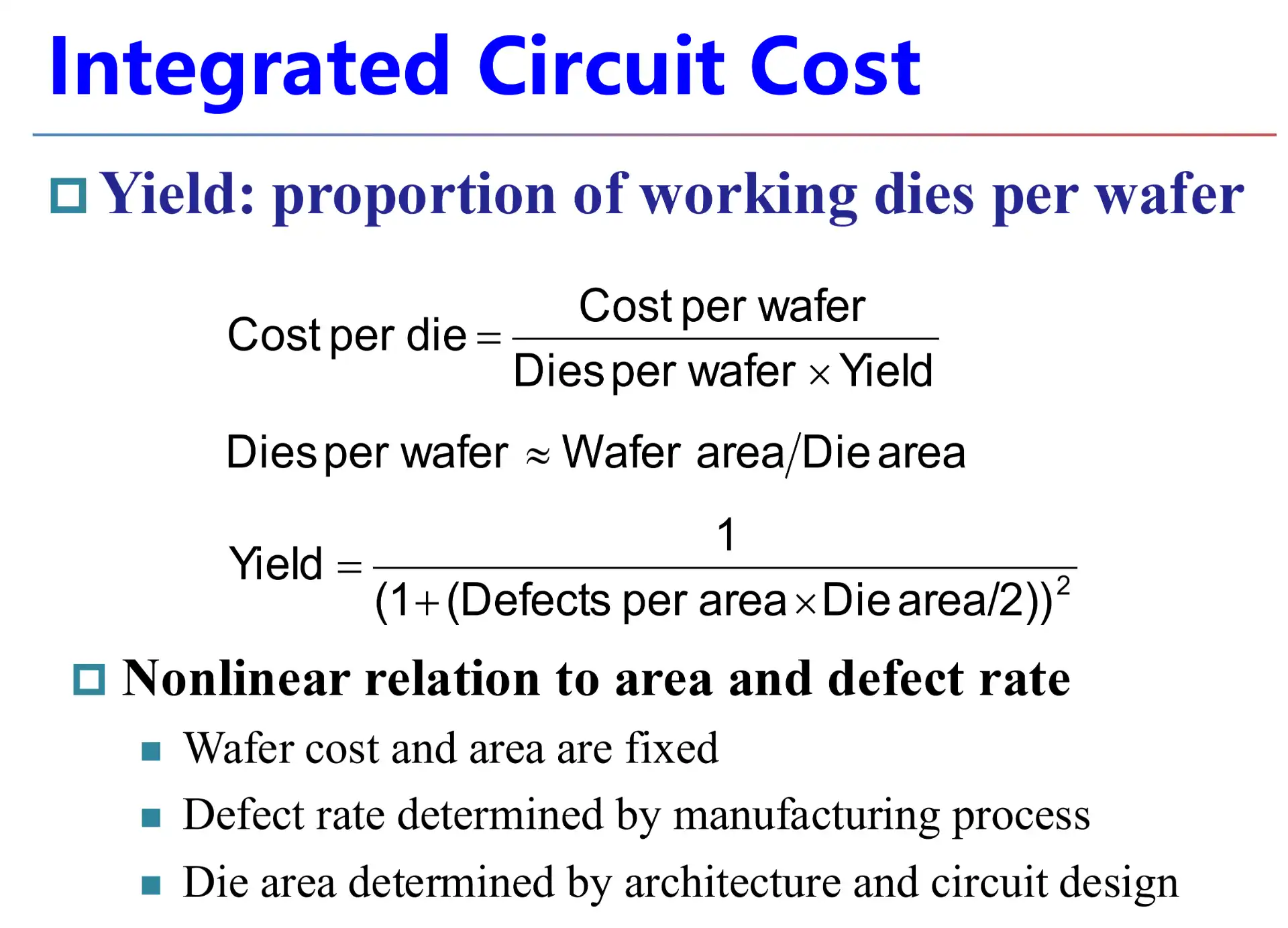
关于制造成本
4 Performance#
4.1 Response Time and Throughput#
- Response time/execution time 响应时间、执行时间,执行一个任务的时间是多长
- Throughput (bandwidth) 吞吐率,单位时间能执行多少任务
- Response time and throughput 的影响因素
- 更好的处理器
- 更多的处理器
4.2 Relative Performance#
- \(perf=1/Exe\,time\)
- x is n times faster than y
\[
perf_x/perf_y=time_y/time_x=n
\]
4.3 CPU Time#
- Elapse Time 是总时间
- CPU Time 是除去 I/O 等其他因素的时间
4.4 Measuring Execution Time#
- Clock period 时钟周期
-
Clock freq(rate) 时钟频率, cycles per sec#
\[
CPU\,Time=CPU\,Clock\,Cycles \times Clock\,Cycle\,Time=\frac{CPU\,CLock\,Cycles}{Clock\,Rate}
\]
- 提升性能,可以减少周期数,也可以提升时钟频率
