Lec.07 OpenMP, MPI 并行计算基础
OpenMP#
Introduction#
Shared Memory Parallel Model#
- UMA (Uniform memory access):所有核心访问一块内存
- NUMA (Non-~):内存分组,跨组访问的速度较低 MPI imp
Hint
- OpenMP - thread - shared
- MPI - process - not shared
OpenMP#
About OpenMP
- 3 language supported
- C/C++
- Fortran (scientific computation)
- provides us an easy way to transform serial programs into parallel
| Hello OpenMP | |
|---|---|
- Import omp header
- Preprocessing directive
- Parallel Region
Thread ID: omp_get_thread_num() 可以获取线程索引
OpenMP directives and constructs#
Directives#
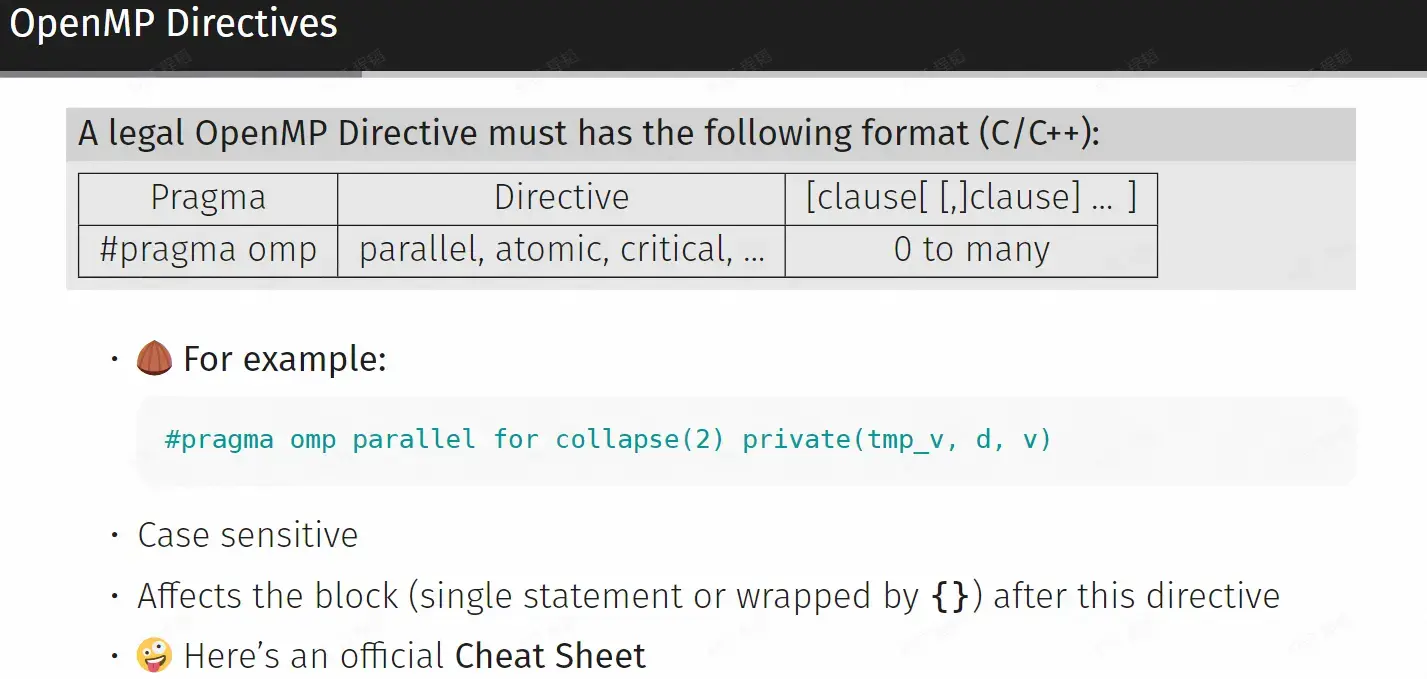
- Official Cheat Sheet => OpenMP_reference.pdf (cheat-sheets.org)
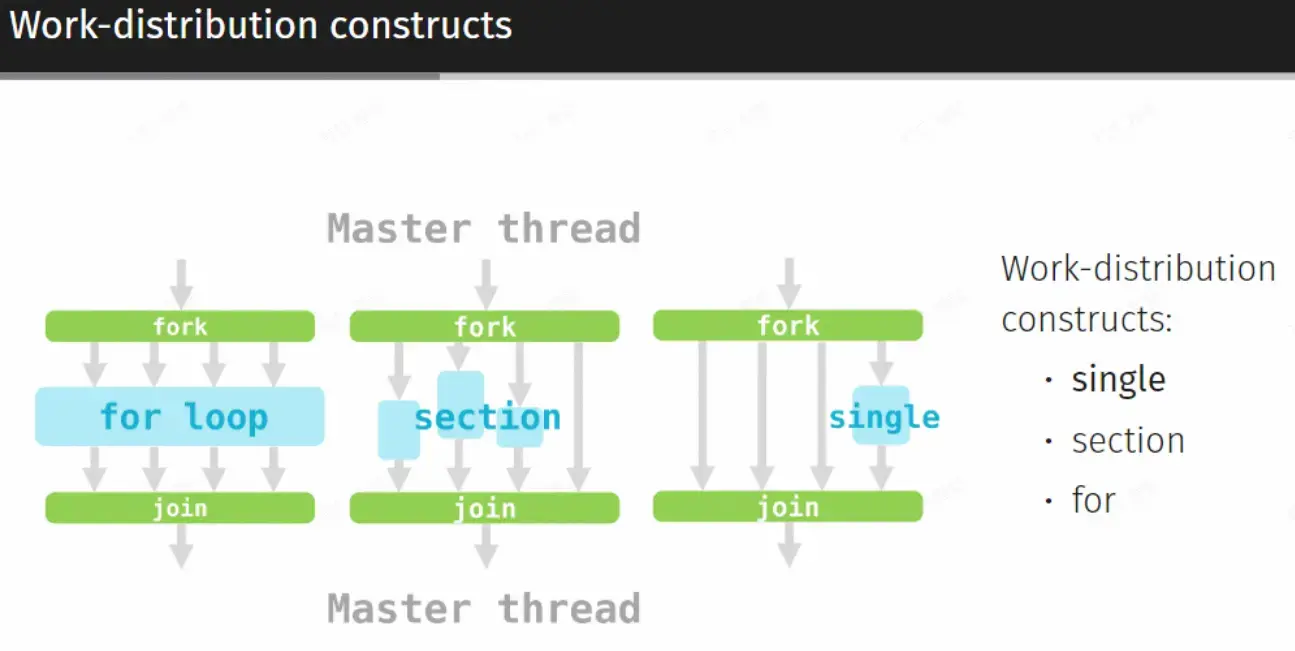
Work-distribution constructs#
| Addition of two vectors | |
|---|---|
Attention
加速倍数!=线程数
Overhead: any combination of excess or indirect computation time, memory, bandwidth, or other resources that are required to perform a specific task.
只能使用等差数列形式的 for loop 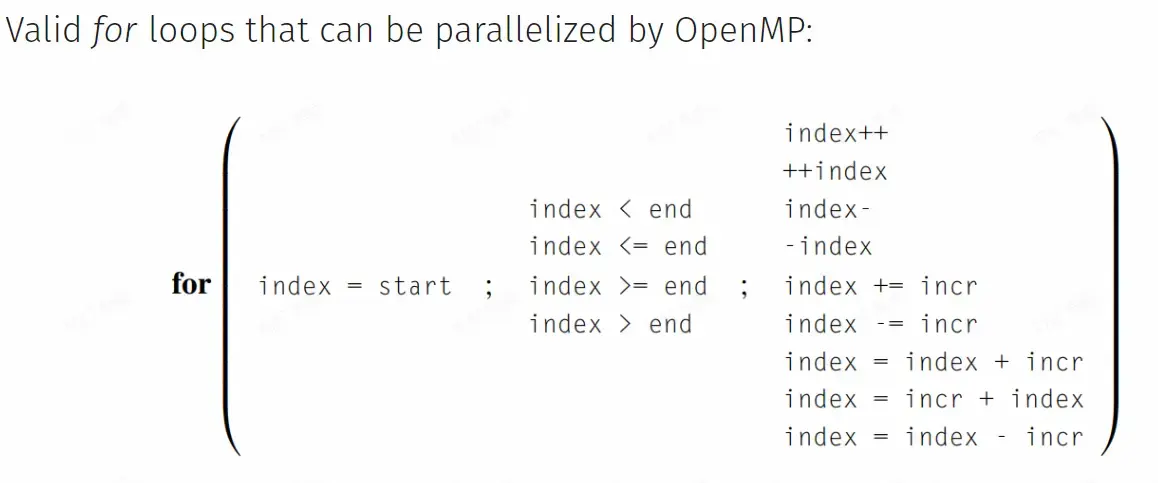
Loop Schedule#
| Unbalanced workload | |
|---|---|
- Chunks: 循环中的子块,是任务分配的单位,可大可小
- Type: static, dynamic, guided, runtime, auto