4.5 Inst Cnt and CPI#
-
\[
Clock\,Cycles=Inst\,Cnt\times CPI
\]
-
\[
CPU\,Time=Inst\,Cnt\times CPI\times Clock\,Cycle\,Time=\frac{Inst\,Cnt\times CPI}{Clock\,Rate}
\]
- 同样的代码,如果 ISA 相同,那么 Inst Cnt 相同
- Weighted average CPI, 如果不同指令 CPI 不同,按照其 Inst Cnt 的比例分配权重
4.6 Perf depends on#
- Algo
- Programming lang, compiler, architecture ch.2, 3
- Processor and memory sys ch.4, 5
- I/O system ch. 6
4.7 Power#
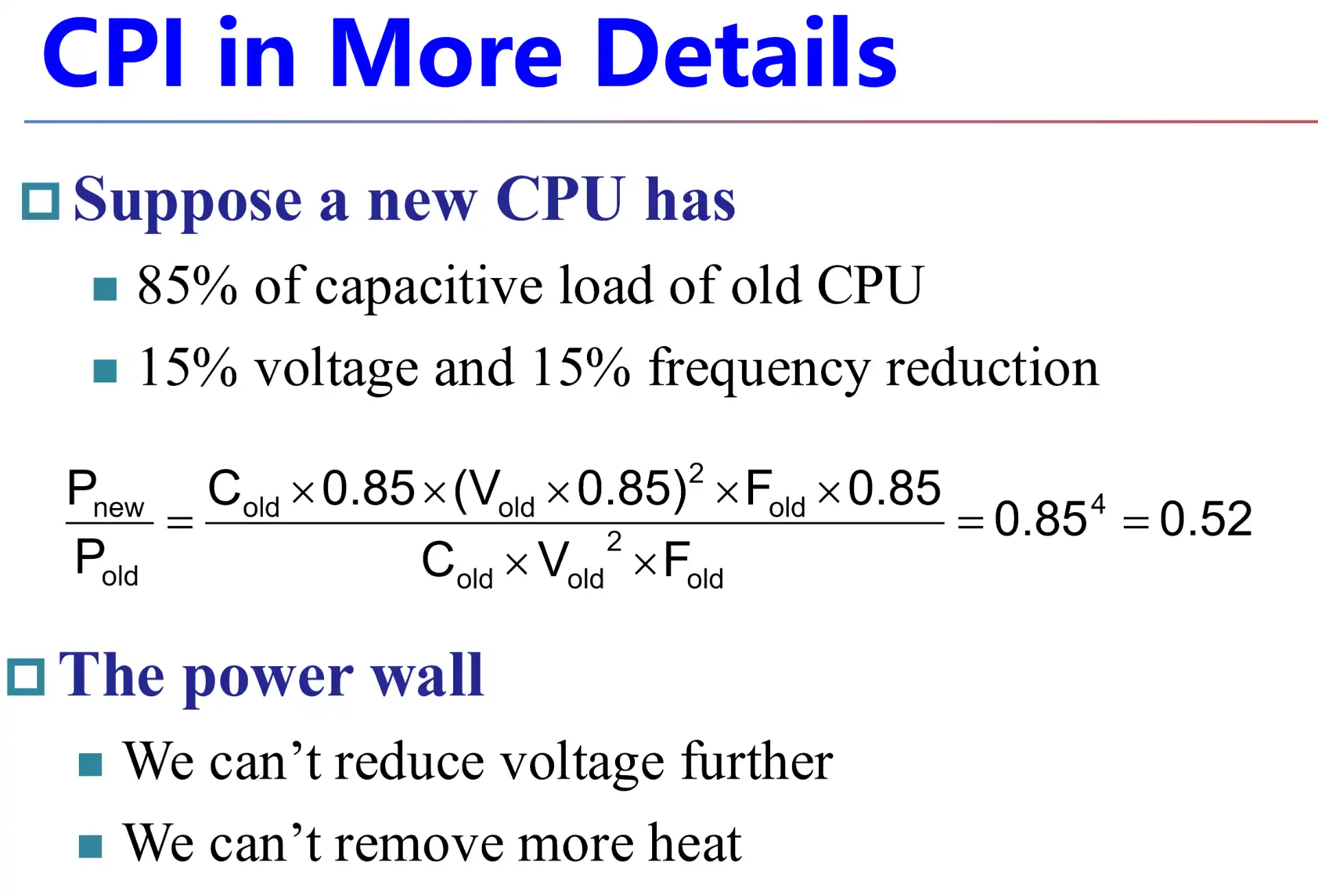
\(P=C\times V^2\times F\)
4.8 Pitfall: Amdahl's Law#
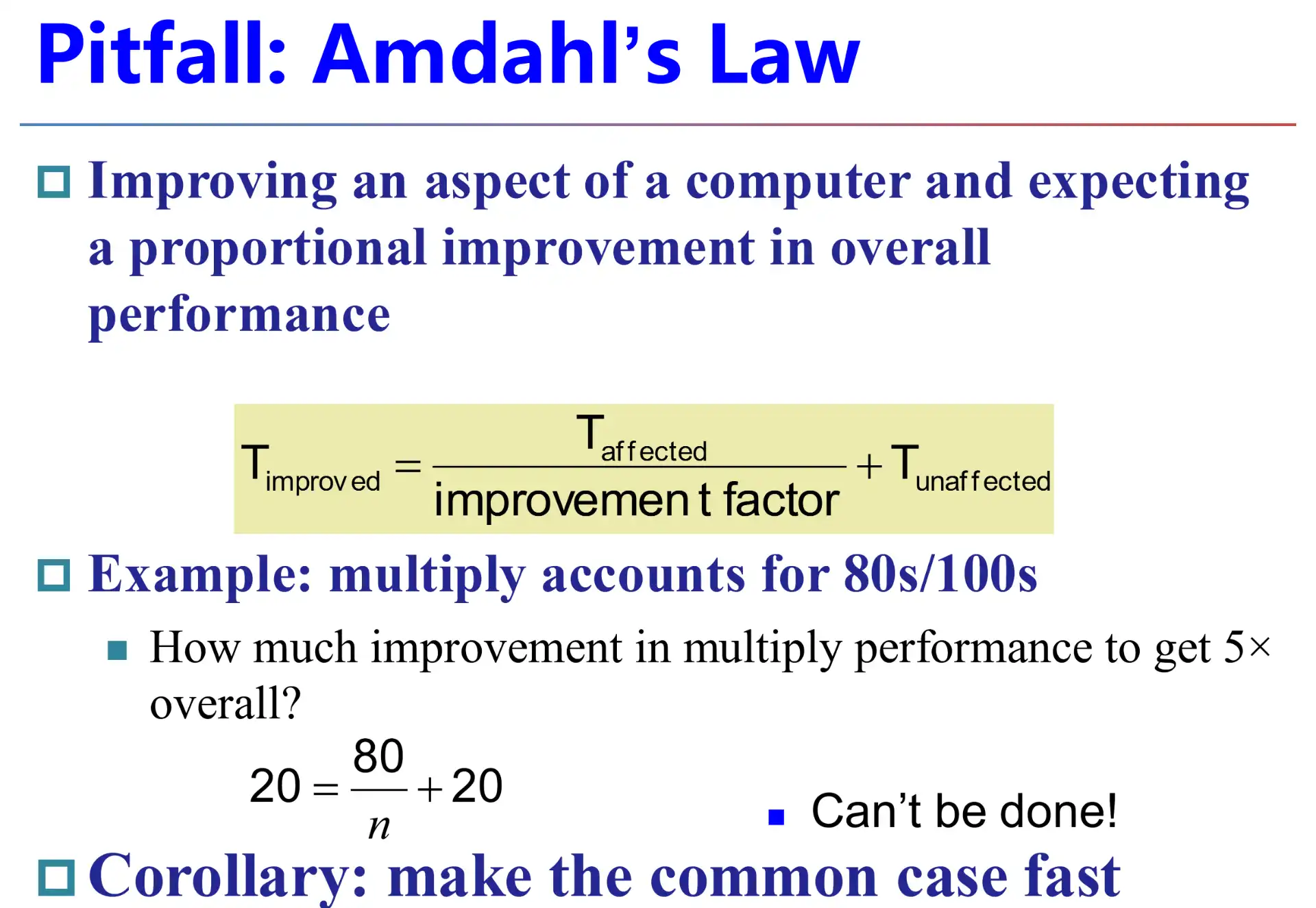
提升部分性能对整体性能的优化具有上限
4.9 Pitfall: MIPS#
- MIPS: Millions of Inst Per Second#
\[
MIPS=\frac{Inst\,Cnt}{Exe\,Time\times 10^6}=\frac{Clock\,Rate}{CPI\times 10^6}
\]
5 Eight Great Ideas#
- Design for Moore's Law 设计紧跟摩尔定律
- Design for where it will be when finishes rather that design for where it starts.
- Use Abstraction to Simplify Design 采用抽象简化设计
- 层次化、模块化
- e.g. ISA 作为标准
- Make the Common Case Fast 加速大概率事件
- 联系 Amdahl's Law
- Performance via Parallelism
- multiprocessor
- 增大位宽
- Performance via Pipelining
- 最好情况下,每一个流程的时间都是均匀的
- Performance via Prediction
- 分支预测
- Hierarchy of Memories 存储器层次
- Disk/Tape -> Main Memory(DRAM) -> L2-Cache(SRAM) -> L1-Cache(On-Chip) -> Registers
- Dependability via Redundancy 通过冗余提高可靠性
- 卡车的多个轮胎