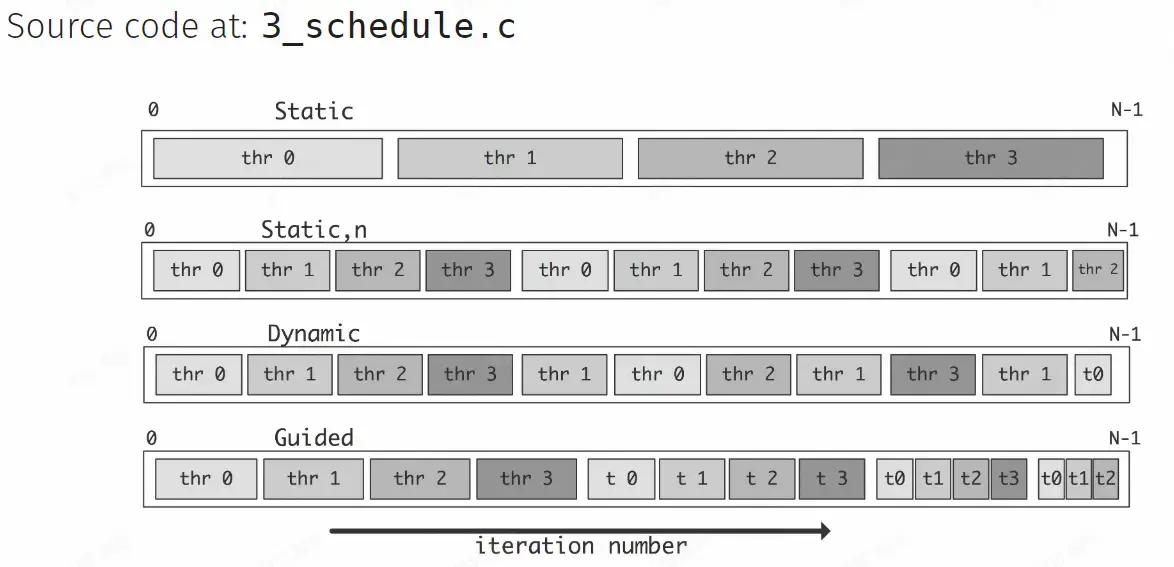
static#
- 就是直接按顺序均分
- pros: less overhead
- cons: unbalanced workload
dynamic#
- 动态分配
- pros: more flexible
- cons: more overhead in scheduling
guided#
- 相比 static: 在某些情况下可能得到更好的 workload balance
- 相比 dynamic: less overhead to dispatch tasks
- 实际上需要多次尝试哪个更好
Nested for loop#
| Matrix addition | |
|---|---|
Attention
It's not always a good idea to parallelize nested loops.
Think anout locality and data dependency before you use collapse clause.
总之,由于局部性,任务分配过于精细可能导致程序执行顺序乱跳,效率反而低
Shared Data and Data Hazards#
| Example: Data Hazards in Summation | |
|---|---|
CPU 执行加法
- 从内存读取到
- 执行加法计算
- 写回内存
- 如果 B 在 A 写之前读,那么 A 的结果会被 B 的结果覆盖
- 如果 A 的任务开始很早,但是写入很晚,可能覆盖其他所有任务
变量作用域#
- Shared & private data in default
- directive 外面定义的就是共享变量,里面的就是私有变量
Explicit scpoes definition#
firstprivate()在开始时从共享作用域读取lastprivate()在最后一个线程结束时写回同名共享变量
Resolve Data Hazard#
Critical Section 临界区#
| critical section solution | |
|---|---|
- 可以包含多个语句
- 控制最多只能有一个线程进入临界区代码,即锁门排队
- 但在求和的问题,其实退化成了串行程序
Atomic Operation 原子操作#
| atomic operation solution | |
|---|---|
- Atomic operation cannot be separated
- Only can be applied to one operation
- Limited set of operatiors supported
Reduciton 归约#
| reduction solution | |
|---|---|
- 对每个线程创建私有变量
- 最终对每个私有变量进行规约
- 规约方式有限
Comparison#
- Critical Region: 软件层面上的锁机制
- Atomic: CPU 层面上的原子化指令调用,通常具有更高的性能
- Reduction: 在最终进行同步
Another Example: Naive GEMM#
| General Matrix Multiplication | |
|---|---|
| a solution | |
|---|---|
Miscellaneous#
Threads Synchronize#
- Locking: wait unitl obtain the lock
- Barrier: wait untill all thread reach here
- MP 都有隐式的 barrier
nowait可以手动去掉每个并行区域的隐式 barrier
Nested Parallel Region#
- OpenMP 默认不会执行嵌套并行区域
- 可以使用
omp_set_nested来调整默认允许 - 建议重构代码
False Sharing#
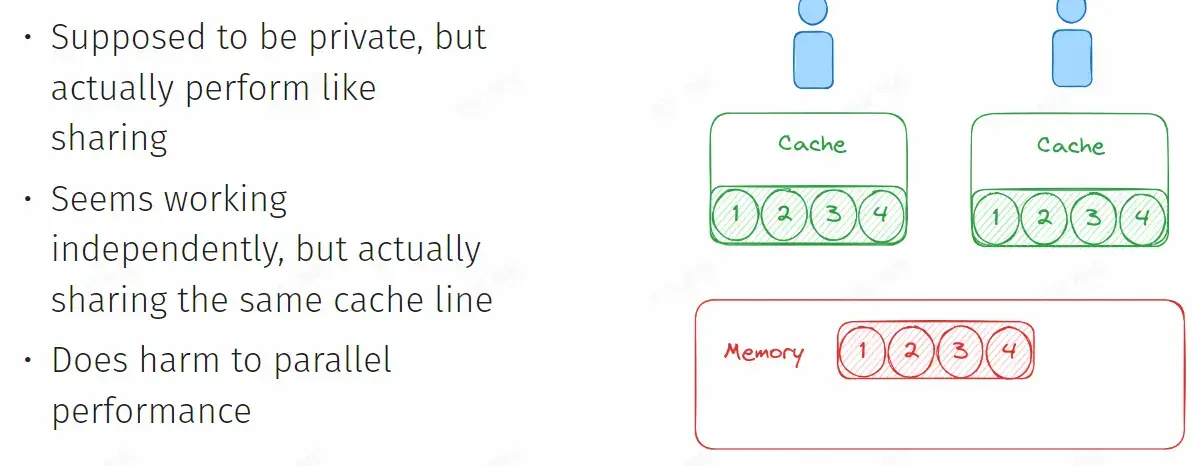
- cache 有最小读写单位 block,每次 A 对自己操作的值进行了修改,由于来自 memory 中相同的 block,A 会通过一种广播机制使得 B 修改 cache,实际上并没有共享
Summary: How to Optimize a program with OpenMP#
- Where to parallelize: Profiling 通过软件分析程序热点,针对热点进行并行化
- Whether to parallelize: Analyze data dependency 访存依赖,不好并行
- How to parallelize: Analysis and Skills
- Sub-task Distribution
- Scheduling Strategy
- Cache and Locality
- Hardware Env
- Sometimes: transform recursion to iteration
- Get Down to Work: Testing
Tips#
- Ensure correctness while parallelizing
- Be aware of overhead
- Check more details in official documents
- for example, OpenMP on GPU
MPI#
Introduction#
MPI, Message Passing Interface
- OpenMPI
- Intel-MPI
- MPICH
| Compile | |
|---|---|
Attention
执行时终端输出顺序和实际执行顺序没有关系。
Basic Concepts#
Communicator#
- A communicator defines a group of processes that have the ability to communicate with one another.
- 每个进程有一个 unique rank 通信域
- 默认是
MPI_COMM_WORLD
- 默认是
- 不保证公平性:可能总是无法接收到某些节点的信息
Point-to-Point Communication#
Blocking Send and Receive#
MPI_Status#
Message Envelope#
Communication Mode#
- Buffer Mode
- Synchronous Mode
- Ready Mode
- Standard Mode
Example: Deadlock#
- 0 和 1 发送之后都一直等待对方接受
- Solution
- 增加 if 语句
- 使用
MPI_Sendrecv - 使用非阻塞通信
MPR_Isend
Collective Communication#
- Synchronizaiton
MPR_Barrier - BroadCast (One to All)
MPPI_Bcast- Why not Send and Receive 会比较慢,
MPI_Bcast使用了树形结构传递数据
- Why not Send and Receive 会比较慢,
- Scatter (One to All)
MPI_Scatter - Gather (All to One)
MPI_Gather - Allgather (All to All)
PI_Allgather - Reduce
MPI_Reuce